
Renewable energy progress in the European Union (EU) is driven by the European Commission's 2023 revision of the Renewable Energy Directive, which raises the EU's binding renewable energy target for 2030 to at least 42.5%, up from the previous target of 32%. Effective since November 20, 2023, across all EU countries, this directive aligns with broader climate objectives, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 and achieving climate neutrality by 2050. Additionally, the Energy 2020 strategy exceeded its goals, with the EU achieving a 22.1% share of renewable energy in 2020, surpassing the 20% target.
Government procurement or public procurement is undertaken by the public authorities of the European Union (EU) and its member states in order to award contracts for public works and for the purchase of goods and services in accordance with principles derived from the Treaties of the European Union. Such procurement represents 13.6% of EU GDP as of March 2023, and has been the subject of increasing European regulation since the 1970s because of its importance to the European single market.

Directive 2003/30/EC was a European Union directive for promoting the use of biofuels for EU transport. The directive entered into force in May 2003, and stipulated that national measures must be taken by countries across the EU aiming at replacing 5.75% of all transport fossil fuels with biofuels by 2010. The directive also called for an intermediate target of 2% by 31 December 2005. The target of 5.75% was to be met by 31 December 2010. These percentages were to be calculated on the basis of energy content of the fuel and were to apply to petrol and diesel fuel for transport purposes placed on the markets of member states. Member states were encouraged to take on national "indicative" targets in conformity with the overall target.

The energy policy of the European Union focuses on energy security, sustainability, and integrating the energy markets of member states. An increasingly important part of it is climate policy. A key energy policy adopted in 2009 is the 20/20/20 objectives, binding for all EU Member States. The target involved increasing the share of renewable energy in its final energy use to 20%, reduce greenhouse gases by 20% and increase energy efficiency by 20%. After this target was met, new targets for 2030 were set at a 55% reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 as part of the European Green Deal. After the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the EU's energy policy turned more towards energy security in their REPowerEU policy package, which boosts both renewable deployment and fossil fuel infrastructure for alternative suppliers.
Taxation in Greece is based on the direct and indirect systems. The total tax revenue in 2017 was €47.56 billion from which €20.62 billion came from direct taxes and €26.94 billion from indirect taxes. The total tax revenue represented 39.4% of GDP in 2017. Taxes in Greece are collected by the Independent Authority for Public Revenue.

As of 2009, the European Union had issued two units of measurement directives. In 1971, it issued Directive 71/354/EEC, which required EU member states to standardise on the International System of Units (SI) rather than use a variety of CGS and MKS units then in use. The second, which replaced the first, was Directive 80/181/EEC, enacted in 1979 and later amended several times, which issued a number of derogations to the United Kingdom and Ireland based on the former directive.
The Directive on the promotion of cogeneration based on a useful heat demand in the internal energy market and amending Directive 92/42/EEC, officially Directive 2004/8/EC, is a European Union directive for promoting the use of cogeneration, popularly better known as the 'Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Directive'.
The Energy Performance of Buildings Directive is the European Union's main legislative instrument aiming to promote the improvement of the energy performance of buildings within the European Union. It was inspired by the Kyoto Protocol which commits the EU and all its parties by setting binding emission reduction targets.

Renewable energy in Spain, comprising bioenergy, wind, solar, and hydro sources, accounted for 15.0% of the Total Energy Supply (TES) in 2019. Oil was the largest contributor at 42.4% of the TES, followed by gas, which made up 25.4%.
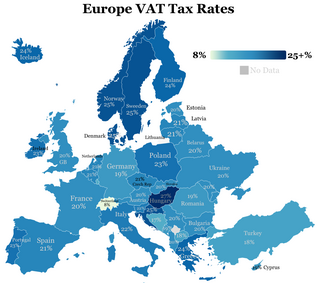
The European Union value-added tax is a value added tax on goods and services within the European Union (EU). The EU's institutions do not collect the tax, but EU member states are each required to adopt in national legislation a value added tax that complies with the EU VAT code. Different rates of VAT apply in different EU member states, ranging from 17% in Luxembourg to 27% in Hungary. The total VAT collected by member states is used as part of the calculation to determine what each state contributes to the EU's budget.

Directive 89/391/EEC is a European Union directive with the objective to introducing measures to encourage improvements in the safety and health of workers at work. It is described as a "Framework Directive" for occupational safety and health (OSH) by the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work.
Strict sustainability standards for biofuel in the European Union (EU) are set by the European Commissioner on Energy. Biofuels are considered a renewable alternative to fossil fuels in the transportation sector for the EU. The EU has played a large role in increasing the use of biofuels in member states; however, it has also aimed, to some extent, to mitigate the potential negative impacts of biofuel production. Current EU legislation on biofuels includes a goal to increase renewable energy consumption by 20%, eliminate biofuel feedstock sourced from carbon-rich land, accounting for emissions caused from land use change as well as solely biofuel usage, and reducing greenhouse gas intensities from fuels used in transport and machinery.
European labour law regulates basic transnational standards of employment and partnership at work in the European Union and countries adhering to the European Convention on Human Rights. In setting regulatory floors to competition for job-creating investment within the Union, and in promoting a degree of employee consultation in the workplace, European labour law is viewed as a pillar of the "European social model". Despite wide variation in employment protection and related welfare provision between member states, a contrast is typically drawn with conditions in the United States.

The Renewable Energy Directive 2018 is a Directive in EU law that requires 42.5 percent of the energy consumed within the European Union to be renewable by 2030. This target is pooled among the member states.
The German National Renewable Energy Action Plan is the National Renewable Energy Action Plan (NREAP) for Germany. The plan was commissioned under EU Renewable Energy Directive 2009/28/EC which required member states of the European Union to notify the European Commission with a road map. The report describes how Germany plans to achieve its legally binding target of an 18% share of energy from renewable sources in gross final consumption of energy by 2020.

European company law is the part of European Union law which concerns the formation, operation and insolvency of companies in the European Union. The EU creates minimum standards for companies throughout the EU, and has its own corporate forms. All member states continue to operate separate companies acts, which are amended from time to time to comply with EU Directives and Regulations. There is, however, also the option of businesses to incorporate as a Societas Europaea (SE), which allows a company to operate across all member states.

The Energy Efficiency Directive 2012/27/EU is a European Union directive which mandates energy efficiency improvements within the European Union. It was approved on 25 October 2012 and entered into force on 4 December 2012. The directive introduces legally binding measures to encourage efforts to use energy more efficiently in all stages and sectors of the supply chain. It establishes a common framework for the promotion of energy efficiency within the EU in order to meet its energy efficiency headline target of 20% by 2020. It also paves the way for further improvements thereafter.

Aviation taxation and subsidies includes taxes and subsidies related to aviation.
Taxation of aviation fuel in the European Union is regulated by the Energy Taxation Directive (2003/96/EG) of 27 October 2003. This prohibits the taxation of commercial aviation fuel, except for commercial domestic flights or by bilateral agreement between member states. As of 2023, commercial aviation fuel is currently tax exempt under the legislation of all member states of the European Union. This tax exemption has been criticised on environmental grounds.






