
The Cenozoic is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66 million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor.
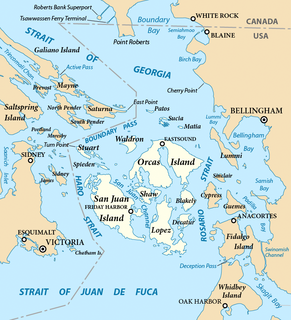
The San Juan Islands are an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of San Juan County.

Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals.

Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine environments for feeding and survival.

The sea otter is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between 14 and 45 kg, making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smallest marine mammals. Unlike most marine mammals, the sea otter's primary form of insulation is an exceptionally thick coat of fur, the densest in the animal kingdom. Although it can walk on land, the sea otter is capable of living exclusively in the ocean.

Ambulocetus is a genus of early amphibious cetacean from the Kuldana Formation in Pakistan, roughly 48 or 47 million years ago during the Early Eocene (Lutetian). It contains one species, Ambulocetus natans, known solely from a single, near-complete fossil. Ambulocetus is among the best-studied of Eocene cetaceans, and serves as instrumental evidence for cetacean evolution and their transition from land to sea, as it was the first cetacean discovered to preserve a suite of adaptations consistent with an amphibious lifestyle. Ambulocetus is classified in the group Archaeoceti—the ancient forerunners of modern cetaceans whose members span the transition from land to sea—and in the family Ambulocetidae, which includes Himalayacetus and Gandakasia.

Enhydra is a genus of mustelid that contains the sea otter and two extinct relatives.

India is the world's 8th most biodiverse region with a 0.46 BioD score on diversity index, 102,718 species of fauna and 23.39% of the nation's geographical area under forest and tree cover in 2020. India encompasses a wide range of biomes: desert, high mountains, highlands, tropical and temperate forests, swamplands, plains, grasslands, areas surrounding rivers, as well as island archipelago. Officially, four out of the 36 Biodiversity Hotspots in the world are present in India: the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, the Indo-Burma region and the Sundaland. To these may be added the Sundarbans and the Terrai-Duar Savannah grasslands for their unique foliage and animal species. These hotspots have numerous endemic species. Nearly 5% of India's total area is formally classified under protected areas.

The marine otter is a rare and relatively unknown South American mammal of the weasel family (Mustelidae). The scientific name means "otter cat", and in Spanish, the marine otter is also often referred to as gato marino: "marine cat". The marine otter only lives in saltwater, coastal environments and rarely ventures into freshwater or estuarine habitats. This saltwater exclusivity is unlike most other otter species, except for the almost fully aquatic sea otter of the North Pacific.

Tributyltin (TBT) is an umbrella term for a class of organotin compounds which contain the (C4H9)3Sn group, with a prominent example being tributyltin oxide. For 40 years TBT was used as a biocide in anti-fouling paint, commonly known as bottom paint, applied to the hulls of oceangoing vessels. Bottom paint improves ship performance and durability as it reduces the rate of biofouling, the growth of organisms on the ship's hull. The TBT slowly leaches out into the marine environment where it is highly toxic toward nontarget organisms. TBT is also an obesogen. After it led to collapse of local populations of organisms, TBT was banned.
The sea otter is a marine mammal that primarily lives on the northern coasts of the Pacific Ocean.

Sea otter conservation began in the early 20th century, when the sea otter was nearly extinct due to large-scale commercial hunting. The sea otter was once abundant in a wide arc across the North Pacific ocean, from northern Japan to Alaska to Mexico. By 1911, hunting for the animal's luxurious fur had reduced the sea otter population to fewer than 2000 individuals in the most remote and inaccessible parts of its range. The IUCN lists the sea otter as an endangered species. Threats to sea otters include oil spills, and a major spill can rapidly kill thousands of the animals.

Enhydrocyon is an extinct genus of bone crushing canid which inhabited North America during the Oligocene and Early Miocene, 30.8—20.4 Ma, existing for approximately 11 million years.

Paleontology in Florida refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Florida. Florida has a very rich fossil record spanning from the Eocene to recent times. Florida fossils are often very well preserved.
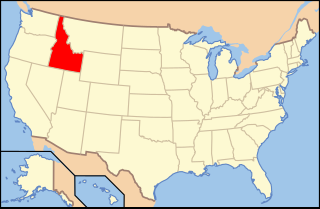
Paleontology in Idaho refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Idaho. The fossil record of Idaho spans much of the geologic column from the Precambrian onward. During the Precambrian, bacteria formed stromatolites while worms left behind trace fossils. The state was mostly covered by a shallow sea during the majority of the Paleozoic era. This sea became home to creatures like brachiopods, corals and trilobites. Idaho continued to be a largely marine environment through the Triassic and Jurassic periods of the Mesozoic era, when brachiopods, bryozoans, corals, ichthyosaurs and sharks inhabited the local waters. The eastern part of the state was dry land during the ensuing Cretaceous period when dinosaurs roamed the area and trees grew which would later form petrified wood.

The sea otter, Enhydra lutris, is a member of the Mustelidae that is fully aquatic. Sea otters are the smallest of the marine mammals, but they are also the most dexterous. Sea otters are known for their ability to use stones as anvils or hammers to facilitate access to hard-to-reach prey items. Furthermore, out of the thirteen currently known species of otters, at least 10 demonstrate stone handling behaviour, suggesting that otters may have a genetic predisposition to manipulate stones. Tool use behavior is more associated with geographic location than sub-species. Most behavioral research has been conducted on Enhydra lutris nereis, the Californian otter, and some has been conducted on Enhydra lutris kenyoni, the Alaska sea otter. Sea otters frequently use rocks as anvils to crack open prey, and they are also observed to rip open prey with their forepaws. While lying on their backs, otters will rip apart coral algae to find food among the debris. The frequency of tool use varies greatly between geographic regions and individual otters. Regardless of the frequency, the use of tools is present in the behavioral repertoire of sea otters and is performed when most appropriate to the situation.

Randall William Davis is an educator and researcher who studies the physiology and behavioral ecology of marine mammals and other aquatic vertebrates. His physiological research focuses on adaptations of marine mammals for deep, prolonged diving. Davis has continually emphasized the importance of studying aquatic animals in their natural environment and has spent many years developing animal-borne instruments that record video and monitor three-dimensional movements, swimming performance and environmental variables to better understand their behavior and ecology. His academic endeavors and 94 research expeditions have taken him to 64 countries and territories on seven continents and all of the world's oceans.
Garforth Island is an uninhabited island located in the U.S. state of Alaska, in the Hoonah-Angoon area of the Unorganized Borough, within Glacier Bay National Park.

Checleset Bay is a bay on the northwest coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It is located southeast of Brooks Peninsula and northwest of Kyuquot Sound. Much of the land around the bay is part of Brooks Peninsula Provincial Park. Checleset Bay has three large inlets, Nasparti Inlet, Ououkinsh Inlet, and Malksope Inlet.
















