The Province of Genoa was a province in the Liguria region of Italy. Its capital was the city of Genoa. It was replaced by Metropolitan City of Genoa.

The House of Fieschi were an old Italian noble family from Genoa, Italy, from whom descend the Fieschi Ravaschieri Princes of Belmonte. Of ancient origin, they took their name from the progenitor Ugo Fliscus, descendants of the counts of Lavagna.

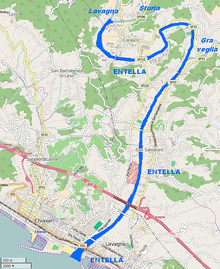
Chiavari is a seaside comune (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Genoa, in Italy. It has about 28,000 inhabitants. It has a beachside promenade and a marina and is situated near the river Entella.

Lavagna is a comune (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Genoa, Italy.

Boccadasse is an old mariners' village of the Italian city of Genoa. It lies within the borders of the neighbourhood of Albaro. In today's administrative subdivision it is located in the Municipio VIII - Medio Levante area which includes the neighbourhoods of Albaro, Foce, San Martino. Boccadasse is bordered on the west side by Via Felice Cavallotti, by Via Caprera on the northern side and by Via Capo di Santa Chiara on the eastern side. Naturally, it is delimited by the sea to the south.

Albaro is an affluent residential neighbourhood of the Italian city of Genoa, located 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) east of the city centre. It was formerly an independent comune, named San Francesco d'Albaro, included in the city of Genoa in 1873. At present, together with the neighbourhoods of Foce and San Martino d'Albaro is part of the Genoa's city VIII Municipio.

Virtus Entella, commonly referred to as Entella, is an Italian professional football club based in Chiavari, Liguria. Founded in 1914, the club currently competes in the Serie C Group B.

Bric delle Camere is a mountain in northern Italy, part of the Ligurian Apennines. It is located in the provinces of Genoa and Alessandria. It lies at an altitude of 1016 metres.

Monte Leco is a mountain in Liguria, northern Italy, part of the Ligurian Apennines. It is located in the provinces of Genoa and Alessandria. It lies at an altitude of 1072 metres.

The Lavagna is an Italian river in the province of Genoa.
Giuseppe Marco Zampano is an Italian footballer who plays as a right-back.

The AMT Genova, formally known as the Azienda Mobilità e Trasporti and formerly as the Azienda Municipalizzata Trasporti, is a joint stock company that holds the concession for public transport in the Italian city of Genoa.

The Metropolitan City of Genoa is one of the fourteen metropolitan cities of Italy, located in the region of Liguria. Its capital is the city of Genoa. It replaced the Province of Genoa.

Bergeggi is an island which lies in the Ligurian Sea off the coast near the village of Bergeggi in the Province of Savona, Liguria, Italy.

The Bisagno is a 25-kilometre (16 mi) river in Liguria, (Italy).

The Stura di Ovada is a 32.9-kilometre (20.4 mi) stream of Liguria and Piedmont (Italy); it is the main tributary of the Orba.

The Steria or Cervo is a 9.6-kilometre (6.0 mi) stream of Liguria (Italy).

The Merula is a 14.7-kilometre (9.1 mi) stream of Liguria (Italy).

The Brevenna is a 16.138-kilometre (10.028 mi) creek of Liguria, Italy.
The Palio Marinaro di San Pietro is a sporting event of historical re-enactment, established in 1955.