Related Research Articles
A special protection area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and certain particularly threatened birds. Together with special areas of conservation (SACs), the SPAs form a network of protected sites across the EU, called Natura 2000. Each SPA has an EU code – for example the North Norfolk Coast SPA has the code UK9009031.
A special area of conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora. They are to protect the 220 habitats and approximately 1,000 species listed in annex I and II of the directive which are considered to be of European interest following criteria given in the directive. They must be chosen from the sites of Community importance by the member states and designated SAC by an act assuring the conservation measures of the natural habitat.

Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectively. The network includes both terrestrial and Marine Protected Areas.
The Habitats Directive is a directive adopted by the European Community in 1992 as a response to the Berne Convention. The European Community was reformed as the European Union the following year, but the directive is still recognised.
This page covers environmental issues in Greece.

Anthemis glaberrima is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is found only in Greece. Its natural habitats are rocky shores and Mediterranean-type shrubby vegetation.

Protected areas of Poland include the following categories, as defined by the Act on Protection of Nature of 16 April 2004, by the Polish Parliament:

Ophrys lunulata, the moon orchid, is a species of orchid native to the islands of Malta and Sicily in the central Mediterranean.

The LIFE programme is the European Union's funding instrument for the environment and climate action. The general objective of LIFE is to contribute to the implementation, updating and development of EU environmental and climate policy and legislation by co-financing projects with European added value. LIFE began in 1992 and to date there have been five phases of the programme. During this period, LIFE has co-financed some 4600 projects across the EU, with a total contribution of approximately 6.5 billion Euros to the protection of the environment and of climate. For the next phase of the programme (2021–2027) the European Commission proposed to raise the budget to 5.45 billion Euro.
Dixton Wood is a 13.14-hectare (32.5-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Gloucestershire, notified in 2000. Dixton Wood is recognised as a Special Area of Conservation (SAC) under the EU Habitats Directive.
The Protected Areas of the Azores are the basic administrative-territorial and conservation structures in the archipelago of the Azores and the surrounding oceans. The areas integrate the entirety of the Azores within its Exclusive Economic Zone, as well as the surrounding waters, under the international agreements and conventions. The network realizes the categorization of management for protected areas adopted by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), adapting it to the specific geographical, environmental, cultural and political-administrative territory of the archipelago.

Many parts of Scotland are protected in accordance with a number of national and international designations because of their environmental, historical or cultural value. Protected areas can be divided according to the type of resource which each seeks to protect. NatureScot has various roles in the delivery of many environmental designations in Scotland, i.e. those aimed at protecting flora and fauna, scenic qualities and geological features. Historic Environment Scotland is responsible for designations that protect sites of historic and cultural importance. Some international designations, such as World Heritage Sites, can cover both categories of site.

The Boreal Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region of Northern Europe that consists primarily of coniferous forests and wetlands.

The biogeographic regions of Europe are biogeographic regions defined by the European Environment Agency. They were initially limited to the European Union member states, but later extended to cover all of Europe west of the Urals, including all of Turkey. The map of biogeographic regions is deliberately simplified and ignores local anomalies. It is intended primarily as a framework for coordinating and reporting overall results of conservation efforts.

The Black Sea Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of land bordering the west and south of the Black Sea, as defined by the European Environment Agency.

The Steppic Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of Europe, as defined by the European Environment Agency.
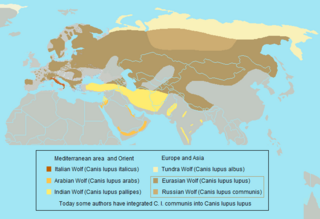
The favourable conservation status of wolves is the definition of a wolf population that is no longer threatened with extinction, that is capable of long-term survival. In Europe the favourable conservation status is defined by the Guidelines for Population Level Management Plans for Large Carnivores. It is the minimum viable population, that can be of different numbers of wolves depending on their connectivity with neighbouring populations. According to the IUCN guidelines, at least 1000 adult animals are required for isolated populations. If a wolf population is effectively linked genetically and demographically with other wolf populations, more than 250 mature wolves may be sufficient.
Ballynafagh Lake is a Special Area of Conservation and wildfowl sanctuary in County Kildare, close to the town of Prosperous in County Kildare, Ireland. This site is also known as the Blackwood Reservoir, the Blackwood Lake or the Prosperous Reservoir.
On February 29, 2024 the Greek Parliament passed a bill that relaxed coastal protection regulations. The bill, which was supported by the majority New Democracy party, passed with 158 votes in favor and 142 against. All eight opposition parties voted against the legislation.
The Four Roads Turlough Special Area of Conservation is a Natura 2000 site based at the village of Four Roads, Ireland, close to Roscommon town, in County Roscommon, Ireland. The Four Roads Turlough is one of a number of seasonal lakes, or turloughs, found in the karst areas of Ireland, west of the River Shannon.