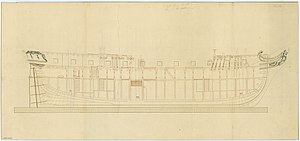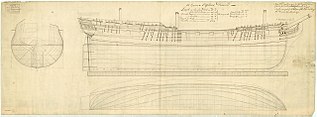
The fourth HMS Diamond was a modified Lowestoffe-class fifth-rate frigate ordered in 1770, launched in 1774, but did not begin service until 1776. Diamond served off the eastern North American coast and shared in the capture at least one brig during the American Revolutionary War. The frigate was paid off in 1779, but returned to service the same year after being coppered. Diamond sailed to the West Indies in 1780, was paid off a final time in 1783 and sold in 1784.

The Minerva-class sailing frigates were a series of four ships built to a 1778 design by Sir Edward Hunt, which served in the Royal Navy during the latter decades of the eighteenth century.

The Coventry-class frigates were 28-gun sixth rate frigates of the Royal Navy, principally in service during the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War. They were designed in 1756 by Britain's Surveyor of the Navy, Sir Thomas Slade, and were largely modeled on HMS Tartar, which was regarded as an exemplar among small frigates due to its speed and maneuverability. The 1750s were a period of considerable experimentation in ship design, and Slade authorized individual builders to make "such alterations withinboard as may be judged necessary" in final construction.

The Ramillies-class ships of the line were a class of nine 74-gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir Thomas Slade.
The Albion-class ships of the line were a class of five 74-gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir Thomas Slade.

The Courageux-class ships of the line were a class of six 74-gun third rates of the Royal Navy. Their design was a direct copy of the French ship Courageux, captured in 1761 by HMS Bellona. This class of ship is sometimes referred to as the Leviathan class. A further two ships of the class were built to a slightly lengthened version of the Courageux draught. A final two ships were ordered to a third modification of the draught.

The Intrepid-class ships of the line were a class of fifteen 64-gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir John Williams. His design, approved on 18 December 1765, was slightly smaller than Sir Thomas Slade's contemporary Worcester-class design of the same year, against which it was evaluated competitively. Following the prototype, four more ships were ordered in 1767–69, and a further ten between 1771 and 1779.
The Mermaid-class frigates were a group of six 28-gun sailing frigates of the sixth rate designed in 1760 by Sir Thomas Slade, based on the scaled-down lines of HMS Aurora.
The Richmond-class frigates were 32-gun sailing frigates of the fifth rate produced for the Royal Navy. They were designed in 1756 by the Navy's Surveyor, William Bately, and were his equivalent of the Southampton-class frigates designed by Bately's co-Surveyor, Thomas Slade. They were faster ships than the Southamptons, and were weatherly craft, remaining dry even in high seas. Three ships were ordered to this design between 1756 and 1757, while a second batch of three ships was ordered between 1761 and 1762 to a slightly modified design.
The Niger-class frigates were 32-gun sailing frigates of the fifth rate produced for the Royal Navy. They were designed in 1757 by Sir Thomas Slade, and were an improvement on his 1756 design for the 32-gun Southampton-class frigates.
The Southampton-class frigates launched from 1820 onwards were 52-gun sailing frigates of the fourth rate produced for the Royal Navy following the close of the Napoleonic War. They were designed in 1816 to carry sixty guns, but were completed with fifty-two guns only. The design, a joint effort by the Surveyors of the Navy, was modified from that of the Java launched in 1815.

The Iphigénie class was a group of nine 32-gun/12-pounder frigates of the French Navy, built during the late 1770s at Lorient and Saint Malo. They were designed by Léon Guignace. The seven built at Saint Malo were initially numbered Nos. 1 – 7 respectively, and not given names until October 1777 and the start of 1778 ; all seven were captured by the British Navy between 1779 and the end of 1800. Of the two built at Lorient, the Spanish captured one, and a storm wrecked the other.
HMS Burford was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at Chatham Dockyard to the draught specified by the 1745 Establishment as amended in 1754, and launched in 1757.

The Lively class were a successful class of sixteen British Royal Navy 38-gun sailing frigates.
The Apollo-class sailing frigates were a series of twenty-seven ships that the British Admiralty commissioned be built to a 1798 design by Sir William Rule. Twenty-five served in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars, two being launched too late.

The Roebuck-class ship was a class of twenty 44-gun sailing two-decker warships of the Royal Navy. The class carried two complete decks of guns, a lower battery of 18-pounders and an upper battery of 9-pounders. This battery enabled the vessel to deliver a broadside of 285 pounds. Most were constructed for service during the American Revolutionary War but continued to serve thereafter. By 1793 five were still on the active list. Ten were hospital ships, troopships or storeships. As troopships or storeships they had the guns on their lower deck removed. Many of the vessels in the class survived to take part in the Napoleonic Wars. In all, maritime incidents claimed five ships in the class and war claimed three.
The Adventure-class ship was a class of eight 44-gun sailing two-decker warships of the Royal Navy, classed as a fifth rate like a frigate, but carrying two complete decks of guns, a lower battery of 18-pounders and an upper battery of 12-pounders. This enabled the vessel to deliver a broadside of 318 pounds.

HMS Surprise was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy, which served throughout the American Revolutionary War and was broken up in 1783.

The Flora-class frigates were 36-gun sailing frigates of the fifth rate produced for the Royal Navy. They were designed in 1778 by Sir John Williams in response to an Admiralty decision to discontinue 32-gun, 12-pounder (5.4 kg), vessels. Williams proposed a frigate with a main battery of twenty-six 18-pound (8.2 kg) guns and a secondary armament of ten 6 pounders (2.7 kg). Four 18-pounder carronades and 12 swivel guns were added to the upperworks in September 1799 and the 6-pound long guns were upgraded to 9-pounders in April 1780, before any of the ships were completed.