Related Research Articles

Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO2) is a colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas. The current concentration is about 0.04% (412 ppm) by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Natural sources include volcanoes, hot springs and geysers, and it is freed from carbonate rocks by dissolution in water and acids. Because carbon dioxide is soluble in water, it occurs naturally in groundwater, rivers and lakes, ice caps, glaciers and seawater. It is present in deposits of petroleum and natural gas. Carbon dioxide has a sharp and acidic odor and generates the taste of soda water in the mouth. However, at normally encountered concentrations it is odorless.
Globalization, or globalisation, is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. Globalization has accelerated since the 18th century due to advances in transportation and communication technology. This increase in global interactions has caused a growth in international trade and the exchange of ideas and culture. Globalization is primarily an economic process of interaction and integration that is associated with social and cultural aspects. However, disputes and diplomacy are also large parts of the history of globalization, and of modern globalization.

The Group of Eight (G8) was an inter-governmental political forum from 1997 until 2014. It had formed from incorporating the country of Russia into the Group of Seven, or G7, and returned to its previous name after Russia was disinvited in 2014.

The Global South is an emerging term, used by the World Bank and other organizations, identifying countries with one side of the underlying global North–South divide, the other side being the countries of the Global North. As such the term does not inherently refer to a geographical south; for example, most of the Global South is actually within the Northern Hemisphere.

The World Economic Forum (WEF), based in Cologny, Geneva Canton, Switzerland, is an international NGO, founded on 24 January 1971. The WEF's mission is stated as "committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and other leaders of society to shape global, regional, and industry agendas".
2G is short for second-generation cellular network. 2G cellular networks were commercially launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja in 1991.

Vodafone Group plc is a British multinational telecommunications company. Its registered office is in Newbury, Berkshire, England and its global headquarters is in London. It predominantly operates services in Asia, Africa, Europe, and Oceania.

My Little Pony (MLP) is a toy line and media franchise mainly targeting girls, developed by American toy company Hasbro, although it has found an unintended audience of bronies. The first toys were developed by Bonnie Zacherle, Charles Muenchinger, and Steve D'Aguanno, and were produced in 1981. The ponies feature colorful bodies, manes and a unique symbol on one or both sides of their flanks. Such symbols are referred to in the two most recent incarnations as "cutie marks". My Little Pony has been revamped several times with new and more modern looks to continue its appeal to the market.

The Gulfstream G550 is a business jet aircraft produced by General Dynamics' Gulfstream Aerospace unit in Savannah, Georgia, US. The certification designation is GV-SP. As of January 2016, there were 450 G550s in service. The final G550 commercially available unit is to be delivered in 2021. A version of the airplane with reduced fuel capacity was marketed as the G500.
A global city, also called a power city, world city, alpha city or world center, is a city which is a primary node in the global economic network. The concept comes from geography and urban studies, and the idea that globalization is created and furthered in strategic geographic locales according to a hierarchy of importance to the operation of the global system of finance and trade.
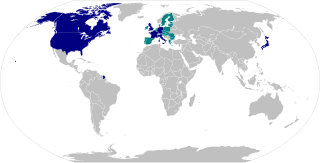
The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental organization consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States. The heads of government of the member states, as well as the representatives of the European Union, meet at the annual G7 Summit.

The NatureServe conservation status system, maintained and presented by NatureServe in cooperation with the Natural Heritage Network, was developed in the United States in the 1980s by The Nature Conservancy (TNC) as a means for ranking or categorizing the relative imperilment of species of plants, animals, or other organisms, as well as natural ecological communities, on the global, national or subnational levels. These designations are also referred to as NatureServe ranks, NatureServe statuses, or Natural Heritage ranks. While the Nature Conservancy is no longer substantially involved in the maintenance of these ranks, the name TNC ranks is still sometimes encountered for them.

The G20 is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability, the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks, have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one.
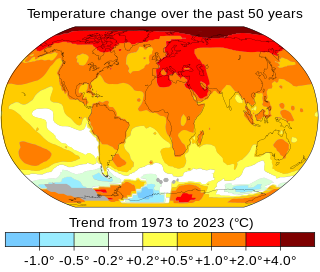
Climate change includes both the global warming driven by human emissions of greenhouse gases, and the resulting large-scale shifts in weather patterns. Though there have been previous periods of climatic change, since the mid-20th century, humans have had unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and caused change on a global scale.
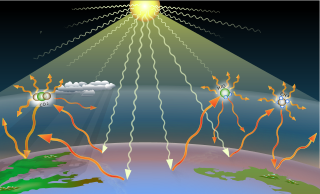
A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H
2O), carbon dioxide (CO
2), methane (CH
4), nitrous oxide (N
2O), and ozone (O3). Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F). The atmospheres of Venus, Mars and Titan also contain greenhouse gases.

Ephelis is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.

In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks which provide connectivity to most current cellphones. 5G networks are predicted to have more than 1.7 billion subscribers worldwide by 2025, according to the GSM Association. Like its predecessors, 5G networks are cellular networks, in which the service area is divided into small geographical areas called cells. All 5G wireless devices in a cell are connected to the Internet and telephone network by radio waves through a local antenna in the cell. The main advantage of the new networks is that they will have greater bandwidth, giving higher download speeds, eventually up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbit/s). Due to the increased bandwidth, it is expected the networks will not exclusively serve cellphones like existing cellular networks, but also be used as general internet service providers for laptops and desktop computers, competing with existing ISPs such as cable internet, and also will make possible new applications in internet of things (IoT) and machine to machine areas. 4G cellphones are not able to use the new networks, which require 5G enabled wireless devices.
The legal and cultural expectations for date and time representation vary between countries, and it is important to be aware of the forms of all-numeric calendar dates used in a particular country to know what date is intended.
Aglossa brabanti is a species of snout moth in the genus Aglossa. It was described by Ragonot in 1884, and is known from France and the Iberian Peninsula.
The Nokia 8.3 5G is a Nokia-branded smartphone released by HMD Global Oy, running Android One. It is HMD's first 5G phone, and was announced on 19 March 2020 alongside the Nokia 5.3, Nokia 1.3, and Nokia 5310 (2020). The Nokia 8.3 5G is claimed to be the first smartphone which is compatible with all existing 5G bands. It was released in September 2020.
References
- ↑ "GlobIZ search". Global Information System on Pyraloidea. Retrieved 2014-07-15.
- ↑ Beccaloni, G.; Scoble, M.; Kitching, I.; Simonsen, T.; Robinson, G.; Pitkin, B.; Hine, A.; Lyal, C., eds. (2003). "Hammocallos brabanti". The Global Lepidoptera Names Index . Natural History Museum . Retrieved May 2, 2018.
| This Odontiinae-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |