
"Junk food" is a term used to describe food that is high in calories from sugar and/or fat, and possibly sodium, but with little dietary fiber, protein, vitamins, minerals, or other important forms of nutritional value. It is also known as HFSS food. The term junk food is a pejorative dating back to the 1950s.

A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics is a 501(c)(6) trade association in the United States. With over 112,000 members, the association claims to be the largest organization of food and nutrition professionals. It has registered dietitian nutritionists (RDNs), nutrition and dietetics technicians registered (NDTRs), and other dietetics professionals as members. Founded in 1917 as the American Dietetic Association, the organization officially changed its name to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics in 2012. According to the group's website, about 65% of its members are RDNs, and another 2% are NDTRs. The group's primary activities include providing testimony at hearings, lobbying the United States Congress and other governmental bodies, commenting on proposed regulations, and publishing statements on various topics pertaining to food and nutrition.

Food policy is the area of public policy concerning how food is produced, processed, distributed, purchased, or provided. Food policies are designed to influence the operation of the food and agriculture system balanced with ensuring human health needs. This often includes decision-making around production and processing techniques, marketing, availability, utilization, and consumption of food, in the interest of meeting or furthering social objectives. Food policy can be promulgated on any level, from local to global, and by a government agency, business, or organization. Food policymakers engage in activities such as regulation of food-related industries, establishing eligibility standards for food assistance programs for the poor, ensuring safety of the food supply, food labeling, and even the qualifications of a product to be considered organic.

Food marketing brings together the food producer and the consumer through a chain of marketing activities.
Nutritional rating systems are used to communicate the nutritional value of food in a more-simplified manner, with a ranking, than nutrition facts labels. A system may be targeted at a specific audience. Rating systems have been developed by governments, non-profit organizations, private institutions, and companies. Common methods include point systems to rank foods based on general nutritional value or ratings for specific food attributes, such as cholesterol content. Graphics and symbols may be used to communicate the nutritional values to the target audience.
Obesity in Mexico is a relatively recent phenomenon, having been widespread since the 1980s with the introduction of processed food into much of the Mexican food market. Prior to that, dietary issues were limited to under and malnutrition, which is still a problem in various parts of the country. Following trends already ongoing in other parts of the world, Mexicans have been foregoing the traditional Mexican diet high in whole grains, fruits, legumes and vegetables in favor of a diet with more animal products and processed foods. It has seen dietary energy intake and rates of overweight and obese people rise with seven out of ten at least overweight and a third clinically obese.

George L. Blackburn was the S. Daniel Abraham Professor of Nutrition and associate director of the division of nutrition at Harvard Medical School. He was also director of the Center for the Study of Nutrition Medicine (CSNM) in the Roberta and Stephen R. Weiner Department of Surgery, and director of the new Feihe Nutrition Laboratory at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), Boston, Massachusetts.
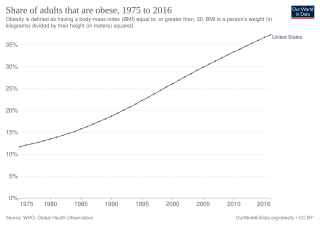
Obesity is common in the United States and is a major health issue associated with numerous diseases, specifically an increased risk of certain types of cancer, coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and cardiovascular disease, as well as significant increases in early mortality and economic costs.
Based in Washington, D.C., Leadership for Healthy Communities is a $10-million national program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation designed to engage and support local and state government leaders nationwide in their efforts to advance public policies that support healthier communities and prevent childhood obesity. The program places an emphasis on policies with the greatest potential for increasing sustainable opportunities for physical activity and healthy eating among children at highest risk for obesity, including African-American, Latino, American Indian and Alaska Native, Asian-American and Pacific Islander children living in lower-income communities. The foundation's primary goal is the reversal of the childhood obesity epidemic by 2015.

Let's Move! is a public health campaign in the United States led by former First Lady Michelle Obama. The campaign aimed to reduce childhood obesity and encourage a healthy lifestyle in children.
The Childhood Obesity Task Force is a United States Government task force charged with reducing childhood obesity in the United States. It was founded on February 9, 2010, by the Obama Administration through a Presidential Memorandum, announcing the establishment of a Task Force on Childhood Obesity. The Task Force aims to develop a plan to reduce childhood obesity. In the announcement, President Barack Obama highlighted the statistics on childhood obesity in the United States and outlined the steps that this new task force would be taking to end childhood obesity. Section 1 of the Memorandum states:
There is established a Task Force on Childhood Obesity to develop an interagency action plan to solve the problem of obesity among our Nation's children within a generation. The Assistant to the President for Domestic Policy shall serve as Chair of the Task Force.
Bon'App, Inc. is a social enterprise in Cambridge, Massachusetts that was founded by Laurent Adamowicz. Bon'App is an open platform that includes applications for Apple mobile devices and Android phones.The Bon'App application is type-and-voice-powered, instantly telling users what is in their food in terms of caloric breakdown, sugar, salt, and "bad fat". With the official lifting of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission's ban on general solicitation on Sept. 23, 2013, Bon'App has officially begun raising capital by offering securities to accredited investors on the crowd-funding platform Fundable.

A sweetened beverage is any beverage with added sugar. It has been described as "liquid candy". Consumption of sweetened beverages has been linked to weight gain, obesity, and associated health risks. According to the CDC, consumption of sweetened beverages is also associated with unhealthy behaviors like smoking, not getting enough sleep and exercise, and eating fast food often and not enough fruits regularly.
The National Policy and Legal Analysis Network to Prevent Childhood Obesity, or NPLAN for short, is a nonprofit organization funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, and which, according to its website, plays an important role in the Foundation's effort to reverse the obesity epidemic by 2015, a commitment that was announced in 2007. Their partners include, in addition to the RWJF, Active Living by Design and the Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity at Yale. They are run by ChangeLab Solutions, originally known as Public Health Law and Policy, which focuses not only on obesity but also on tobacco regulation. The NPLAN advocates for a soda tax, specifically an excise tax, and have published model legislation which earmarks the funds raised to go to programs to prevent and treat obesity. According to the American Public Health Association, they provide "legal technical assistance focused on childhood obesity prevention policy." The Network has also "developed model menu labeling ordinances, requiring chain restaurants to post calorie and other nutrition information on menus." NPLAN has advocated for the use of licensing and zoning laws to "shape the way land is used and how businesses operate," and has praised regulations requiring nutrition standards on foods sold in snack machines in schools. According to their website, they "work on four broad issue areas: healthy community food systems, healthy schools, healthy land use planning, and food marketing." The American Bar Association's director of public health and policy Marice Ashe wrote the following soon after the NPLAN's founding was announced: "NPLAN will serve as an incubator where lawyers, policymakers, advocates, and scientists collaborate to produce legal and policy tools and resources. As research and products are developed, NPLAN will also operate as a national one-stop source for access to practical, efficient, and effective legal technical assistance products."

FriendsLearn is a privately held life science research and biotechnology mHealth company, with offices in San Francisco California and Chennai. The company was founded in 2011 and develops mobile health technologies, best known as the producer and developer of fooya!. FriendsLearn is a pioneer of Digital Vaccines, which Carnegie Mellon University featured as one of the top breakthroughs in technology as part of the annual "Year in Review" publication. The company is known for first in class therapeutic candidates in the field of neuromodulation and neurocognitive training through the use of artificial intelligence, virtual reality technology, neuropsychology based behavior design, gamification and learnified entertainment.
Laurent Adamowicz is a French businessman, entrepreneur, lecturer, author, and public health advocate. He is the founder and president of the public charity EChO – Eradicate Childhood Obesity Foundation and a member of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Nutrition Round Table.

Sugarwise is the international certification authority for sugar claims on food and drink. It assesses foods and beverages on the basis of their sugar claims.

Chile's food labelling and advertising law, formally titled Ley 20.606, sobre la composición de los alimentos y su publicidad establishes a regulatory framework on food security and healthy food with the intention of guiding consumers towards behaviour patterns that promote public health. After the 2012 law was enacted, its accompanying regulations came into full force on June 27, 2016. Andrew Jacobs, writing for The New York Times, has characterized this measure as "the world’s most ambitious attempt to remake a country’s food culture" and suggests it "could be a model for how to turn the tide on a global obesity epidemic that researchers say contributes to four million premature deaths a year."

The Health Star Rating System (HSR) is an Australian and New Zealand Government initiative that assigns health ratings to packaged foods and beverages. The purpose for the Health Star Rating is to provide a visual comparison of like for like products, to assist consumers into distinguishing and choosing the healthier options. It was designed to target time-deprived working adults as well as parents and children who were less likely to check how healthy each individual product was, through examination of the nutritional facts label on the back of products.











