Common Era (CE) is one of the year notations used for the Gregorian calendar, the world's most widely used calendar era. Before the Common Era (BCE) is the era before CE. BCE and CE are alternatives to the Dionysian BC and AD notations, respectively. The Dionysian era distinguishes eras using the notations BC and AD. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: "2021 CE" and "AD 2021" each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are each the same year. The Gregorian calendar is used throughout the world today, and is an international standard for civil calendars.
The timeline of the evolutionary history of life represents the current scientific theory outlining the major events during the development of life on planet Earth. In biology, evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organization, from kingdoms to species, and individual organisms and molecules, such as DNA and proteins. The similarities between all present day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species, living and extinct, have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described. However, a May 2016 scientific report estimates that 1 trillion species are currently on Earth, with only one-thousandth of one percent described.

The Phanerozoic Eon is the current geologic eon in the geologic time scale, and the one during which abundant animal and plant life has existed. It covers 541 million years to the present, and it began with the Cambrian Period when animals first developed hard shells preserved in the fossil record. The time before the Phanerozoic, called the Precambrian, is now divided into the Hadean, Archaean and Proterozoic eons.
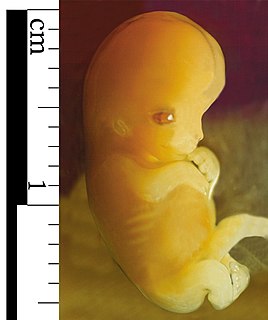
An embryo is the early stage of development of a multicellular organism. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization and continues through the formation of body structures, such as tissues and organs. Each embryo starts development as a zygote, a single cell resulting from the fusion of gametes. In the first stages of embryonic development, a single-celled zygote undergoes many rapid cell divisions, called cleavage, to form a blastula, which looks similar to a ball of cells. Next, the cells in a blastula-stage embryo start rearranging themselves into layers in a process called gastrulation. These layers will each give rise to different parts of the developing multicellular organism, such as the nervous system, connective tissue, and organs.

Egyptology is the study of ancient Egyptian history, language, literature, religion, architecture and art from the 5th millennium BC until the end of its native religious practices in the 4th century AD. A practitioner of the discipline is an "Egyptologist". In Europe, particularly on the Continent, Egyptology is primarily regarded as being a philological discipline, while in North America it is often regarded as a branch of archaeology.

The Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS) is an American partnership of federal agencies designed to provide consistent and reliable information on the taxonomy of biological species. ITIS was originally formed in 1996 as an interagency group within the US federal government, involving several US federal agencies, and has now become an international body, with Canadian and Mexican government agencies participating. The database draws from a large community of taxonomic experts. Primary content staff are housed at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History and IT services are provided by a US Geological Survey facility in Denver. The primary focus of ITIS is North American species, but many biological groups exist worldwide and ITIS collaborates with other agencies to increase its global coverage.

Wildlife conservation refers to the practice of protecting wild species and their habitats in order to maintain healthy wildlife species or populations and to restore, protect or enhance natural ecosystems. Major threats to wildlife include habitat destruction, degradation, fragmentation, overexploitation, poaching, pollution and climate change. The IUCN estimates that 27,000 species of the ones assessed are at risk for extinction. Expanding to all existing species, a 2019 UN report on biodiversity put this estimate even higher at a million species. It is also being acknowledged that an increasing number of ecosystems on Earth containing endangered species are disappearing. To address these issues, there have been both national and international governmental efforts to preserve Earth's wildlife. Prominent conservation agreements include the 1973 Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) and the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). There are also numerous nongovernmental organizations (NGO's) dedicated to conservation such as the Nature Conservancy, World Wildlife Fund, and Conservation International.

Lachesillidae is a family of Psocoptera, or fateful barklice, belonging to the suborder Psocomorpha. Members of the family are characterised by a rounded, free areola postica in their wings. Males have diverse sclerotized genitalic structures. The family includes more than 400 species, most of them in the genus Lachesilla.

The Ropalomeridae are a family of acalyptrate flies.

Saltwater fish, also called marine fish, are fish that live in ocean water. Saltwater fish can swim and live alone or in a large group called a school.

Eratoneura affinis is a species of leafhopper in the family Cicadellidae.

Eratoneura ardens is a species of leafhopper in the family Cicadellidae.

Eratoneura ligata is a species of leafhopper in the family Cicadellidae.

Eratoneura osborni is a species of leafhopper in the family Cicadellidae.

Eriocampa is a genus of common sawflies in the family Tenthredinidae. There are about ten described species in Eriocampa.

Trogiidae is a family of granary booklice in the order Psocodea. There are about 11 genera and more than 50 described species in Trogiidae.

The fauna of Romania comprises all the animal species inhabiting the country of Romania and its coastal territory in the Black Sea.

Reiwa is the current era of Japan's official calendar. It began on 1 May 2019, the day on which Emperor Akihito's elder son, Naruhito, ascended the throne as the 126th Emperor of Japan. The day before, Emperor Akihito abdicated the Chrysanthemum Throne, marking the end of the Heisei era. The year 2019 corresponds with Heisei 31 from 1 January through 30 April, and with Reiwa 1 from 1 May. Reiwa is interpreted as "beautiful harmony".
















