Related Research Articles

Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation with their odor.

In chemistry, aromaticity means a molecule has a cyclic (ring-shaped) structure with pi bonds in resonance. Aromatic rings give increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term aromaticity with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning.

Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.

Phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a colorless, crystal-like solid, but can also appear yellow. Phenanthrene is used to make dyes, plastics and pesticides, explosives and drugs. It has also been used to make bile acids, cholesterol and steroids.

Coronene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) comprising seven peri-fused benzene rings. Its chemical formula is C
24H
12. It is a yellow material that dissolves in common solvents including benzene, toluene, and dichloromethane. Its solutions emit blue light fluorescence under UV light. It has been used as a solvent probe, similar to pyrene.

A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are found in coal and in oil deposits, and are also produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter—for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires.
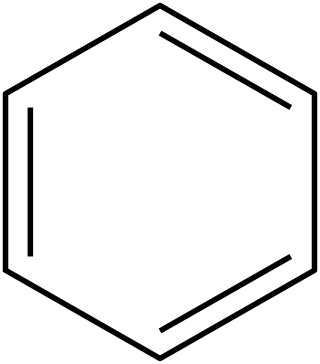
In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule predicts that a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties if it has 4n + 2 π electrons, where n is a non-negative integer. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931. The succinct expression as the 4n + 2 rule has been attributed to W. v. E. Doering (1951), although several authors were using this form at around the same time.
A non-Kekulé molecule is a conjugated hydrocarbon that cannot be assigned a classical Kekulé structure.

Fluorene, or 9H-fluorene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2CH2. It forms white crystals that exhibit a characteristic, aromatic odor similar to that of naphthalene. It has a violet fluorescence, hence its name. For commercial purposes it is obtained from coal tar. It is insoluble in water and soluble in many organic solvents. Although sometimes classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the five-membered ring has no aromatic properties. Fluorene is mildly acidic.
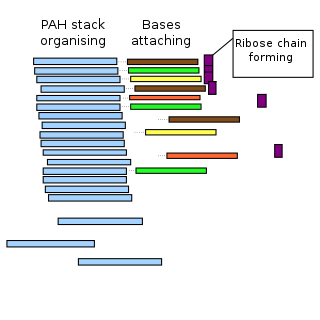
The PAH world hypothesis is a speculative hypothesis that proposes that polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), known to be abundant in the universe, including in comets, and assumed to be abundant in the primordial soup of the early Earth, played a major role in the origin of life by mediating the synthesis of RNA molecules, leading into the RNA world. However, as yet, the hypothesis is untested.
In organic and physical organic chemistry, Clar's rule is an empirical rule that relates the chemical stability of a molecule with its aromaticity. It was introduced in 1972 by the Austrian organic chemist Erich Clar in his book The Aromatic Sextet. The rule states that given a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the resonance structure most important to characterize its properties is that with the largest number of aromatic π-sextets i.e. benzene-like moieties.
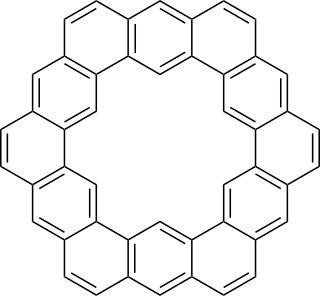
Kekulene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon which consists of 12 fused benzene rings arranged in a circle. It is therefore classified as a [12]-circulene with the chemical formula C48H24. It was first synthesized in 1978, and was named in honor of August Kekulé, the discoverer of the structure of the benzene molecule.

Zethrene (dibenzo[de,mn]naphthacene) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of two phenalene units fused together. According to Clar's rule, the two exterior naphthalene units are truly aromatic and the two central double bonds are not aromatic at all. For this reason the compound is of some interest to academic research. Zethrene has a deep-red color and it is light sensitive - complete decomposition under a sunlight lamp occurs within 12 hours. The melting point is 262 °C.
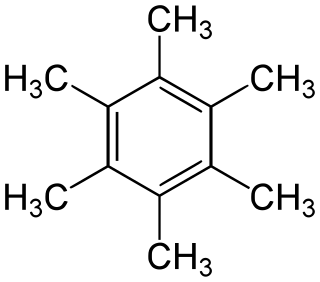
Hexamethylbenzene, also known as mellitene, is a hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C12H18 and the condensed structural formula C6(CH3)6. It is an aromatic compound and a derivative of benzene, where benzene's six hydrogen atoms have each been replaced by a methyl group. In 1929, Kathleen Lonsdale reported the crystal structure of hexamethylbenzene, demonstrating that the central ring is hexagonal and flat and thereby ending an ongoing debate about the physical parameters of the benzene system. This was a historically significant result, both for the field of X-ray crystallography and for understanding aromaticity.
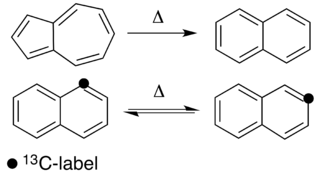
Thermal rearrangements of aromatic hydrocarbons are considered to be unimolecular reactions that directly involve the atoms of an aromatic ring structure and require no other reagent than heat. These reactions can be categorized in two major types: one that involves a complete and permanent skeletal reorganization (isomerization), and one in which the atoms are scrambled but no net change in the aromatic ring occurs (automerization). The general reaction schemes of the two types are illustrated in Figure 1.

2-Methylnaphthalene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH).
Sir James Wilfred Cook FRS FRSE DSc LLD (1900–1975) was an English chemist, best known for his research of organic chemistry of carcinogenic compounds. Friends knew him simply as Jim Cook.

Trinaphthylene is a chemical compound of the group of Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, can be obtained from triphthalylbenzene.

Staci Simonich is an American environmental scientist who is a professor and dean for the College of Agricultural Sciences at Oregon State University. Her research considers how chemicals move through the environment. She was appointed Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 2021.
References
- ↑ "Dr. Erich (Eric) Clar" . Retrieved 2014-01-20.
- ↑ German patents 551 447 (1930), 553 000 (1930), and 549 206 (1930) issued I. G. Farbenindustrie with E. Clar as inventor
- ↑ "High award for Glasgow scientist". The Glasgow Herald. October 29, 1965. p. 8. Retrieved 2014-01-20.
- ↑ "New titular professors at Glasgow". The Glasgow Herald. June 29, 1966. p. 5. Retrieved 2014-01-20.
- ↑ "ISPAC Awards". Archived from the original on 2016-03-14. Retrieved 2014-01-20.