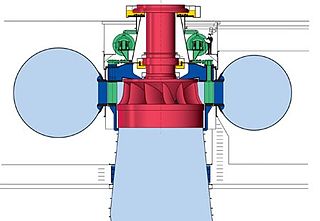
Dartmouth Dam is a large rock-fill embankment dam with an uncontrolled chute spillway across the Mitta Mitta, Gibbo, and Dart rivers, the Morass Creek and a number of small tributaries. The dam is located near Mount Bogong in the north-east of the Australian state of Victoria. The dam's purpose includes irrigation, the generation of hydro-electric power, water supply and conservation. The impounded reservoir is called Dartmouth Reservoir, sometimes called Lake Dartmouth. The Dartmouth Power Station, a hydro-electric power station that generates power to the national grid, is located near the dam wall.

The Haditha Dam or Qadisiya Dam is an earth-fill dam on the Euphrates, north of Haditha (Iraq), creating Lake Qadisiyah. The dam is just over 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) long and 57 metres (187 ft) high. The purpose of the dam is to generate hydroelectricity, regulate the flow of the Euphrates and provide water for irrigation. It is the second-largest hydroelectric contributor to the power system in Iraq behind the Mosul Dam.

The Temengor Dam or Temengor Hydro-Electric Project or Temengor Power Station is a dam in Gerik, Perak, Malaysia. It is located on Perak River about 200 km northeast of Ipoh. Construction of the dam impounded Temenggor Lake.
Chenderoh Power Station or Chenderoh Dam is the oldest hydroelectric dam and power station in Malaysia. The dam is located in Tasik Chenderoh, near Kuala Kangsar, Perak. It was constructed on the early 1920s by the British Federated Malay States administration.

Kaptai Dam is on the Karnaphuli River at Kaptai, 65 kilometres (40 mi) upstream from Chittagong in Rangamati District, Bangladesh. It is an earth-fill embankment dam with a reservoir water storage capacity of 6,477 million cubic metres (5,251,000 acre⋅ft). The primary purpose of the dam and reservoir was to generate hydroelectric power. Construction was completed in 1962. The generators in the 230 megawatts (310,000 hp) Karnafuli Hydroelectric Power Station were commissioned between 1962 and 1988. It is the only hydroelectric power station in Bangladesh.

Canyon Ferry Dam is a concrete gravity dam in a narrow valley of the Missouri River, United States, where the Big Belt Mountains and the Spokane Hills merge, approximately 68 miles (109 km) downstream from the confluence of the Gallatin, Madison, and Jefferson rivers, and about 20 miles (32 km) east of the city of Helena, Montana. The dam is for flood control, irrigation, recreation and hydroelectric power. The building of the dam created a reservoir known as Canyon Ferry Lake.

Pantabangan Dam is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Pampanga River located in Pantabangan in Nueva Ecija province of the Philippines. The multi-purpose dam provides water for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation while its reservoir, Pantabangan Lake, affords flood control. The reservoir is considered one of the largest in Southeast Asia and also one of the cleanest in the Philippines. Construction on the dam began in 1971 and it was completed in 1974.

The Serra da Mesa Dam, once known as Sao Felix, is an embankment dam on the Tocantins River near Minaçu in Goiás, Brazil. The dam serves an associated hydroelectric power plant with a 1,275 megawatts (1,710,000 hp) installed capacity. The dam creates the largest reservoir by volume in Brazil.

The Fengman Dam is a concrete gravity dam 20 km (12 mi) from Jilin City on the Second Songhua River in Jilin Province, China. The main purposes of the dam are hydroelectric power generation and flood control. Construction of the dam began in 1937 and was complete in 1953. Northeast China Grid Company Limited, the dam's owner, plans on rebuilding it in the future.

The Yantan Dam is a gravity dam on the Hongshui River near Dahua County, Guangxi China. The main purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and it has an associated 1,210 MW power station consisting of 4 x 302.5 MW Francis turbine-generators.

The Chirkey Dam is an arch dam on the Sulak River in Dagestan, Russia. The main purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and it supports a 1,000 MW power station. Construction on the dam began in 1964, the first generator was operational by 1974, the last in 1976 while the project was officially completed in 1978. It is the tallest arch dam in Russia.

The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, formerly known as the Millennium Dam and sometimes referred to as Hidase Dam, is a gravity dam on the Blue Nile River in Ethiopia that has been under construction since 2011. It is in the Benishangul-Gumuz Region of Ethiopia, about 15 km (9 mi) east of the border with Sudan. At 6.45 gigawatts, the dam will be the largest hydroelectric power plant in Africa when completed, as well as the 7th largest in the world. As of August 2017, the work stood at 60% completion. Once completed, the reservoir will take from 5 to 15 years to fill with water.

Ruskin Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Stave River in Ruskin, British Columbia, Canada. The dam was completed in 1930 for the primary purpose of hydroelectric power generation. The dam created Hayward Lake, which supplies water to a 105 MW powerhouse and flooded the Stave's former lower canyon, which ended in a small waterfall approximately where the dam is today.

Stave Falls Dam is a dual-dam power complex on the Stave River in Stave Falls, British Columbia, Canada. The dam was completed in 1912 for the primary purpose of hydroelectric power production. To increase the capacity of Stave Lake, the dam was raised in 1925 and the Blind Slough Dam constructed in an adjacent watercourse 500 m (1,600 ft) to the north, which was the site of the eponymous Stave Falls. In 2000, the dam's powerhouse was replaced after a four-year upgrade. The powerhouse was once British Columbia's largest hydroelectric power source and is a National Historic Site of Canada.
The Ichari Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Tons River 13 km (8 mi) north of Dakpathar in Uttarakhand, India. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and it is a run-of-the-river-type. It was completed in 1972. The dam diverts water to the Chibro Power Station which is then returned to the Tons River before being fed to the Khodri Power Station.

The Koteshwar Dam is a gravity dam on the Bhagirathi River, located 22 km (14 mi) downstream of the Tehri Dam in Tehri District, Uttarakhand, India. The dam is part of the Tehri Hydropower Complex and serves to regulate the Tehri Dam's tailrace for irrigation and create the lower reservoir of the Tehri Pumped Storage Power Station. In addition, the dam has a 400 MW run-of-the-river power station. The project was approved in 2000 and its first generator was commissioned on 27 March 2011, the second on 30 March 2011. The construction site had been inundated in September 2010 by floods. The diversion tunnel was later blocked heaving/collapse of the hill in December 2010. The spillway was commissioned in Jan,2011. The last two generators were made operational in March 2012.

The Dongfeng Dam is an arch dam on the Wu River 65 km (40 mi) northwest of Qingzhen in Guizhou Province, China. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 570 MW power station. Construction on the dam began in 1989 and the first generator was operational in 1994, the last in 1995. The generators were up-rated between 2004 and 2005; bringing their capacity from 170 MW each to 190 MW.

The Panjiakou Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Luan River in Qianxi County, Hebei Province, China. The primary purpose of the dam is to provide water for the cities of Tianjin and Tangshan, located to the south. The dam also provides flood control and its power plant has an installed capacity of 420 MW which includes a 270 MW pumped storage power station.

The Vianden Pumped Storage Plant is located just north of Vianden in Diekirch District, Luxembourg. The power plant uses the pumped-storage hydroelectric method to generate electricity and serves as a peaking power plant. Its lower reservoir is located on the Our River, bordering Germany, and the upper is elevated above on the nearby Saint Nicholas Mountain. Construction on the plant began in 1959 and the first pump-generators were commissioned in 1962. A tenth pump-generator was installed in 1976 bringing the plant's installed generating capacity to 1,096 megawatts (1,470,000 hp). The plant generates an average of 1,650 gigawatt-hours (5,900 TJ) annually and is owned by Société Electrique de l'Our and RWE. Construction on an eleventh pump-generator began in 2010 and it is expected to be commissioned in 2013, which will bring the plant's installed capacity to 1,296 megawatts (1,738,000 hp).

The Lubuge Dam is a rock-fill embankment dam on the Huangni River, a tributary of the Nanpan River, located near Lubugexiang in Luoping County on the border of Guizhou and Yunnan Provinces, China. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 600 MW power station. Construction on the project began in 1982 and it was completed in 1991. Funded by the World Bank, it was the first loan offered by the bank to China's power sector.