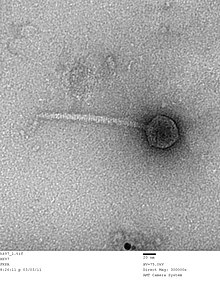
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The capsid and inner genome is called the nucleocapsid.

A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: Duplodnaviria and Varidnaviria, and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm Monodnaviria, which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom Pararnavirae in the realm Riboviria.

Enterobacteria phage λ is a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, that infects the bacterial species Escherichia coli. It was discovered by Esther Lederberg in 1950. The wild type of this virus has a temperate life cycle that allows it to either reside within the genome of its host through lysogeny or enter into a lytic phase, during which it kills and lyses the cell to produce offspring. Lambda strains, mutated at specific sites, are unable to lysogenize cells; instead, they grow and enter the lytic cycle after superinfecting an already lysogenized cell.

Escherichia virus T4 is a species of bacteriophages that infect Escherichia coli bacteria. It is a double-stranded DNA virus in the subfamily Tevenvirinae from the family Myoviridae. T4 is capable of undergoing only a lytic life cycle and not the lysogenic life cycle. The species was formerly named T-even bacteriophage, a name which also encompasses, among other strains, Enterobacteria phage T2, Enterobacteria phage T4 and Enterobacteria phage T6.

Filamentous bacteriophages are a family of viruses (Inoviridae) that infect bacteria, or bacteriophages. They are named for their filamentous shape, a worm-like chain, about 6 nm in diameter and about 1000-2000 nm long. This distinctive shape reflects their method of replication: the coat of the virion comprises five types of viral protein, which are located in the inner membrane of the host bacterium during phage assembly, and these proteins are added to the nascent virion's DNA as it is extruded through the membrane. The simplicity of filamentous phages makes them an appealing model organism for research in molecular biology, and they have also shown promise as tools in nanotechnology and immunology.

Caudoviricetes is a class of viruses known as the tailed bacteriophages. Under the Baltimore classification scheme, the Caudoviricetes are group I viruses as they have double stranded DNA (dsDNA) genomes, which can be anywhere from 18,000 base pairs to 500,000 base pairs in length. The virus particles have a distinct shape; each virion has an icosahedral head that contains the viral genome, and is attached to a flexible tail by a connector protein. The order encompasses a wide range of viruses, many containing genes of similar nucleotide sequence and function. However, some tailed bacteriophage genomes can vary quite significantly in nucleotide sequence, even among the same genus. Due to their characteristic structure and possession of potentially homologous genes, it is believed these bacteriophages possess a common origin.

The phi X 174 bacteriophage is a single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) virus that infects Escherichia coli. This virus was isolated in 1935 by Nicolas Bulgakov in Félix d'Hérelle's laboratory at the Pasteur Institute, from samples collected in Paris sewers. Its characterization and the study of its replication mechanism were carried out from the 1950s onwards. It was the first DNA-based genome to be sequenced. This work was completed by Fred Sanger and his team in 1977. In 1962, Walter Fiers and Robert Sinsheimer had already demonstrated the physical, covalently closed circularity of ΦX174 DNA. Nobel prize winner Arthur Kornberg used ΦX174 as a model to first prove that DNA synthesized in a test tube by purified enzymes could produce all the features of a natural virus, ushering in the age of synthetic biology. In 1972–1974, Jerard Hurwitz, Sue Wickner, and Reed Wickner with collaborators identified the genes required to produce the enzymes to catalyze conversion of the single stranded form of the virus to the double stranded replicative form. In 2003, it was reported by Craig Venter's group that the genome of ΦX174 was the first to be completely assembled in vitro from synthesized oligonucleotides. The ΦX174 virus particle has also been successfully assembled in vitro. In 2012, it was shown how its highly overlapping genome can be fully decompressed and still remain functional.

Bacteriophage T7 is a bacteriophage, a virus that infects bacteria. It infects most strains of Escherichia coli and relies on these hosts to propagate. Bacteriophage T7 has a lytic life cycle, meaning that it destroys the cell it infects. It also possesses several properties that make it an ideal phage for experimentation: its purification and concentration have produced consistent values in chemical analyses; it can be rendered noninfectious by exposure to UV light; and it can be used in phage display to clone RNA binding proteins.
Salmonella virus P22 is a bacteriophage in the Podoviridae family that infects Salmonella typhimurium. Like many phages, it has been used in molecular biology to induce mutations in cultured bacteria and to introduce foreign genetic material. P22 has been used in generalized transduction and is an important tool for investigating Salmonella genetics.
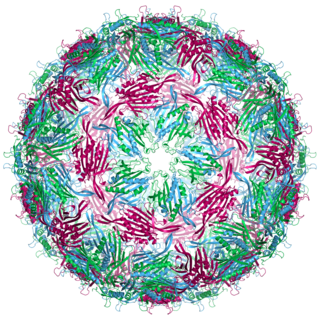
Bacteriophage MS2, commonly called MS2, is an icosahedral, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that infects the bacterium Escherichia coli and other members of the Enterobacteriaceae. MS2 is a member of a family of closely related bacterial viruses that includes bacteriophage f2, bacteriophage Qβ, R17, and GA.

Bacillus virus Φ29 is a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) bacteriophage with a prolate icosahedral head and a short tail that belongs to the genus Salasvirus, order Caudovirales, and family Salasmaviridae. They are in the same order as phages PZA, Φ15, BS32, B103, M2Y (M2), Nf, and GA-1. First discovered in 1965, the Φ29 phage is the smallest Bacillus phage isolated to date and is among the smallest known dsDNA phages.

T7 DNA polymerase is an enzyme used during the DNA replication of the T7 bacteriophage. During this process, the DNA polymerase “reads” existing DNA strands and creates two new strands that match the existing ones. The T7 DNA polymerase requires a host factor, E. coli thioredoxin, in order to carry out its function. This helps stabilize the binding of the necessary protein to the primer-template to improve processivity by more than 100-fold, which is a feature unique to this enzyme. It is a member of the Family A DNA polymerases, which include E. coli DNA polymerase I and Taq DNA polymerase.

Bacteriophage Qbeta, commonly referred to as Qbeta or Qβ, is a species consisting of several strains of positive-strand RNA virus which infects bacteria that have F-pili, most commonly Escherichia coli. Its linear genome is packaged into an icosahedral capsid with a diameter of 28 nm. Bacteriophage Qβ enters its host cell after binding to the side of the F-pilus.

Escherichia virus T5, sometimes called Bacteriophage T5 is a caudal virus within the family Demerecviridae. This bacteriophage specifically infects E. coli bacterial cells and follows a lytic life cycle.
A prohead or procapsid is an immature viral capsid structure formed in the early stages of self-assembly of some bacteriophages, including the Caudovirales or tailed bacteriophages. Production and assembly of stable proheads is an essential precursor to bacteriophage genome packaging; this packaging activity can be replicated in vitro. The prohead structure may take a different shape from the head of a mature virion, as seen with the prohead of Bacillus subtilis phage φ29.

Ff phages is a group of almost identical filamentous phage including phages f1, fd, M13 and ZJ/2, which infect bacteria bearing the F fertility factor. The virion is a flexible filament measuring about 6 by 900 nm, comprising a cylindrical protein tube protecting a single-stranded circular DNA molecule at its core. The phage codes for only 11 gene products, and is one of the simplest viruses known. It has been widely used to study fundamental aspects of molecular biology. George Smith and Greg Winter used f1 and fd for their work on phage display for which they were awarded a share of the 2018 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Early experiments on Ff phages used M13 to identify gene functions, and M13 was also developed as a cloning vehicle, so the name M13 is sometimes used as an informal synonym for the whole group of Ff phages.
Escherichia virus T3, also called bacteriophage T3 and T3 phage, is a bacteriophage capable of infecting susceptible bacterial cells, including strains of Escherichia coli. This phage is closely related to T7 phage in structure though the two viruses may differ in capsid maturation.

The jelly roll or Swiss roll fold is a protein fold or supersecondary structure composed of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded sheets. The name of the structure was introduced by Jane S. Richardson in 1981, reflecting its resemblance to the jelly or Swiss roll cake. The fold is an elaboration on the Greek key motif and is sometimes considered a form of beta barrel. It is very common in viral proteins, particularly viral capsid proteins. Taken together, the jelly roll and Greek key structures comprise around 30% of the all-beta proteins annotated in the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database.

Helios Murialdo is a Chilean-Canadian molecular biologist, fiction writer, and ecologist. His research in the field of the assembly and structure of bacterial viruses contributed to the development of the first system for the cloning of human genes. He has published six novels and is a member of a group of conservationists that established a Natural Reserve in the central part of the Chilean Biodiversity Hotspot. Son of an Italian immigrant father and a Chilean mother of French descent, he has a brother and a sister. He is a member of the board of directors of the non-profit Fundación Ciencia & Vida, a scientific and technological institution with headquarters in Santiago, Chile. He is president of the NGO Corporación Altos de Cantillana, which manages the 26,000 acres of the Altos de Cantillana Natural Reserve in the coastal mountains of central Chile. He makes his home in this Natural Reserve, and spends the rest of the year in Toronto, Canada.

Duplodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all double-stranded DNA viruses that encode the HK97 fold major capsid protein. The HK97 fold major capsid protein is the primary component of the viral capsid, which stores the viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Viruses in the realm also share a number of other characteristics, such as an icosahedral capsid, an opening in the viral capsid called a portal, a protease enzyme that empties the inside of the capsid prior to DNA packaging, and a terminase enzyme that packages viral DNA into the capsid.