
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of an array of programmable logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit wouldn't be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities.

An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. In 2009, it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems.
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, usually to design application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and to program field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs).

Synopsys, Inc. is an American electronic design automation (EDA) company headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, that focuses on silicon design and verification, silicon intellectual property and software security and quality. Synopsys supplies tools and services to the semiconductor design and manufacturing industry. Products include tools for logic synthesis and physical design of integrated circuits, simulators for development, and debugging environments that assist in the design of the logic for chips and computer systems. As of 2023, the company is a component of the Nasdaq-100 and S&P 500 indices.
Esterel is a synchronous programming language for the development of complex reactive systems. The imperative programming style of Esterel allows the simple expression of parallelism and preemption. As a consequence, it is well suited for control-dominated model designs.

Ansys, Inc. is an American multinational company with its headquarters based in Canonsburg, Pennsylvania. It develops and markets CAE/multiphysics engineering simulation software for product design, testing and operation and offers its products and services to customers worldwide.
Lustre is a formally defined, declarative, and synchronous dataflow programming language for programming reactive systems. It began as a research project in the early 1980s. A formal presentation of the language can be found in the 1991 Proceedings of the IEEE. In 1993 it progressed to practical, industrial use in a commercial product as the core language of the industrial environment SCADE, developed by Esterel Technologies. It is now used for critical control software in aircraft, helicopters, and nuclear power plants.

Gérard Philippe Berry is a French computer scientist, member of the French Academy of Sciences, French Academy of Technologies, and Academia Europaea. He was the Chief Scientist Officer of Esterel Technologies from 2000 to 2009. He held the 2007-2008 yearly Liliane Bettencourt chair of Technological Innovation at the Collège de France. He was Director of Research at INRIA Sophia-Antipolis and held the 2009-2010 yearly Informatics and Digital Sciences chair at the Collège de France. Berry's work, which spans over more than 30 years, brought important contributions to three main fields:
I-Logix was a provider of collaborative Model-driven development (MDD) solutions for systems design and software development, particularly focused on real-time embedded applications. Founded in 1987 and based in Andover, Massachusetts, the company specialized in products that facilitated collaboration among engineers working on embedded systems. Additionally, I-Logix was a member of the UML Partners, a consortium dedicated to the development of the Unified Modeling Language (UML).
ARINC 661 is a standard which aims to normalize the definition of a Cockpit Display System (CDS), and the communication between the CDS and User Applications (UA) which manage aircraft avionics functions. The GUI definition is completely defined in binary Definition Files (DF).
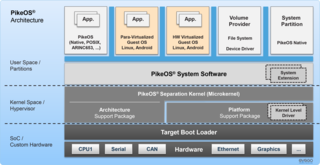
PikeOS is a commercial hard real-time operating system (RTOS) which features a separation kernel-based hypervisor. This hypervisor supports multiple logical partition types for various operating systems (OS) and applications, each referred to as a GuestOS. PikeOS is engineered to support the creation of certifiable smart devices for the Internet of Things (IoT), ensuring compliance with industry standards for quality, safety, and security across various sectors. In instances where memory management units (MMU) are not present but memory protection units (MPU) are available on controller-based systems, PikeOS for MPU is designed for critical real-time applications and provides up-to-standard safety and security.
Rational Rhapsody, a modeling environment based on UML, is a visual development environment for systems engineers and software developers creating real-time or embedded systems and software. Rational Rhapsody uses graphical models to generate software applications in various languages including C, C++, Ada, Java and C#.
NESSUS is a general-purpose, probabilistic analysis program that simulates variations and uncertainties in loads, geometry, material behavior and other user-defined inputs to compute probability of failure and probabilistic sensitivity measures of engineered systems. Because NESSUS uses highly efficient and accurate probabilistic analysis methods, probabilistic solutions can be obtained even for extremely large and complex models. The system performance can be hierarchically decomposed into multiple smaller models and/or analytical equations. Once the probabilistic response is quantified, the results can be used to support risk-informed decisions regarding reliability for safety critical and one-of-a-kind systems, and to maintain a level of quality while reducing manufacturing costs for larger quantity products.
Zemax is a software program used for designing and simulating optical systems. It is widely used in the field of optics and photonics for designing and analyzing the performance of lenses, cameras, telescopes, microscopes, and other optical systems. With the software, the behavior of light interacting with various optical components can be modelled, and optical designs can be optimized for desired performance.
Rational Synergy is a software tool that provides software configuration management (SCM) capabilities for all artifacts related to software development including source code, documents and images as well as the final built software executable and libraries. Rational Synergy also provides the repository for the change management tool known as Rational Change. Together these two tools form an integrated configuration management and change management environment that is used in software development organizations that need controlled SCM processes and an understanding of what is in a build of their software.
DDC-I, Inc. is a privately held company providing software development of real-time operating systems, software development tools, and software services for safety-critical embedded applications, headquartered in Phoenix, Arizona. It was first created in 1985 as the Danish firm DDC International A/S, a commercial outgrowth of Dansk Datamatik Center, a Danish software research and development organization of the 1980s. The American subsidiary was created in 1986. For many years, the firm specialized in language compilers for the programming language Ada.
SIGNAL is a programming language based on synchronized dataflow : a process is a set of equations on elementary flows describing both data and control.
Siemens Digital Industries Software is an American computer software company specializing in 3D & 2D Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software. The company is a business unit of Siemens, operates under the legal name of Siemens Industry Software Inc, and is headquartered in Plano, Texas.
AbsInt is a software-development tools vendor based in Saarbrücken, Germany. The company was founded in 1998 as a technology spin-off from the Department of Programming Languages and Compiler Construction of Prof. Reinhard Wilhelm at Saarland University. AbsInt specializes in software-verification tools based on abstract interpretation. Its tools are used worldwide by Fortune 500 companies, educational institutions, government agencies and startups.
Cantata++, commonly referred to as Cantata in newer versions, is a commercial computer program designed for dynamic testing, with a focus on unit testing and integration testing, as well as run time code coverage analysis for C and C++ programs. It is developed and marketed by QA Systems, a multinational company with headquarters in Waiblingen, Germany.






