
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. In 2009, it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems.

AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology in 2016. These are modified Harvard architecture 8-bit RISC single-chip microcontrollers. AVR was one of the first microcontroller families to use on-chip flash memory for program storage, as opposed to one-time programmable ROM, EPROM, or EEPROM used by other microcontrollers at the time.
Atmel Corporation was a creator and manufacturer of semiconductors before being subsumed by Microchip Technology in 2016. Atmel was founded in 1984. The company focused on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products included microcontrollers radio-frequency (RF) devices including Wi-Fi, EEPROM, and flash memory devices, symmetric and asymmetric security chips, touch sensors and controllers, and application-specific products. Atmel supplies its devices as standard products, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), or application-specific standard product (ASSPs) depending on the requirements of its customers.

TinyOS is an embedded, component-based operating system and platform for low-power wireless devices, such as those used in wireless sensor networks (WSNs), smartdust, ubiquitous computing, personal area networks, building automation, and smart meters. It is written in the programming language nesC, as a set of cooperating tasks and processes. It began as a collaboration between the University of California, Berkeley, Intel Research, and Crossbow Technology, was released as free and open-source software under a BSD license, and has since grown into an international consortium, the TinyOS Alliance.
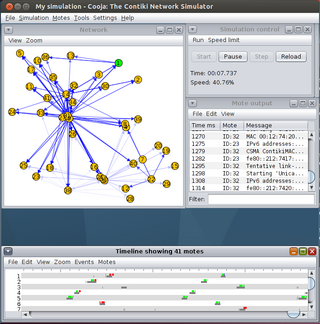
Contiki is an operating system for networked, memory-constrained systems with a focus on low-power wireless Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Contiki is used for systems for street lighting, sound monitoring for smart cities, radiation monitoring and alarms. It is open-source software released under the BSD-3-Clause license.
TCP offload engine (TOE) is a technology used in some network interface cards (NIC) to offload processing of the entire TCP/IP stack to the network controller. It is primarily used with high-speed network interfaces, such as gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet, where processing overhead of the network stack becomes significant. TOEs are often used as a way to reduce the overhead associated with Internet Protocol (IP) storage protocols such as iSCSI and Network File System (NFS).
Atmel ARM-based processors are microcontrollers and microprocessors integrated circuits, by Microchip Technology, that are based on various 32-bit ARM processor cores, with in-house designed peripherals and tool support.
Microchip Technology Incorporated is a publicly listed American corporation that manufactures microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog, and Flash-IP integrated circuits. Its products include microcontrollers, Serial EEPROM devices, Serial SRAM devices, embedded security devices, radio frequency (RF) devices, thermal, power, and battery management analog devices, as well as linear, interface and wireless products.
EtherCAT is an Ethernet-based fieldbus system developed by Beckhoff Automation. The protocol is standardized in IEC 61158 and is suitable for both hard and soft real-time computing requirements in automation technology.

Arduino is an Italian open-source hardware and software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardware products are licensed under a CC BY-SA license, while the software is licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) or the GNU General Public License (GPL), permitting the manufacture of Arduino boards and software distribution by anyone. Arduino boards are available commercially from the official website or through authorized distributors.

PICkit is a family of programmers for PIC microcontrollers made by Microchip Technology. They are used to program and debug microcontrollers, as well as program EEPROM. Some models may also feature logic analyzers and serial communications (UART) tools.

ChibiOS/RT is a compact and fast real-time operating system supporting multiple architectures and released under a mix of the GNU General Public License version 3 (GPL3) and the Apache License 2.0. It is developed by Giovanni Di Sirio.
The uIP is an open-source implementation of the TCP/IP network protocol stack intended for use with tiny 8- and 16-bit microcontrollers. It was initially developed by Adam Dunkels of the Networked Embedded Systems group at the Swedish Institute of Computer Science, licensed under a BSD style license, and further developed by a wide group of developers.
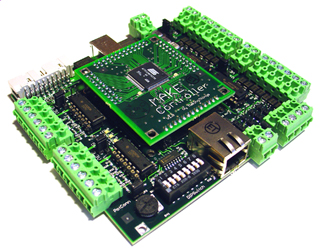
A single-board microcontroller is a microcontroller built onto a single printed circuit board. This board provides all of the circuitry necessary for a useful control task: a microprocessor, I/O circuits, a clock generator, RAM, stored program memory and any necessary support ICs. The intention is that the board is immediately useful to an application developer, without requiring them to spend time and effort to develop controller hardware.
OBDuino is an open source trip computer design based on the Arduino platform. An OBDuino may be assembled and customised by an electronics hobbyist; it displays information such as instantaneous fuel economy, engine tuning parameters etc. on an LCD.

Faustino is a physical computing platform geared towards process monitoring and control. The faustino platform consists of a single-board microcontroller with embedded analog and digital I/O support, an input module with LCD, sensors and actuators in form of solid state relays. The development software is based on Eclipse and WinAVR, a variant of GCC for AVR microcontrollers. For visual presentation of measurements, a XML-configured Windows status monitor application is available.
CubeSat Space Protocol (CSP) is a small network-layer delivery protocol designed for CubeSats. The idea was developed by a group of students from Aalborg University in 2008, and further developed for the AAUSAT3 CubeSat mission that was launched in 2013. The protocol is based on a 32-bit header containing both network and transport layer information. Its implementation is designed for embedded systems such as the 8-bit AVR microprocessor and the 32-bit ARM and AVR from Atmel. The implementation is written in C and is ported to run on FreeRTOS and POSIX and pthreads-based operating systems such as Linux. The three-letter acronym CSP was adopted as an abbreviation for CAN Space Protocol because the first MAC-layer driver was written for CAN-bus. The physical layer has since been extended to include several other technologies, and the name was therefore extended to the more general CubeSat Space Protocol without changing the abbreviation.
Tinkerforge is an open-source hardware platform of stackable microcontroller building blocks (Bricks) that can control different modules (Bricklets). The primary communication interface of the building blocks can be extended using Master Extensions. The hardware can be controlled by external programs written in C, C++, C#, Object Pascal, Java, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Shell and VB.NET over a USB, Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection, and running on Windows, Linux and macOS. This non-embedded programming approach eliminates the typical requirements and limitations of conventional embedded software development. Tinkerforge hardware and software are both open source, and all files are hosted on GitHub.

Apache Mynewt is a modular real-time operating system for connected Internet of things (IoT) devices that must operate for long times under power, memory, and storage constraints. It is free and open-source software incubating under the Apache Software Foundation, with source code distributed under the Apache License 2.0, a permissive license that is conducive to commercial adoption of open-source software.











