
The Ethiopian National Defense Force (ENDF) is the military force of Ethiopia. Civilian control of the military is carried out through the Ministry of Defense, which oversees the Ground Forces, Air Force, Naval Force as well as the Defense Industry Sector.

The United Nations (UN) is a diplomatic and political international organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and serve as a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest international organization. The UN is headquartered in New York City, and the UN has other offices in Geneva, Nairobi, Vienna, and The Hague, where the International Court of Justice is headquartered at the Peace Palace.

The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers as outlined in the United Nations Charter include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with authority to issue resolutions that are binding on member states.

The history of the United Nations has its origins in World War II beginning with the Declaration of St James's Palace. Taking up the Wilsonian mantle in 1944–1945, US President Franklin D. Roosevelt pushed as his highest postwar priority the establishment of the United Nations to replace the defunct League of Nations. Roosevelt planned that it would be controlled by the United States, Soviet Union, United Kingdom and China. He expected this Big Four would resolve all major world problems at the powerful Security Council. However the UN was largely paralyzed by the veto of the Soviet Union when dealing with Cold War issues from 1947 to 1989. Since then its aims and activities have expanded to make it the archetypal international body in the early 21st century.

A United Nations Medal is an international decoration awarded by the United Nations (UN) to the various world countries members for participation in joint international military and police operations such as peacekeeping, humanitarian efforts, and disaster relief. The medal is ranked in militaries and police forces as a service medal. The United Nations awarded its first medal during the Korean War (1950–1953). Since 1955, many additional United Nations medals have been created and awarded for participation in various United Nations missions and actions around the world.

The Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) is an eight-country trade bloc in Africa. It includes governments from the Horn of Africa, Nile Valley and the African Great Lakes. It is headquartered in Djibouti.

The United Nations Operation in the Congo was a United Nations peacekeeping force which was deployed in the Republic of the Congo in 1960 in response to the Congo Crisis. The ONUC was the UN's first peacekeeping mission with significant military capability, and remains one of the largest UN operations in size and scope.

United Nations Operation in Somalia I was the first part of a United Nations (UN) sponsored effort to provide, facilitate, and secure humanitarian relief in Somalia, as well as to monitor the first UN-brokered ceasefire of the Somali Civil War conflict in the early 1990s.

Francis K. Butagira is a Ugandan lawyer, judge, politician and retired diplomat, who serves as the chairman of the Uganda Registration Services Bureau (URSB), an agency of the Ugandan government responsible for maintaining registration data. He was appointed to that position in October 2015. He concurrently serves as the Managing Partner of Butagira and Company Advocates, a Kampala-based legal practice.
Various international and local diplomatic and humanitarian efforts in the Somali Civil War have been in effect since the conflict first began in the early 1990s. The latter include diplomatic initiatives put together by the African Union, the Arab League and the European Union, as well as humanitarian efforts led by the Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), UNICEF, the World Food Programme (WFP), the Puntland Maritime Police Force (PMPF) and the Somali Red Crescent Society (SRCS).
The United Nations Peacekeeping efforts began in 1948. Its first activity was in the Middle East to observe and maintain the ceasefire during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. Since then, United Nations peacekeepers have taken part in a total of 72 missions around the globe, 12 of which continue today. The peacekeeping force as a whole received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1988.

The United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq (UNAMI) was formed on 14 August 2003 by United Nations Security Council (UNSC) Resolution 1500 at the request of the Iraqi government to support national development efforts.
A United Nations Resident Coordinator is the highest United Nations official and the chief of UN diplomatic mission in a country.

An international organization, also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is an organization that is established by a treaty or other type of instrument governed by international law and possesses its own legal personality, such as the United Nations, the World Health Organization, International Union for Conservation of Nature, and NATO. International organizations are composed of primarily member states, but may also include other entities, such as other international organizations, firms, and nongovernmental organizations. Additionally, entities may hold observer status. An alternative definition is that an international organization is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states and other actors in the international system.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1725, adopted unanimously on December 6, 2006, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Somalia, particularly resolutions 733 (1992), 1356 (2001) and 1425 (2002), the Council authorised the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) and African Union to establish a protection and training mission in the country.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1744, adopted unanimously on 20 February 2007, authorizing the African Union mission replacing and subsuming the IGAD Peace Support Mission in Somalia or IGASOM, which was a proposed Intergovernmental Authority on Development protection and training mission to Somalia approved by the African Union on 14 September 2006. IGASOM was also approved by the United Nations Security Council on 6 December 2006.
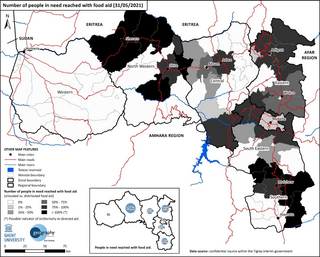
Beginning with the onset of the Tigray War in November 2020, acute food shortages leading to death and starvation became widespread in northern Ethiopia, and the Tigray, Afar and Amhara Regions in particular. As of August 2022, there are 13 million people facing acute food insecurity, and an estimated 150,000–200,000 had died of starvation by March 2022. In the Tigray Region alone, 89% of people are in need of food aid, with those facing severe hunger reaching up to 47%. In a report published in June 2021, over 350,000 people were already experiencing catastrophic famine conditions. It is the worst famine to happen in East Africa since 2011–2012.

The Tigrayan peace process encompasses the series of proposals, meetings, agreements and actions that aimed to resolve the Tigray War.

The events of the Tigray War have sparked numerous reactions and protests worldwide.

The Ethiopia–Tigray peace agreement, commonly called the Pretoria Agreement or the Cessation of Hostilities Agreement (CoHA), is a peace treaty between the government of Ethiopia and the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) that was signed 2 November 2022, wherein both parties agreed to a "permanent cessation of hostilities" to end the Tigray War. The agreement was made effective the next day on 3 November, marking the two-year anniversary of the war.















