
Computer software, or simply software, is a collection of data or computer instructions that tell the computer how to work. This is in contrast to physical hardware, from which the system is built and actually performs the work. In computer science and software engineering, computer software is all information processed by computer systems, programs and data. Computer software includes computer programs, libraries and related non-executable data, such as online documentation or digital media. Computer hardware and software require each other and neither can be realistically used on its own.

A database is an organized collection of data, generally stored and accessed electronically from a computer system. Where databases are more complex they are often developed using formal design and modeling techniques.

In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The SI unit of energy is the joule, which is the energy transferred to an object by the work of moving it a distance of 1 metre against a force of 1 newton.

In statistical mechanics, entropy is an extensive property of a thermodynamic system. It is closely related to the number Ω of microscopic configurations that are consistent with the macroscopic quantities that characterize the system. Under the assumption that each microstate is equally probable, the entropy is the natural logarithm of the number of microstates, multiplied by the Boltzmann constant kB. Formally,
Microsoft Windows is a group of several graphical operating system families, all of which are developed, marketed, and sold by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Windows families include Windows NT and Windows Embedded; these may encompass subfamilies, e.g. Windows Embedded Compact or Windows Server. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile and Windows Phone.

macOS is a series of graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac family of computers. Within the market of desktop, laptop and home computers, and by web usage, it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows.

The nervous system is the part of an animal that coordinates its actions by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In vertebrates it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor or efferent nerves, while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory or afferent. Spinal nerves serve both functions and are called mixed nerves. The PNS is divided into three separate subsystems, the somatic, autonomic, and enteric nervous systems. Somatic nerves mediate voluntary movement. The autonomic nervous system is further subdivided into the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is activated in cases of emergencies to mobilize energy, while the parasympathetic nervous system is activated when organisms are in a relaxed state. The enteric nervous system functions to control the gastrointestinal system. Both autonomic and enteric nervous systems function involuntarily. Nerves that exit from the cranium are called cranial nerves while those exiting from the spinal cord are called spinal nerves.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.

The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system, and is the most widely used system of measurement. It comprises a coherent system of units of measurement built on seven base units, which are the ampere, kelvin, second, metre, kilogram, candela, mole, and a set of twenty prefixes to the unit names and unit symbols that may be used when specifying multiples and fractions of the units. The system also specifies names for 22 derived units, such as lumen and watt, for other common physical quantities.
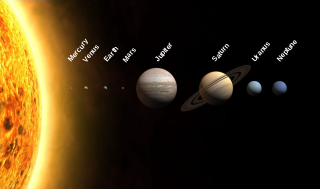
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound planetary system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of the objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the eight planets, with the remainder being smaller objects, such as the five dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that orbit the Sun indirectly—the moons—two are larger than the smallest planet, Mercury.

System of a Down is an Armenian-American heavy metal band from Glendale, California, formed in 1994. The band currently consists of Serj Tankian, Daron Malakian, Shavo Odadjian, and John Dolmayan (drums).

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
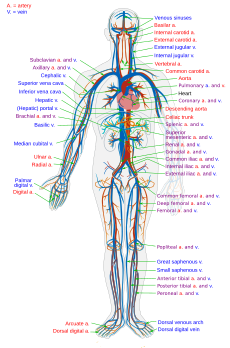
The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system or the vascular system, is an organ system that permits blood to circulate and transport nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body to provide nourishment and help in fighting diseases, stabilize temperature and pH, and maintain homeostasis.

A system administrator, or sysadmin, is a person who is responsible for the upkeep, configuration, and reliable operation of computer systems; especially multi-user computers, such as servers. The system administrator seeks to ensure that the uptime, performance, resources, and security of the computers they manage meet the needs of the users, without exceeding a set budget when doing so.

In computing, a Digital Object Identifier or DOI is a persistent identifier or handle used to uniquely identify objects, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). An implementation of the Handle System, DOIs are in wide use mainly to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports and data sets, and official publications though they also have been used to identify other types of information resources, such as commercial videos.

The FIFA World Ranking is a ranking system for men's national teams in association football, currently led by Belgium. The teams of the member nations of FIFA, football's world governing body, are ranked based on their game results with the most successful teams being ranked highest. The rankings were introduced in December 1992, and eight teams have held the top position, of which Brazil have spent the longest ranked first.

Linux is a family of free and open-source software operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, development starting in the 1970s at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to store, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data, or information, often in the context of a business or other enterprise. IT is considered to be a subset of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system is generally an information system, a communications system or, more specifically speaking, a computer system – including all hardware, software and peripheral equipment – operated by a limited group of users.



















