Related Research Articles

A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discrete global grid. DEMs are used often in geographic information systems (GIS), and are the most common basis for digitally produced relief maps. A digital terrain model (DTM) represents specifically the ground surface while DEM and DSM may represent tree top canopy or building roofs.

Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geophysics, geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines. It also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others.

The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) is a Japanese remote sensing instrument onboard the Terra satellite launched by NASA in 1999. It has been collecting data since February 2000.

Geomatics is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as the "discipline concerned with the collection, distribution, storage, analysis, processing, presentation of geographic data or geographic information". Under another definition, it consists of products, services and tools involved in the collection, integration and management of geographic (geospatial) data. Surveying engineering was the widely used name for geomatic(s) engineering in the past. Geomatics was placed by the UNESCO Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems under the branch of technical geography.

Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant imagery and other phenomena.

Geoinformatics is a scientific field primarily within the domains of Computer Science and technical geography. It focuses on the programming of applications, spatial data structures, and the analysis of objects and space-time phenomena related to the surface and underneath of Earth and other celestial bodies. The field develops software and web services to model and analyse spatial data, serving the needs of geosciences and related scientific and engineering disciplines. The term is often used interchangeably with Geomatics, although the two have distinct focuses; Geomatics emphasizes acquiring spatial knowledge and leveraging information systems, not their development. At least one publication has claimed the discipline is pure computer science outside the realm of geography.

Seasat was the first Earth-orbiting satellite designed for remote sensing of the Earth's oceans and had on board one of the first spaceborne synthetic-aperture radar (SAR). The mission was designed to demonstrate the feasibility of global satellite monitoring of oceanographic phenomena and to help determine the requirements for an operational ocean remote sensing satellite system. Specific objectives were to collect data on sea-surface winds, sea-surface temperatures, wave heights, internal waves, atmospheric water, sea ice features and ocean topography. Seasat was managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and was launched on 27 June 1978 into a nearly circular 800 km (500 mi) orbit with an inclination of 108°. Seasat operated until 10 October 1978 (UTC), when a massive short circuit in the Agena-D bus electrical system ended the mission.

The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is an international research effort that obtained digital elevation models on a near-global scale from 56°S to 60°N, to generate the most complete high-resolution digital topographic database of Earth prior to the release of the ASTER GDEM in 2009. SRTM consisted of a specially modified radar system that flew on board the Space Shuttle Endeavour during the 11-day STS-99 mission in February 2000. The radar system was based on the older Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR), previously used on the Shuttle in 1994. To acquire topographic data, the SRTM payload was outfitted with two radar antennas. One antenna was located in the Shuttle's payload bay, the other – a critical change from the SIR-C/X-SAR, allowing single-pass interferometry – on the end of a 60-meter (200-foot) mast that extended from the payload bay once the Shuttle was in space. The technique employed is known as interferometric synthetic aperture radar. Intermap Technologies was the prime contractor for processing the interferometric synthetic aperture radar data.

MEdium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MERIS) was one of the main instruments on board the European Space Agency (ESA)'s Envisat platform. The sensor was in orbit from 2002 to 2012. ESA formally announced the end of Envisat's mission on 9 May 2012.
Geomorphometry, or geomorphometrics, is the science and practice of measuring the characteristics of terrain, the shape of the surface of the Earth, and the effects of this surface form on human and natural geography. It gathers various mathematical, statistical and image processing techniques that can be used to quantify morphological, hydrological, ecological and other aspects of a land surface. Common synonyms for geomorphometry are geomorphological analysis, terrain morphometry, terrain analysis, and land surface analysis. Geomorphometrics is the discipline based on the computational measures of the geometry, topography and shape of the Earth's horizons, and their temporal change. This is a major component of geographic information systems (GIS) and other software tools for spatial analysis.

A fault trace describes the intersection of a geological fault with the Earth's surface, which leaves a visible disturbance on the surface, usually looking like a crack in the surface with jagged rock structures protruding outward. The term also applies to a line plotted on a geological map to represent a fault. These fractures tend to occur when a slip surface expands from a fault core, especially during an earthquake. This tends to occur with fault displacement, in which surfaces on both sides of a fault, known as fault blocks, separate horizontally or vertically.

The Earth and Mission Science Division is a group of European Space Agency (ESA) staff mission scientists, contractors, research fellows, young graduates, trainees, and administrative staff working within the Climate Action, Sustainability and Science Department of the Directorate of Earth Observation Programmes. The Division is located at ESA's European Space Research and Technology Centre in Noordwijk, South Holland, The Netherlands.

Barry N. Haack is an American geographer and Emeritus Professor in the Department of Geography and Geoinformation Science at George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia. He is an international authority on remote sensing, geographic information systems (GIS), and technology transfer from developed to developing nations. Haack is a visiting physical scientist at the United States Geological Survey and an elected Fellow in the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ASPRS). Through education and collaboration, Haack has influenced the careers of scientists and decision makers from many United States federal agencies and in universities and agencies in nearly thirty countries. He has held formal arrangements with the United Nations, World Bank, Inter-American Development Bank, NASA, the European Space Agency, the National Geographic Society, and many other international organizations and country governmental agencies.

Manfred Ferdinand Buchroithner is an Austrian cartographer, developer of autostereoscopic cartographic visualisations, geologist, mountain researcher and mountaineer.
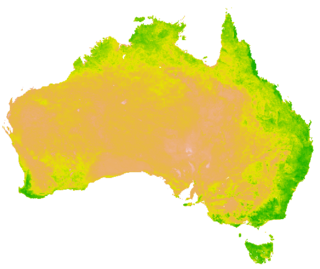
A vegetation index (VI) is a spectral imaging transformation of two or more image bands designed to enhance the contribution of vegetation properties and allow reliable spatial and temporal inter-comparisons of terrestrial photosynthetic activity and canopy structural variations.
JoBea Way Holt is an American planetary scientist who has worked for NASA. Holt studied the carbon cycle in Earth's atmosphere. She is also a member of the Climate Project, and is the author of several books and research papers.
Dr. Y. S. Rao is a professor at the Centre of Studies in Resources Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai, India. He is working in the field of microwave remote sensing and land based applications for more than 34 years. His early research was focused on the use of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry for landslides and land deformation monitoring, Digital Elevation Model generation, snow and glacier monitoring. He is also actively involved in developing several techniques for soil moisture estimation using passive and active microwave remote sensing data for more than 25 years. His current research involves SAR Polarimetry for crop characterization, classification, biophysical parameter retrieval using linear and compact-pol SAR data. Apart from applications, he has also contributed in the field of Polarimetric SAR system calibration and software tool development.
The European Journal of Remote Sensing (EuJRS) is an academic journal about remote sensing published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the Associazione Italiana di Telerilevamento and co-sponsored by the European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories (EARSeL). Its editor-in-chief is Marco Marchetti; its 2018 impact factor is 1.904.
Land cover maps are tools that provide vital information about the Earth's land use and cover patterns. They aid policy development, urban planning, and forest and agricultural monitoring.
Shubha Platt, known professionally as Shubha Sathyendranath, is a marine scientist known for her work on marine optics and remote sensing of ocean colour. She is the 2021 recipient of the A.G. Huntsman Award for Excellence in the Marine Sciences.
References
- ↑ Heck, A. (2004). StarBriefs Plus: A Dictionary of Abbreviations, Acronyms and Symbols in Astronomy and Related Space Sciences. Developments in Hydrobiology Series. Springer Netherlands. p. 287. ISBN 978-1-4020-1925-8 . Retrieved 2020-08-27.
- ↑ GUDMANDSEN, P.; BODECHTEL, J.; CASSINIS, R. (1992). "European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories: a scientific network of co-operation". International Journal of Remote Sensing. 13 (6–7). Informa UK Limited: 1071–1082. Bibcode:1992IJRS...13.1071G. doi:10.1080/01431169208904180. ISSN 0143-1161.
- ↑ Madeleine Godefroy, Gunnar Ostrem and Robin Vaughan (2008), "EARSeL's History: The First 30 Years of the European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories", 115 pp., ISBN 978-3-00-024311-0.
- ↑ MASSUE, J. P. (1992). "The European remote sensing scientific community and the Council of Europe". International Journal of Remote Sensing. 13 (6–7). Informa UK Limited: 1059–1063. Bibcode:1992IJRS...13.1059M. doi:10.1080/01431169208904178. ISSN 0143-1161.
- ↑ "EARSeL, European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories". EARSeL, European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories. 2018-04-30. Retrieved 2020-08-27.
- ↑ "European Journal of Remote Sensing - EARSeL, European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories". EARSeL, European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories. 2020-08-13. Retrieved 2020-08-27.
- ↑ "Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing". Springer. Retrieved 2020-08-27.
- ↑ "Symposium proceedings - EARSeL, European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories". EARSeL, European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories. 2016-11-22. Retrieved 2020-08-27.