Related Research Articles

At the time of the Roman Empire, the area of modern Croatia comprised two Roman provinces, Pannonia and Dalmatia. After the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, the area was subjugated by the Ostrogoths for 50 years, before being incorporated into the Byzantine Empire.

Culture of Croatia has historically been influenced by Central European, Mediterranean and other Balkan cultures. Croatia's unique culture and identity can be traced back to the historical llyricum. The Croatian language is believed to have been formed in the 6th or 7th century, and the written language is present in Glagolitic texts from the 11th century.

The Kingdom of Croatia entered a personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary in 1102, after a period of rule of kings from the Trpimirović and Svetoslavić dynasties and a succession crisis following the death of king Demetrius Zvonimir. With the coronation of King Coloman of Hungary as "King of Croatia and Dalmatia" in 1102 in Biograd, the realm passed to the Árpád dynasty until 1301, when the (male) line of the dynasty died out. Then, kings from the Capetian House of Anjou, who were also cognatic descendants of the Árpád kings, ruled the kingdoms. Later centuries were characterized by conflicts with the Mongols, who sacked Zagreb in 1242, competition with Venice for control over Dalmatian coastal cities, and internal warfare among Croatian nobility. Various individuals emerged during the period, such as Paul I Šubić of Bribir, who was representing the most powerful Croatian dynasty at the time, the Šubić noble family. These powerful individuals were on occasion able to de facto secure great deal of independence for their fiefdoms. The Ottoman incursion into Europe in the 16th century significantly reduced Croatian territories and left the country weak and divided. After the death of Louis II in 1526 during the Battle of Mohács and a brief period of dynastic dispute, both crowns passed to the Austrian House of Habsburg, and the realms became part of the Habsburg monarchy.

The Irish Gospels of St. Gall or Codex Sangallensis 51 is an 8th-century Insular Gospel Book, written either in Ireland or by Irish monks in the Abbey of St. Gall in Switzerland, where it is now in the Abbey library of St. Gallen as MS 51. It has 134 folios. Amongst its eleven illustrated pages are a Crucifixion, a Last Judgement, a Chi Rho monogram page, a carpet page, and Evangelist portraits.
Tomislav was the first king of Croatia. He became Duke of Croatia c. 910 and was crowned king in 925, reigning until 928. During Tomislav's rule, Croatia forged an alliance with the Byzantine Empire against Bulgaria. Croatia's struggles with the First Bulgarian Empire eventually led to war, which culminated in the decisive Battle of the Bosnian Highlands in 926. In the north, Croatia often clashed with the Principality of Hungary; the state retained its borders and, to some extent, expanded with the disintegrated Lower Pannonia.
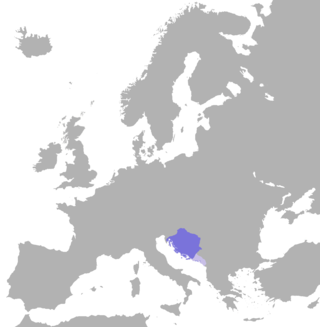
The Kingdom of Croatia, or Croatian Kingdom, was a medieval kingdom in Southern Europe comprising most of what is today Croatia, as well as most of the modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Croatian Kingdom was ruled for part of its existence by ethnic dynasties, and the Kingdom existed as a sovereign state for nearly two centuries. Its existence was characterized by various conflicts and periods of peace or alliance with the Bulgarians, Byzantines, Hungarians, and competition with Venice for control over the eastern Adriatic coast. The goal of promoting the Croatian language in the religious service was initially introduced by the 10th century bishop Gregory of Nin, which resulted in a conflict with the Pope, later to be put down by him. In the second half of the 11th century Croatia managed to secure most coastal cities of Dalmatia with the collapse of Byzantine control over them. During this time the kingdom reached its peak under the rule of kings Peter Krešimir IV (1058–1074) and Demetrius Zvonimir (1075–1089).
Branimir was a ruler of Duchy of Croatia who reigned as duke from 879 to c. 892. His country received papal recognition as a state from Pope John VIII on 7 June 879. During his reign, Croatia retained its sovereignty from both Carolingian and Byzantine rule and became de jure independent. His rule marks the first real peak of early medieval Croatia. It was characterized by establishing closer relations with the Holy See, ecclestical re-organization in the former Roman province of Dalmatia, Christianization, and (re)construction of churches. Branimir is mentioned, for the period, in many reliable primary and secondary written and ephigraphic sources.
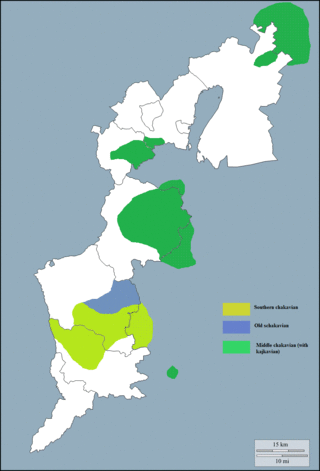
Burgenland Croatian is a regional variety of the Chakavian dialect of Croatian spoken in Austria, Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia. Burgenland Croatian is recognized as a minority language in the Austrian state of Burgenland, where it is spoken by 19,412 people according to official reports (2001). Many of the Burgenland Croatian speakers in Austria also live in Vienna and Graz, due to the process of urbanization, which is mostly driven by the poor economic situation of large parts of Burgenland.
The Evangeliary or Book of the Gospels is a liturgical book containing only those portions of the four gospels which are read during Mass or in other public offices of the Church. The corresponding terms in Latin are Evangeliarium and Liber evangeliorum.

Codex Basilensis, designated by Ee, 07 or ε 55, is a Greek uncial manuscript of the four Gospels, dated paleographically to the 8th century.
Codex Vaticanus 2066, designed by 046 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), α 1070 (von Soden), formerly it was known also as Codex Basilianus, previously it was designated by Br or B2. It is a Greek uncial manuscript of the New Testament written on vellum. The manuscript paleographically has been assigned to the 10th century by the INTF, though some palaeographers proposed the 9th century. Scrivener proposed even the 8th century.
Codex Vaticanus Graecus 2061, usually known as Uncial 048, α1 (Soden), is a Greek uncial manuscript on parchment. It contains some parts of the New Testament, homilies of several authors, and Strabo's Geographica. Formerly it was known also as the Codex Basilianus 100, earlier as Codex Patriniensis 27. It was designated by ב a, p.

Hval's Codex or Hval's Manuscript is a Bosnian Cyrillic manuscript of 353 pages written in 1404, in Split, for Duke Hrvoje Vukčić Hrvatinić. It was illuminated by Gothic artists from the Dalmatian littoral.
Croatian literature refers to literary works attributed to the medieval and modern culture of the Croats, Croatia, and Croatian. Besides the modern language whose shape and orthography was standardized in the late 19th century, it also covers the oldest works produced within the modern borders of Croatia, written in Church Slavonic and Medieval Latin, as well as vernacular works written in Čakavian and Kajkavian dialects.
Viktor Novak was a Yugoslav Croat historian, professor at the University of Belgrade and full member of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts (SANU), and a corresponding member of the Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts (JAZU).
István Blazsetin was a Croatian writer, cultural worker and pedagogue from Hungary. According to some authors, he is considered to be a Croatian writer from Vojvodina, Serbia. He wrote poetry, novels and children's literature. Blažetin was an important collector of oral literature heritage of the Pomurje Croats.
Josip Mikoczy-Blumenthal was an 18th-century Croatian historian known as the first proponent of the Iranian-Caucasian theory on the origins of the Croats, which he presented in a lost paper published in 1797.

Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term Lower Pannonia was used to designate those areas of the Pannonian plain that lie to the east and south of the river Rába, with the division into Upper and Lower inherited from the Roman terminology.
Neven Budak is a Croatian historian and professor at the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Zagreb.

Medieval literary heritage of Bosnia and Herzegovina, as part of a Bosnia and Herzegovina literature, is based on local language traditions and literacy and can be assessed starting with the High Middle Ages. The oldest preserved Bosnian inscriptions is considered to be the Humac tablet, inscribed into stone tablet between the 10th and 12th century, which means that probably predates Charter of Ban Kulin written on 29 August 1189.
References
- ↑ Hrvatska opća enciklopedija, str. 145.
- ↑ Nina Glibetic (2010). "The Early Byzantine and Latin Liturgical History Among Balkan Slavs". Bollettino della Badia Greca di Grottaferrata. 7: 95. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- ↑ Svend Dahl (1965). Dzieje książki. Wrocław: Zakład Narodowy im. Ossolińskich. p. 83.
- ↑ Evangeliarium Spalatense (Splitski evanđelistar 6-8 st.najstarija knjiga u Hrvata) 28.02.2008.
- ↑ Zvonimir Kulundžić (1967). Zgodovina knjige. Ljubljana: Državna založba Slovenije. p. 317.
- ↑ Evangeliarium Spalatense. Faksimilno izdanje izrađeno prema izvorniku iz Arhiva splitske prvostnolnice (sign. KAS 621), Split 2004