Customer relationship management (CRM) is a process in which a business or other organization administers its interactions with customers, typically using data analysis to study large amounts of information.

In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabling operating systems and other computer programs to access hardware functions without needing to know precise details about the hardware being used.

An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. In 2009, it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems.
Middleware in the context of distributed applications is software that provides services beyond those provided by the operating system to enable the various components of a distributed system to communicate and manage data. Middleware supports and simplifies complex distributed applications. It includes web servers, application servers, messaging and similar tools that support application development and delivery. Middleware is especially integral to modern information technology based on XML, SOAP, Web services, and service-oriented architecture.

The point of sale (POS) or point of purchase (POP) is the time and place at which a retail transaction is completed. At the point of sale, the merchant calculates the amount owed by the customer, indicates that amount, may prepare an invoice for the customer, and indicates the options for the customer to make payment. It is also the point at which a customer makes a payment to the merchant in exchange for goods or after provision of a service. After receiving payment, the merchant may issue a receipt, as proof of transaction, which is usually printed but can also be dispensed with or sent electronically.
A management information system (MIS) is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of information in an organization. The study of the management information systems involves people, processes and technology in an organizational context. In other words, it serves, as the functions of controlling, planning, decision making in the management level setting.
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people, structure, and technology. Information systems can be defined as an integration of components for collection, storage and processing of data of which the data is used to provide information, contribute to knowledge as well as digital products that facilitate decision making.
An application program is a computer program designed to carry out a specific task other than one relating to the operation of the computer itself, typically to be used by end-users. Word processors, media players, and accounting software are examples. The collective noun "application software" refers to all applications collectively. The other principal classifications of software are system software, relating to the operation of the computer, and utility software ("utilities").

A decision support system (DSS) is an information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSSs serve the management, operations and planning levels of an organization and help people make decisions about problems that may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance—i.e., unstructured and semi-structured decision problems. Decision support systems can be either fully computerized or human-powered, or a combination of both.
An Enterprise Information System (EIS) is any kind of information system which improves the functions of enterprise business processes by integration. This means typically offering high quality of service, dealing with large volumes of data and capable of supporting some large and possibly complex organization or enterprise. An EIS must be able to be used by all parts and all levels of an enterprise.
Business software is any software or set of computer programs used by business users to perform various business functions. These business applications are used to increase productivity, measure productivity, and perform other business functions accurately.
Cincom Systems, Inc., is a privately held multinational computer technology corporation founded in 1968 by Tom Nies, Tom Richley, and Claude Bogardus.

Digital signage is a segment of electronic signage. Digital displays use technologies such as LCD, LED, OLED, projection and e-paper to display digital images, video, web pages, weather data, restaurant menus, or text. They can be found in public spaces, transportation systems, museums, stadiums, retail stores, hotels, restaurants and corporate buildings etc., to provide wayfinding, exhibitions, marketing and outdoor advertising. They are used as a network of electronic displays that are centrally managed and individually addressable for the display of text, animated or video messages for advertising, information, entertainment and merchandising to targeted audiences.
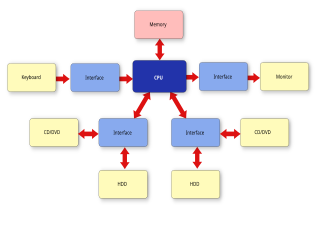
A system architecture is the conceptual model that defines the structure, behavior, and more views of a system. An architecture description is a formal description and representation of a system, organized in a way that supports reasoning about the structures and behaviors of the system.

In computer information systems, a dashboard is a type of graphical user interface which often provides at-a-glance views of data relevant to a particular objective or process through a combination of visualizations and summary information. In other usage, "dashboard" is another name for "progress report" or "report" and is considered a form of data visualization.
Mobile app development is the act or process by which a mobile app is developed for one or more mobile devices, which can include personal digital assistants (PDA), enterprise digital assistants (EDA), or mobile phones. Such software applications are specifically designed to run on mobile devices, taking numerous hardware constraints into consideration. Common constraints include CPU architecture and speeds, available memory (RAM), limited data storage capacities, and considerable variation in displays and input methods. These applications can be pre-installed on phones during manufacturing or delivered as web applications, using server-side or client-side processing to provide an "application-like" experience within a web browser.
A system monitor is a hardware or software component used to monitor system resources and performance in a computer system.

A computer appliance is a computer system with a combination of hardware, software, or firmware that is specifically designed to provide a particular computing resource. Such devices became known as appliances because of the similarity in role or management to a home appliance, which are generally closed and sealed, and are not serviceable by the user or owner. The hardware and software are delivered as an integrated product and may even be pre-configured before delivery to a customer, to provide a turn-key solution for a particular application. Unlike general purpose computers, appliances are generally not designed to allow the customers to change the software and the underlying operating system, or to flexibly reconfigure the hardware.
A marketing information system (MIS) is a management information system (MIS) designed to support marketing decision making. Jobber (2007) defines it as a "system in which marketing data is formally gathered, stored, analysed and distributed to managers in accordance with their informational needs on a regular basis." In addition, the online business dictionary defines Marketing Information System (MKIS) as "a system that analyzes and assesses marketing information, gathered continuously from sources inside and outside an organization or a store." Furthermore, "an overall Marketing Information System can be defined as a set structure of procedures and methods for the regular, planned collection, analysis and presentation of information for use in making marketing decisions."
Mobile Business Intelligence is defined as “Mobile BI is a system comprising both technical and organizational elements that present historical and/or real-time information to its users for analysis on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, to enable effective decision-making and management support, for the overall purpose of increasing firm performance.”. Business intelligence (BI) refers to computer-based techniques used in spotting, digging-out, and analyzing business data, such as sales revenue by products and/or departments or associated costs and incomes.








