
Thermogenin is an uncoupling protein found in the mitochondria of brown adipose tissue (BAT). It is used to generate heat by non-shivering thermogenesis, and makes a quantitatively important contribution to countering heat loss in babies which would otherwise occur due to their high surface area-volume ratio.
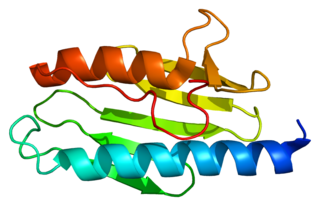
Frataxin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FXN gene.
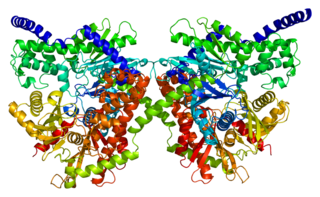
Hexokinase-1 (HK1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HK1 gene on chromosome 10. Hexokinases phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), the first step in most glucose metabolism pathways. This gene encodes a ubiquitous form of hexokinase which localizes to the outer membrane of mitochondria. Mutations in this gene have been associated with hemolytic anemia due to hexokinase deficiency. Alternative splicing of this gene results in five transcript variants which encode different isoforms, some of which are tissue-specific. Each isoform has a distinct N-terminus; the remainder of the protein is identical among all the isoforms. A sixth transcript variant has been described, but due to the presence of several stop codons, it is not thought to encode a protein. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]

DnaJ homolog subfamily A member 3, mitochondrial, also known as Tumorous imaginal disc 1 (TID1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJA3 gene on chromosome 16. This protein belongs to the DNAJ/Hsp40 protein family, which is known for binding and activating Hsp70 chaperone proteins to perform protein folding, degradation, and complex assembly. As a mitochondrial protein, it is involved in maintaining membrane potential and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) integrity, as well as cellular processes such as cell movement, growth, and death. Furthermore, it is associated with a broad range of diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, and cancers.

Annexin A7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANXA7 gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJC3 gene.

Phosphate carrier protein, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A3 gene. The encoded protein is a transmembrane protein located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and catalyzes the transport of phosphate ions across it for the purpose of oxidative phosphorylation. There are two significant isoforms of this gene expressed in human cells, which differ slightly in structure and function. Mutations in this gene can cause mitochondrial phosphate carrier deficiency (MPCD), a fatal disorder of oxidative phosphorylation symptomized by lactic acidosis, neonatal hypotonia, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and death within the first year of life.

Transforming growth factor beta regulator 4 (TBRG4), also known as cell cycle progression restoration protein 2 (CPR2) and FAST kinase domain-containing protein 4 (FASTKD4), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBRG4 gene on chromosome 7. This protein is part of the FASTKD family, which is known for regulating the energy balance of mitochondria under stress and cell cycle progression. TBRG4 is involved in cell proliferation in hematopoiesis and multiple myeloma.

Mitochondrial-processing peptidase subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PMPCB gene. This gene is a member of the peptidase M16 family and encodes a protein with a zinc-binding motif. This protein is located in the mitochondrial matrix and catalyzes the cleavage of the leader peptides of precursor proteins newly imported into the mitochondria, though it only functions as part of a heterodimeric complex.

Apoptosis-inducing factor 2 (AIFM2), also known as apoptosis-inducing factor-homologous mitochondrion-associated inducer of death (AMID), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AIFM2 gene, also known as p53-responsive gene 3 (PRG3), on chromosome 10.
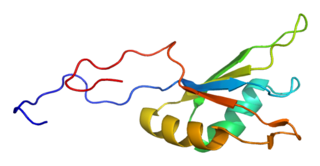
Fox-1 homolog A, also known as ataxin 2-binding protein 1 (A2BP1) or hexaribonucleotide-binding protein 1 (HRNBP1) or RNA binding protein, fox-1 homolog (Rbfox1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBFOX1 gene.

tRNA modification GTPase GTPBP3, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in human is encoded by the GTPBP3 gene on chromosome 19.

Hexokinase 2 also known as HK2 is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the HK2 gene on chromosome 2. Hexokinases phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), the first step in most glucose metabolism pathways. This gene encodes hexokinase 2, the predominant form found in skeletal muscle. It localizes to the outer membrane of mitochondria. Expression of this gene is insulin-responsive, and studies in rat suggest that it is involved in the increased rate of glycolysis seen in rapidly growing cancer cells. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]
Mitochondrial biogenesis is the process by which cells increase mitochondrial mass. It was first described by John Holloszy in the 1960s, when it was discovered that physical endurance training induced higher mitochondrial content levels, leading to greater glucose uptake by muscles. Mitochondrial biogenesis is activated by numerous different signals during times of cellular stress or in response to environmental stimuli, such as aerobic exercise.

FAST kinase domain-containing protein 3 (FASTKD3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FASTKD3 gene on chromosome 5. This protein is part of the Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase domain (FASTKD) containing protein family, which is known for regulating the energy balance of mitochondria under stress.

Solute carrier family 25, member 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A5 gene on the X chromosome.

FAST kinase domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FASTKD1 gene on chromosome 2. This protein is part of the FASTKD family, which is known for regulating the energy balance of mitochondria under stress. FASTKD1 is also an RNA-binding protein and has been associated with endometrial cancer.

FAST kinase domain-containing protein 2 (FASTKD2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FASTKD2 gene on chromosome 2. This protein is part of the FASTKD family, which is known for regulating the energy balance of mitochondria under stress. FASTKD2 has been implicated in mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, breast cancer, and prostate cancer.

Regulator of microtubule dynamics protein 3 (RMDN3), more commonly known as Protein tyrosine phosphatase interacting protein 51 (PTPIP51), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RMDN3 gene on chromosome 15. This protein contributes to multiple biological functions, including cellular differentiation, proliferation, motility, cytoskeleton formation, and apoptosis, and has been associated with numerous cancers.

5',3'-nucleotidase, mitochondrial, also known as 5'(3')-deoxyribonucleotidase, mitochondrial (mdN) or deoxy-5'-nucleotidase 2 (dNT-2), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NT5M gene. This gene encodes a 5' nucleotidase that localizes to the mitochondrial matrix. This enzyme dephosphorylates the 5'- and 2'(3')-phosphates of uracil and thymine deoxyribonucleotides. The gene is located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17.





















