
The Handley Page Type O was a biplane bomber used by Britain during the First World War. When built, the Type O was one of the largest aircraft in the world. There were two main variants, the Handley Page O/100 (H.P.11) and the Handley Page O/400 (H.P.12).

The Schneider CA 1 was the first French tank, developed during the First World War.

The Saint-Chamond was the second French tank to enter service during the First World War, with 400 manufactured from April 1917 to July 1918. Although not a tank by a strict definition of a heavily armoured turreted vehicle, it is generally accepted and described as such in accounts of early tank development. It takes its name from the commune of Saint-Chamond where its manufacturers Compagnie des forges et aciéries de la marine et d'Homécourt (FAMH) were based.

The char 2C, also known as the FCM 2C, was a French post WWI heavy tank landship, later considered a super-heavy tank. It was developed during World War I but not deployed until after the war. It was, in total volume or physical dimensions, the largest operational tank ever made.

The Arjun is a third generation main battle tank developed by the Combat Vehicles Research and Development Establishment (CVRDE) of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), for the Indian Army. The tank is named after Arjuna, the archer prince who is the main protagonist of the Indian epic poem Mahabharata. Design work began in 1986 and was finished in 1996. The Arjun main battle tank entered service with the Indian Army in 2004. The 43rd Armoured Regiment, formed in 2009, was the first regiment to receive the Arjun.

The Gun Carrier Mark I was a British vehicle of the First World War. The gun carrier was designed to transport a 6-inch howitzer or a 60-pounder gun forward soon after an attack to support infantry in advanced positions. Gun carriers were first used in the Battle of Pilckem Ridge during the Third Battle of Ypres. The carriers moved guns and equipment but were used for the rest of the war mainly for carrying equipment and supplies through areas under fire, where porters in the open would have suffered many casualties. The 6-inch howitzer could be fired while mounted, making the Gun Carrier Mark I the first modern self-propelled gun, a weapon capable of independent action and having tactical mobility on the battlefield.

The Mark VIII tank also known as the Liberty or The International was a British-American tank design of the First World War intended to overcome the limitations of the earlier British designs and be a collaborative effort to equip France, the UK and the US with a single heavy tank design.

The Char B1 was a French heavy tank manufactured before World War II.

The development of tanks in World War I was a response to the stalemate that developed on the Western Front. Although vehicles that incorporated the basic principles of the tank had been projected in the decade or so before the War, it was the alarmingly heavy casualties of the start of its trench warfare that stimulated development. Research took place in both Great Britain and France, with Germany only belatedly following the Allies' lead.

Tanks were initially deployed in World War I, engineered to overcome the deadlock of trench warfare. Between the two world wars, tanks were further developed. Although they had demonstrated their battlefield effectiveness, only a few nations had the industrial resources to design and build them. During and after World War I, Britain and France pioneered tank technology, with their models generally serving as a blueprint for other countries. However, this initial advantage would slowly diminish during the 1930s, shifting in favor of the Soviet Union and, to a lesser degree, Nazi Germany.

The Hotchkiss H35 or Char léger modèle 1935 H was a French cavalry tank developed prior to World War II. Despite having been designed from 1933 as a rather slow but well-armoured light infantry support tank, the type was initially rejected by the French Infantry because it proved difficult to steer while driving cross-country, and was instead adopted in 1936 by the French Cavalry arm.

The FCM 36 or Char léger Modèle 1936 FCM, was a light infantry tank designed for the French Army prior to World War II. It had a crew of two and was equipped with a short 37mm main armament and a 7.5mm coaxial machine gun.
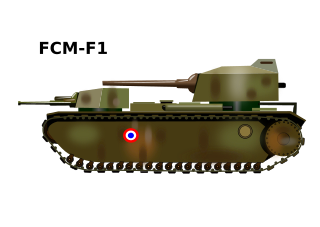
The FCM F1 was a French super-heavy tank developed during the late Interbellum by the Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée (FCM) company. Twelve were ordered in 1940 to replace the char 2C, but France was defeated before construction could begin, a wooden mock-up being all that was finished. The FCM F1 was large and elongated, and had two turrets: one in front and one in the back, with a single high-velocity gun in each turret. The rear turret was superfiring, meaning it was raised higher and fired over the top of the forward one, a common practice in naval vessels. The vehicle was intended to be heavily armoured. Its size and protection level made it by 1940, at about 140 tons, the heaviest tank ever to have actually been ordered for production. Despite two engines its speed would have been low. The primary purpose of the tank was to breach German fortification lines, not to fight enemy tanks. The development path of the FCM F1 was extremely complex, due to the existence of a number of parallel super-heavy tank projects with overlapping design goals, the specifications of which were regularly changed. For each project in turn several companies submitted one or more competing proposals.

The ARL 44 was a French heavy tank and tank destroyer, the development of which started just before the end of the Second World War. Only sixty of these tanks were ever completed, from 1949 onwards. The type proved to be unsatisfactory and only entered limited service. The tank was phased out in 1953.

The Char D1 was an Interwar French light tank.
The Char G1 was a French replacement project for the Char D2 medium tank. Several prototypes from different companies were developed from 1936 onwards, but not a single one had been fully completed at the time of the Fall of France in 1940. The projects represented some of the most advanced French tank design of the period and finally envisaged a type that would have been roughly equal in armament and mobility to later World War II standard tanks of other nations, such as the Soviet T-34 and the American M4 Sherman, but possessing several novel features, such as gun stabilisation, a semi-automatic loader and an optical rangefinder.

The Skeleton tank also known as the Spider tank was an experimental prototype tank built in 1918 by the Pioneer Tractor Company, Winona, Minnesota for $15,000. The prototype was ready for trials by October 1918. Designed with several innovative features, some of which were controversial at the time, the Skeleton Tank project did not proceed beyond the single prototype.

The AMX 50 or AMX-50 is a French heavy tank designed in the immediate post Second World War period. It was proposed as, in succession, the French medium, heavy, and main battle tank, incorporating many advanced features. It was cancelled in the late 1950s however, due to unfavourable economic and political circumstances after serious delays in development.

French development into tanks began during World War I as an effort to overcome the stalemate of trench warfare, and largely at the initiative of the manufacturers. The Schneider CA1 was the first tank produced by France, and 400 units were built. The French also experimented with various tank designs, such as the Frot-Laffly landship, Boirault machine and Souain experiment. Another 400 Saint-Chamond tanks were manufactured from April 1917 to July 1918 but they were underpowered and were of limited utility because the caterpillar tracks were too short for the tank's length and weight. The most significant French tank development during the war was the Renault FT light tank, which set the general layout for future tank designs and was used or redesigned by various military forces, including those of the United States.
The AMX 38 was a prototype French tank designed in 1937 at the AMX works. Designed as AMX's response to the 20-tonne tank programme intended to replace the aging Char D2, it was a faster and heavier alternative to Renault R35, in practice a cross-over between a light tank and medium tank.

















