Related Research Articles

A flagellum is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
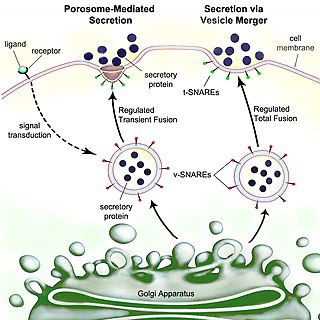
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.

The bacterial outer membrane is found in gram-negative bacteria. Its composition is distinct from that of the inner cytoplasmic cell membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the outer membrane of many gram-negative bacteria includes a complex lipopolysaccharide whose lipid portion acts as an endotoxin - and in some bacteria such as E. coli it is linked to the cell's peptidoglycan by Braun's lipoprotein.
In molecular biology, the Signal Peptide Peptidase (SPP) is a type of protein that specifically cleaves parts of other proteins. It is an intramembrane aspartyl protease with the conserved active site motifs 'YD' and 'GxGD' in adjacent transmembrane domains (TMDs). Its sequences is highly conserved in different vertebrate species. SPP cleaves remnant signal peptides left behind in membrane by the action of signal peptidase and also plays key roles in immune surveillance and the maturation of certain viral proteins.
The twin-arginine translocation pathway is a protein export, or secretion pathway found in plants, bacteria, and archaea. In contrast to the Sec pathway which transports proteins in an unfolded manner, the Tat pathway serves to actively translocate folded proteins across a lipid membrane bilayer. In plants, the Tat translocase is located in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast, where it acts to export proteins into the thylakoid lumen. In bacteria, the Tat translocase is found in the cytoplasmic membrane and serves to export proteins to the cell envelope, or to the extracellular space. The existence of a Tat translocase in plant mitochondria is also proposed.
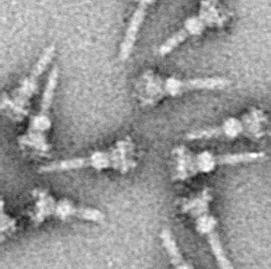
The type III secretion system, also called the injectisome, is one of the bacterial secretion systems used by bacteria to secrete their effector proteins into the host's cells to promote virulence and colonisation. The T3SS is a needle-like protein complex found in several species of pathogenic gram-negative bacteria.
Autoinducers are signaling molecules that are produced in response to changes in cell-population density. As the density of quorum sensing bacterial cells increases so does the concentration of the autoinducer. Detection of signal molecules by bacteria acts as stimulation which leads to altered gene expression once the minimal threshold is reached. Quorum sensing is a phenomenon that allows both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria to sense one another and to regulate a wide variety of physiological activities. Such activities include symbiosis, virulence, motility, antibiotic production, and biofilm formation. Autoinducers come in a number of different forms depending on the species, but the effect that they have is similar in many cases. Autoinducers allow bacteria to communicate both within and between different species. This communication alters gene expression and allows bacteria to mount coordinated responses to their environments, in a manner that is comparable to behavior and signaling in higher organisms. Not surprisingly, it has been suggested that quorum sensing may have been an important evolutionary milestone that ultimately gave rise to multicellular life forms.
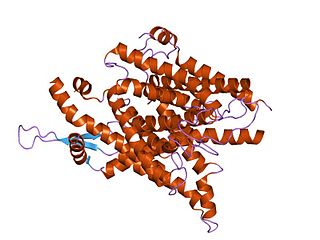
The SecY protein is the main transmembrane subunit of the bacterial Sec export pathway and of a protein-secreting ATPase complex, also known as a SecYEG translocon. Homologs of the SecYEG complex are found in eukaryotes and in archaea, where the subunit is known as Sec61α.

In molecular biology, LcrV is a protein found in Yersinia pestis and several other bacterial species. It forms part of the Yersinia pestis virulence protein factors that also includes all Yops, or Yersinia outer protein, but the name has been kept out of convention. LcrV's main function is not actually known, but it is essential for the production of other Yops.

The fimbrial usher protein is involved in biogenesis of the pilus in Gram-negative bacteria. The biogenesis of some fimbriae requires a two-component assembly and transport system which is composed of a periplasmic chaperone and a pore-forming outer membrane protein which has been termed a molecular 'usher'; this is the chaperone-usher pathway.
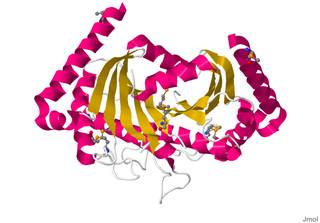
Motility protein B also known as MotB is a bacterial protein that is encoded by the motB gene. It's a component of the flagellar motor. More specifically, MotA and MotB makes the stator of a flagellum and surround the rotor as a ring of about 8-10 particles. MotA and MotB are integral membrane proteins. While both MotA and MotB surround the MS ring, MotB also anchors MotA to cell wall peptidoglycan. These two proteins form pores that harvest energy for flagellar mechanical movement by proton motive force (PMF) across the membrane. Cellular metabolic processes such as the electron transport chain move protons outside the cell, creating more protons and more positive charge in the extracellular space. When the protons flow back into the cell through MotA and MotB along concentration and charge gradients, they release energy that is used for flagellar rotation. The speed of the flagellar motor is dependent on the magnitude of the PMF acting on MotA and MotB.
The RTX toxin superfamily is a group of cytolysins and cytotoxins produced by bacteria. There are over 1000 known members with a variety of functions. The RTX family is defined by two common features: characteristic repeats in the toxin protein sequences, and extracellular secretion by the type I secretion systems (T1SS). The name RTX refers to the glycine and aspartate-rich repeats located at the C-terminus of the toxin proteins, which facilitate export by a dedicated T1SS encoded within the rtx operon.
In molecular biology, the flagellar motor switch protein(Flig) is one of three proteins in certain bacteria coded for by the gene fliG. The other two proteins are FliN coded for by fliN, and FliM coded for by fliM. The protein complex regulates the direction of flagellar rotation and hence controls swimming behaviour. The switch is a complex apparatus that responds to signals transduced by the chemotaxis sensory signalling system during chemotactic behaviour. CheY, the chemotaxis response regulator, is believed to act directly on the switch to induce a switch in the flagellar motor direction of rotation.

In molecular biology, the OmpA domain is a conserved protein domain with a beta/alpha/beta/alpha-beta(2) structure found in the C-terminal region of many Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane proteins, such as porin-like integral membrane proteins, small lipid-anchored proteins, and MotB proton channels. The N-terminal half of these proteins is variable although some of the proteins in this group have the OmpA-like transmembrane domain at the N terminus. OmpA from Escherichia coli is required for pathogenesis, and can interact with host receptor molecules. MotB serve two functions in E. coli, the MotA(4)-MotB(2) complex attaches to the cell wall via MotB to form the stator of the flagellar motor, and the MotA-MotB complex couples the flow of ions across the cell membrane to movement of the rotor.

In molecular biology, trimeric autotransporter adhesins (TAAs), are proteins found on the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Bacteria use TAAs in order to infect their host cells via a process called cell adhesion. TAAs also go by another name, oligomeric coiled-coil adhesins, which is shortened to OCAs. In essence, they are virulence factors, factors that make the bacteria harmful and infective to the host organism.

OmpT is an aspartyl protease found on the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. OmpT is a subtype of the family of omptin proteases, which are found on some gram-negative species of bacteria.
Autodisplay is a genetic engineering technique which is used to insert a protein of interest on the outer surface of gram-negative bacteria. This is accomplished by attaching the protein of interest to a protein which is known to localize to the surface of the bacterial outer membrane. First introduced in the 1990s, the technique is now widely used in research science and in biotechnology to manipulate bacteria for protein studies, drug discovery, and vaccine development.
An archaeosortase is a protein that occurs in the cell membranes of some archaea. Archaeosortases recognize and remove carboxyl-terminal protein sorting signals about 25 amino acids long from secreted proteins. A genome that encodes one archaeosortase may encode over fifty target proteins. The best characterized archaeosortase target is the Haloferax volcanii S-layer glycoprotein, an extensively modified protein with O-linked glycosylations, N-linked glycosylations, and a large prenyl-derived lipid modification toward the C-terminus. Knockout of the archaeosortase A (artA) gene, or permutation of the motif Pro-Gly-Phe (PGF) to Pro-Phe-Gly in the S-layer glycoprotein, blocks attachment of the lipid moiety as well as blocking removal of the PGF-CTERM protein-sorting domain. Thus archaeosortase appears to be a transpeptidase, like sortase, rather than a simple protease.
Membrane vesicle trafficking in eukaryotic animal cells involves movement of biochemical signal molecules from synthesis-and-packaging locations in the Golgi body to specific release locations on the inside of the plasma membrane of the secretory cell. It takes place in the form of Golgi membrane-bound micro-sized vesicles, termed membrane vesicles (MVs).

Bacterial secretion systems are protein complexes present on the cell membranes of bacteria for secretion of substances. Specifically, they are the cellular devices used by pathogenic bacteria to secrete their virulence factors to invade the host cells. They can be classified into different types based on their specific structure, composition and activity. Generally, proteins can be secreted through two different processes. One process is a one-step mechanism in which proteins from the cytoplasm of bacteria are transported and delivered directly through the cell membrane into the host cell. Another involves a two-step activity in which the proteins are first transported out of the inner cell membrane, then deposited in the periplasm, and finally through the outer cell membrane into the host cell.
References
- ↑ Wei ZM, Beer SV (December 1993). "HrpI of Erwinia amylovora functions in secretion of harpin and is a member of a new protein family". J. Bacteriol. 175 (24): 7958–67. doi:10.1128/jb.175.24.7958-7967.1993. PMC 206975 . PMID 8253684.
- 1 2 Gough CL, Genin S, Lopes V, Boucher CA (June 1993). "Homology between the HrpO protein of Pseudomonas solanacearum and bacterial proteins implicated in a signal peptide-independent secretion mechanism". Mol. Gen. Genet. 239 (3): 378–92. doi:10.1007/bf00276936. PMID 8316211. S2CID 28775466.
- ↑ Wandersman C (September 1992). "Secretion across the bacterial outer membrane". Trends Genet. 8 (9): 317–22. doi:10.1016/0168-9525(92)90264-5. PMID 1365398.
- ↑ Lory S (June 1992). "Determinants of extracellular protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria". J. Bacteriol. 174 (11): 3423–8. doi:10.1128/jb.174.11.3423-3428.1992. PMC 206022 . PMID 1592799.