
The Wiskott–Aldrich Syndrome protein (WASp) is a 502-amino acid protein expressed in cells of the hematopoietic system that in humans is encoded by the WAS gene. In the inactive state, WASp exists in an autoinhibited conformation with sequences near its C-terminus binding to a region near its N-terminus. Its activation is dependent upon CDC42 and PIP2 acting to disrupt this interaction, causing the WASp protein to 'open'. This exposes a domain near the WASp C-terminus that binds to and activates the Arp2/3 complex. Activated Arp2/3 nucleates new F-actin.
The Rho family of GTPases is a family of small signaling G proteins, and is a subfamily of the Ras superfamily. The members of the Rho GTPase family have been shown to regulate many aspects of intracellular actin dynamics, and are found in all eukaryotic kingdoms, including yeasts and some plants. Three members of the family have been studied in detail: Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. All G proteins are "molecular switches", and Rho proteins play a role in organelle development, cytoskeletal dynamics, cell movement, and other common cellular functions.
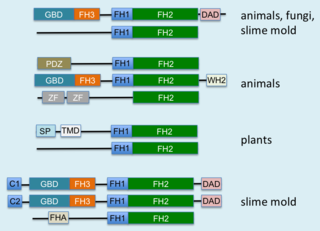
Formins are a group of proteins that are involved in the polymerization of actin and associate with the fast-growing end of actin filaments. Most formins are Rho-GTPase effector proteins. Formins regulate the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton and are involved in various cellular functions such as cell polarity, cytokinesis, cell migration and SRF transcriptional activity. Formins are multidomain proteins that interact with diverse signalling molecules and cytoskeletal proteins, although some formins have been assigned functions within the nucleus.

Dynamin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNM2 gene.

Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein family member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WASF2 gene.

Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein family member 1, also known as WASP-family verprolin homologous protein 1 (WAVE1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WASF1 gene.
Pre-mRNA-processing factor 40 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRPF40A gene.

Formin-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FNBP1 gene.

Protein diaphanous homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DIAPH1 gene.

FH1/FH2 domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FHOD1 gene.

Dynamin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNM3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dynamin family which possess mechanochemical properties involved in actin-membrane processes, predominantly in membrane budding. DNM3 is upregulated in Sézary's syndrome.

RhoD is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rac subfamily of the family Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RHOD.

Rnd2 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rnd subgroup of the Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RND2.

Cdc42 effector protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDC42EP1 gene.

Scinderin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCIN gene. Scinderin is an actin severing protein belonging to the gelsolin superfamily. It was discovered in Dr. Trifaro's laboratory at the University of Ottawa, Canada. Secretory tissues are rich in scinderin. In these tissues scinderin, a calcium dependent protein, regulates cortical actin networks. Normally secretory vesicles are excluded from release sites on the plasma membrane by the presence of a cortical actin filament network. During cell stimulation, calcium channels open allowing calcium ions to enter the secretory cell. Increase in intracellular calcium activates scinderin with the consequent actin filament severing and local dissociation of actin filament networks. This allows the movement of secretory vesicles to release sites on the plasma membrane.

SLIT-ROBO Rho GTPase-activating protein 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SRGAP3 gene.

WAS/WASL-interacting protein family member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WIPF2 gene.

Formin-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FMNL1 gene.
Disheveled-associated activator of morphogenesis 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DAAM1 gene. Evidence of alternative splicing has been observed for this gene but the full-length nature of these variants has not been determined.
mDia1 is a member of the protein family called the formins and is a Rho effector. It is the mouse version of the diaphanous homolog 1 of Drosophila. mDia1 localizes to cells' mitotic spindle and midbody, plays a role in stress fiber and filopodia formation, phagocytosis, activation of serum response factor, formation of adherens junctions, and it can act as a transcription factor. mDia1 accelerates actin nucleation and elongation by interacting with barbed ends of actin filaments. The gene encoding mDia1 is located on Chromosome 18 of Mus musculus and named Diap1.


















