The Egyptian hieroglyph for "black" in Gardiner's sign list is numbered I6. Its phonetic value is km. The Wörterbuch der ägyptischen Sprache lists no less than 24 different terms of km indicating 'black' such as black stone, metal, wood, hair, eyes, and animals, and in one instance applied to a person's name.

A quadrat block is a virtual rectangle or square in Egyptian hieroglyphic text.
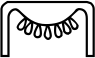
The Egyptian hieroglyph representing gold, phonetic value nb, is important due to its use in the Horus-of-Gold name, one of the Fivefold Titulary names of the Egyptian pharaoh.
The ancient Egyptian Branch hieroglyph, also called a Stick, is a member of the trees and plants hieroglyphs.
The Illustrated Hieroglyphics Handbook is part of a new genre of books focused on Egyptian hieroglyphs. The book is a graphics based book with four to seven word examples of each Egyptian hieroglyph; the words are graphically explained for each component of the word, and links to the other entries in the book; each hieroglyph is in extreme-artistic-detail and can vary for each hieroglyph, word-to-word. The determinatives ending a word are explained,. Some determinatives are specific to individual trades, i.e. metallurgy, for example and are not in the Gardiner's sign list of Egyptian hieroglyphs.

The ancient Egyptian Hare hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. E34 (𓃹) is a portrayal of the desert hare or Cape hare, Lepus capensis of Egypt, within the Gardiner signs for mammals. The ancients used the name of sekhat for the hare.

The ancient Egyptian Sky hieroglyph,, is Gardiner sign listed no. N1, within the Gardiner signs for sky, earth, and water.
The ancient Egyptian b-hieroglyph represents a foot or lower leg.

The Egyptian hieroglyph Townsite-city-region is Gardiner sign listed no. O49 for the intersection of a town's streets. In some Egyptian hieroglyph books it is called a city plan.

The use of the Spine with fluid hieroglyph is for words showing "length", as opposed to 'breadth',. Some example words for 'length' are: to be long, length, to extend, extended; and for to expand, to dilate, words like: joy, gladness, pleasure, delight.
The Ancient Egyptian Swallow hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. G36 for swallow birds. The Sparrow hieroglyph appears similar in size and shape, though it lacks the swallow's forked tail and is used to represent small, or bad items.

The ancient Egyptian Two Whips with Shen ring hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. S23 is a portrayal of the Shen ring with two Egyptian flails-(Crook and flail); it is a member of the Gardiner subset for "crowns, dress, staves, etc".

In the Egyptian language, the single stair hieroglyph is used as a determinative.

The Egyptian hieroglyph ndj (nḏ) has the shape of a cross. It presumably depicts some type of tool such as a mill. It is often written alongside the nu "pot" hieroglyph (W24). It is used as an ideogram or determinative in the context of "grains", "grinding stone", "grind", "to rub out".

The Three-Fox-Skins (hieroglyph) is Gardiner's sign listed no. F31, in the series of parts of animals. It consists of 3-fox skins tied at one end, and hanging, creating flowing skins.

The Egyptian hieroglyph representing a honey bee. It is used as an ideogram for "bee" (bjt), but most frequently as part of the title of the King of Upper and Lower Egypt, rendered nswt-bjtj.

The Land, irrigated hieroglyph represents "district, nome". It is a determinative in the name of provinces and regions in the noun ḥsp, for "garden", "vegetable garden", and "orchard".

In Egyptian hieroglyphs, the hieroglyph is used for the phonetic value of sma, with meanings of to join together, to unite with.

The ancient Egyptian Bread bun hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. X1 for the side view of a bread bun. It is also the simple shape of a semicircle. The hieroglyph is listed under the Gardiner category of loaves and cakes.














