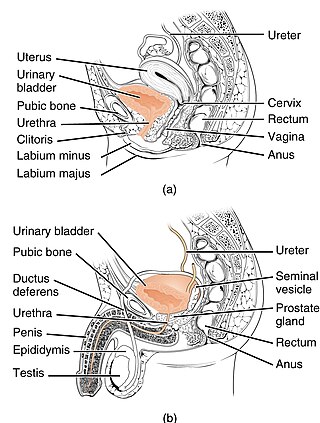
The urethra is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which placental mammals urinate and ejaculate. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the urethra also transports semen but is separate from the urinary tract.

The bladder is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more.
Azotemia, also spelled azotaemia, is a medical condition characterized by abnormally high levels of nitrogen-containing compounds in the blood. It is largely related to insufficient or dysfunctional filtering of blood by the kidneys. It can lead to uremia and acute kidney injury if not controlled.

The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra.
The excretory system is a passive biological system that removes excess, unnecessary materials from the body fluids of an organism, so as to help maintain internal chemical homeostasis and prevent damage to the body. The dual function of excretory systems is the elimination of the waste products of metabolism and to drain the body of used up and broken down components in a liquid and gaseous state. In humans and other amniotes, most of these substances leave the body as urine and to some degree exhalation, mammals also expel them through sweating.

The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lined with urothelial cells, a form of transitional epithelium, and feature an extra layer of smooth muscle in the lower third to aid in peristalsis. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. Stenosis is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children.

The collecting duct system of the kidney consists of a series of tubules and ducts that physically connect nephrons to a minor calyx or directly to the renal pelvis. The collecting duct participates in electrolyte and fluid balance through reabsorption and excretion, processes regulated by the hormones aldosterone and vasopressin.

Transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching. The transitional epithelium usually appears cuboidal when relaxed and squamous when stretched. This tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand in order to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the urinary system and is known here as urothelium. The bladder, for example, has a need for great distension.
Ureteroscopy is an examination of the upper urinary tract, usually performed with a ureteroscope that is passed through the urethra and the bladder, and then directly into the ureter. The procedure is useful in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders such as kidney stones and urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Smaller stones in the bladder or lower ureter can be removed in one piece, while bigger ones are usually broken before removal during ureteroscopy.

Transitional cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from the transitional epithelium, a tissue lining the inner surface of these hollow organs. It typically occurs in the urothelium of the urinary system; in that case, it is also called urothelial carcinoma. It is the most common type of bladder cancer and cancer of the ureter, urethra, and urachus. Symptoms of urothelial carcinoma in the bladder include hematuria. Diagnosis includes urine analysis and imaging of the urinary tract (cystoscopy).

Urethral cancer is a rare cancer originating from the urethra. The disease has been classified by the TNM staging system and the World Health Organization.

Uroplakin-1b (UP1b), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the UPK1B gene.

Uroplakin-1a (UP1a) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPK1A gene.

Uroplakin-3a(UP3a) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPK3A gene.
Urologic diseases or conditions include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder control problems, and prostate problems, among others. Some urologic conditions do not affect a person for that long and some are lifetime conditions. Kidney diseases are normally investigated and treated by nephrologists, while the specialty of urology deals with problems in the other organs. Gynecologists may deal with problems of incontinence in women.

Papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential (PUNLMP) is an exophytic, (microscopically) nipple-shaped pre-malignant growth of the lining of the upper genitourinary tract, which includes the renal pelvis, ureters, urinary bladder and part of the urethra.
Bladder outlet obstruction occurs when urine is unable to flow from the kidneys through the ureters and out of the bladder through the urethra. Decreased flow of urine leads to swelling of the urinary tract, called hydronephrosis. This process of decreased flow of urine through the urinary tract can begin as early as during intrauterine life and it prevents normal development of fetal kidneys and fetal urine. Low levels of fetal urine leads to low amniotic fluid levels and incomplete lung maturation. Older children and adults can also experience bladder outlet obstruction; however, this process is usually reversible and isn't associated with as many poor outcomes as in infants with congenital bladder outlet obstruction.

Ureteral cancer is cancer of the ureters, muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. It is also known as ureter cancer, renal pelvic cancer, and rarely ureteric cancer or uretal cancer. Cancer in this location is rare. Ureteral cancer becomes more likely in older adults, usually ages 70–80, who have previously been diagnosed with bladder cancer.

Invasive urothelial carcinoma is a type of transitional cell carcinoma. It is a type of cancer that develops in the urinary system: the kidney, urinary bladder, and accessory organs. Transitional cell carcinoma is the most common type of bladder cancer and cancer of the ureter, urethra, renal pelvis, the ureters, the bladder, and parts of the urethra and urachus. It originates from tissue lining the inner surface of these hollow organs - transitional epithelium. The invading tumors can extend from the kidney collecting system to the bladder.
The rock dove, Columbia livia, has a number of special adaptations for regulating water uptake and loss.











