Faya-Largeau is the largest city in northern Chad and was the capital of the region of Bourkou-Ennedi-Tibesti. It is now in the Borkou Region, which was formed in 2008 from the Borkou Department of the former Bourkou-Ennedi-Tibesti region.

The Tibesti Mountains are a mountain range in the central Sahara, primarily located in the extreme north of Chad, with a small portion located in southern Libya. The highest peak in the range, Emi Koussi, lies to the south at a height of 3,415 meters (11,204 ft) and is the highest point in both Chad and the Sahara. Bikku Bitti, the highest peak in Libya, is located in the north of the range. The central third of the Tibesti is of volcanic origin and consists of five volcanoes topped by large depressions: Emi Koussi, Tarso Toon, Tarso Voon, Tarso Yega and Toussidé. Major lava flows have formed vast plateaus that overlie Paleozoic sandstone. The volcanic activity was the result of a continental hotspot that arose during the Oligocene and continued in some places until the Holocene, creating fumaroles, hot springs, mud pools and deposits of natron and sulfur. Erosion has shaped volcanic spires and carved an extensive network of canyons through which run rivers subject to highly irregular flows that are rapidly lost to the desert sands.

The Aouzou Strip is a strip of land in northern Chad that lies along the border with Libya, extending south to a depth of about 100 kilometers into Chad's Borkou, Ennedi Ouest, Ennedi Est, and Tibesti Regions for an area of 114,000 km2. It is named after the small town and oasis of Aouzou. The strip played a significant role in the Chadian–Libyan War when it was claimed by Libya.

Saharan rock art is a significant area of archaeological study focusing on artwork carved or painted on the natural rocks of the central Sahara desert. The rock art dates from numerous periods starting c. 12,000 years ago, and is significant because it shows the culture of ancient African societies.

The Ennedi Plateau is located in the northeast of Chad, in the regions of Ennedi-Ouest and Ennedi-Est. It is considered a part of the group of mountains known as the Ennedi Massif found in Chad, which is one of the nine countries that make up the Sahelian belt that spans the Atlantic Ocean to Sudan. The Ennedi is a sandstone bulwark in the middle of the Sahara, which was formed by erosion from wind and temperature. Many people occupied this area, such as hunters-gatherers and pastoralists. The Ennedi area is also known for its large collection of rock art depicting mainly cattle, as these animals had the greatest financial, environmental, and cultural impact. This art dates back nearly 7,000 years ago. Today, two semi-nomadic groups, mainly Muslim, live in the Ennedi during the rainy months and pass through the area during the dry season. They rely on their herds of camels, donkeys, sheep, and goats to survive.
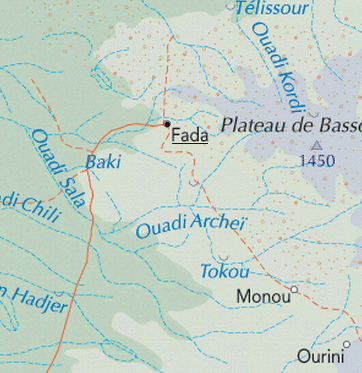
The Battle of Fada took place in northern Chad in 1987, and was a turning point of the Chadian–Libyan conflict.
The Chadian–Libyan War was a series of military campaigns in Chad between 1978 and 1987, fought between Libyan and allied Chadian forces against Chadian groups supported by France, with the occasional involvement of other foreign countries and factions.

The Guelta d'Archei is one of the most famous gueltas in the Sahara. It is located in the Ennedi Plateau, in north-eastern Chad, south-east of the town of Fada. The Guelta d'Archei is inhabited by several kinds of animals, most notably the West African crocodile. Middle Holocene remains, as well as rock paintings, indicate that this species once thrived across most of today's Sahara Desert and in swamps and rivers along South Mediterranean shores. The small group of surviving crocodiles in the Guelta d'Archei represents one of the last colonies known in the Sahara today; the Tagant Plateau colony in Mauritania has likely been extinct since 1996.
Zouar is a town in the Tibesti Ouest department of the Tibesti region in northern Chad, located in an oasis in the Tibesti Mountains. Prior to 2008 it was in the Tibesti Department of the former Bourkou-Ennedi-Tibesti region.

The Toyota War, also known as the Great Toyota War, which took place in 1987 in Northern Chad and on the Chad–Libya border, was the last phase of the Chadian–Libyan War. It takes its name from the Toyota pickup trucks, primarily the Toyota Hilux and the Toyota Land Cruiser, used to provide mobility for the Chadian troops as they fought against the Libyans, and as technicals. The 1987 war resulted in a heavy defeat for Libya, which, according to American sources, lost one tenth of its army, with 7,500 men killed and US$1.5 billion worth of military equipment destroyed or captured. Chadian forces suffered 1,000 deaths.
Fada Airport is an airport serving Fada, located in the Ennedi-Ouest Region in Chad.
Ounianga Kébir is a town in the Sahara Desert in the Ennedi Region of northern Chad. Located within the Ennedi Department, Ounianga also makes up a sub-prefecture.

Ennedi Region was a former region of Chad. It was created in 2008 from the Ennedi Est Department and Ennedi Ouest Department of the former Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti Region. The capital of the Ennedi region was Fada. In 2012 it was split into two new regions: the department of Wadi Hawar became Ennedi-Est Region and the department of Ennedi became Ennedi-Ouest Region.

Tibesti Region is a region of Chad, located in far northwest of the country. Its capital is Bardaï. It was created in 2008 when the former Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti Region was split into three, with the Tibesti Department becoming the Tibesti Region. The region is named for the Tibesti Mountains, one of the most prominent mountain chains in the Sahara Desert. Tibesti is the least populated region of Chad, and also has the lowest GDP in the country.

The Mourdi Depression is a prominent desert depression of northeastern Chad. It lies adjacent to the Ennedi Plateau. The cleft lies "between the Erdi plateau and the eastern slopes of Ennedi, and the mouth of the Wadi Guroguro." The depression is characterized by a rocky valley, about 30 miles (48 km) wide from north to south, sloping from an altitude of about 1,800 feet (550 m) down towards the west to Djourab.

Ennedi Est Region is one of the twenty-three regions of Chad. The capital of the region is Am-Djarass. The region's current governor is General Hassan Djorobo.

Ennedi-Ouest Region is one of the twenty-three regions of Chad.
The Battle of B'ir Kora was a military engagement during the Toyota War. Fought between the Libyan army and the Chadian FANT on the morning of 19 March 1987, the battle saw the Chadians encircle and destroy several Libyan units.