Related Research Articles

Mount Erebus is the southernmost active volcano on Earth, located on Ross Island in the Ross Dependency in Antarctica. With a summit elevation of 3,792 metres (12,441 ft), it is the second most prominent mountain in Antarctica and the second-highest volcano in Antarctica. It is the highest point on Ross Island, which is also home to three inactive volcanoes: Mount Terror, Mount Bird, and Mount Terra Nova. It makes Ross Island the sixth-highest island on Earth.
The Scott Mountains are a large number of isolated peaks lying south of Amundsen Bay in Enderby Land of East Antarctica, Antarctica. Discovered on 13 January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Sir Douglas Mawson. He named the feature Scott Range after Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy. The term mountains is considered more appropriate because of the isolation of its individual features.
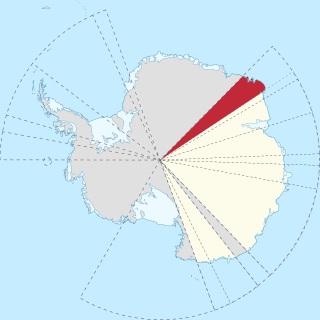
Enderby Land is a projecting landmass of Antarctica. Its shore extends from Shinnan Glacier at about 67°55′S44°38′E to William Scoresby Bay at 67°24′S59°34′E, approximately 1⁄24 of the earth's longitude. It was first documented in western and eastern literature in February 1831 by John Biscoe aboard the whaling brig Tula, and named after the Enderby Brothers of London, the ship's owners who encouraged their captains to combine exploration with sealing.
Ufs Island is a rocky island 3.2 km (2 mi) wide, lying in the east part of Howard Bay, Antarctica, just north of the Lachal Bluffs, and about 4 km (2.5 mi) west of Allison Bay. Cape Simpson, the north end of this island, was discovered by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson in February 1931, but the feature's insularity was first recognized by Norwegian cartographers working from aerial photographs taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37. They named it Ufsoy.
Howard Bay is a 2-mile (3 km) wide body of water in Antarctica, lying between Byrd Head to the west and Ufs Island and the Lachal Bluffs to the east. It was discovered in February 1931 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Douglas Mawson, and was named by him after A. Howard, the expedition's hydrologist.
Surveyors Range is a 30 miles (48 km) long mountain range in the Churchill Mountains of Antarctica.
Kirkby Head is a sheer coastal outcrop on Tange Promontory in Enderby Land, Antarctica, which is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. Continental ice reaches almost to the top on its southern side. It is located at the east side of the entrance to Alasheyev Bight.

Posadowsky Glacier is a glacier about 9 nautical miles long, flowing north to Posadowsky Bay immediately east of Gaussberg. Posadowsky Bay is an open embayment, located just east of the West Ice Shelf and fronting on the Davis Sea in Kaiser Wilhelm II Land. Kaiser Wilhelm II Land is the part of East Antarctica lying between Cape Penck, at 87°43'E, and Cape Filchner, at 91°54'E, and is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. Other notable geographic features in this area include Drygalski Island, located 45 mi NNE of Cape Filchner in the Davis Sea, and Mirny Station, a Russian scientific research station.
All-Blacks Nunataks is a group of conspicuous nunataks lying midway between Wallabies Nunataks and Wilhoite Nunataks at the southeast margin of the Byrd Névé in Antarctica. Named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (1960–61) after the well-known New Zealand national rugby union team.
The Boobyalla Islands are two small islands 4 kilometres (2 nmi) northeast of Kirkby Head, Enderby Land. They were plotted from air photos taken from Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions aircraft in 1956, and named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia after the Australian native willow, "Boobyalla".
Borradaile Island is one of the Balleny Islands. It was the site of the first landing south of the Antarctic Circle, and features the "remarkable pinnacle" called Beale Pinnacle, near Cape Beale on its south-eastern coast, and Cape Scoresby on its north-western coast.
Jennings Bluff is a dark, flat-topped outcrop in the Nicholas Range of Antarctica, 10 nautical miles (19 km) north of Mount Storegutt. It rises about 100 metres (330 ft) above the general ice level and has a steep eastern side, backing to an ice scarp in the west. The bluff was discovered by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition, 1929–31, under Mawson. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from aerial photos taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37, and called Brattstabben. It was photographed from Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions aircraft in 1956 and remapped, and was renamed by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia in 1961 for Noel Durrent Jennings, an assistant diesel mechanic at Mawson Station in 1960.
The Krat Rocks are an area of submerged rocks with a least depth of about 1 metre (3 ft), lying at the west side of Davis Anchorage, 0.8 nautical miles (1.5 km) south of Bluff Island, off the Vestfold Hills, Ingrid Christensen Coast, Antarctica. The reef was delineated by d'A.T. Gale, an Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions surveyor aboard the Thala Dan in 1961, and was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia after Ingemann Krat, Danish chief engineer on the Thala Dan.
Turbulence Bluffs is an area with three high bluffs with vertical faces on the northwest that merges with an ice sheet on the southeast. It is located along the east side of Robert Glacier, 18.5 miles (29.8 km) northeast of Rayner Peak in Enderby Land. The area was mapped through ANARE surveys and air photos between 1954 and 1966. It received its name due to severe turbulence encountered while attempting a helicopter landing in 1965.
Pearce Peak is a partially snow-covered ridge, 1,200 m, which appears as a peak when viewed from the north, standing 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) south of Moyes Peak and 15 nautical miles (28 km) south-southwest of Falla Bluff. Discovered in February 1931 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson, who named it for Sir George Pearce, Chairman of the Australian Antarctic Committee, 1929.
In Antarctica, Moyes Peak is a small rock peak projecting slightly above the ice sheet 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) north of Pearce Peak, 12 nautical miles (22 km) southwest of Falla Bluff.
The Stanton Group is a group of small rocky islands close to the coast at the east side of Utstikkar Bay, 4 nautical miles (7 km) northeast of Falla Bluff discovered in February 1931 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Mawson. He named it for A. M. Stanton, first officer of the Discovery, 1930–31.
Mount Hordern is a peak, 1,510 metres (4,950 ft) high, standing 4 nautical miles (7 km) south of Mount Coates in the David Range of Antarctica. It was discovered in February 1931 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Mawson, and named for Sir Samuel Hordern, a patron of this expedition and of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition under Mawson, 1911–14.
The Lachal Bluffs are a group of rocky headlands located just south of Ufs Island and east of Howard Bay, and about 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) west of Allison Bay, on the Mawson Coast of Mac. Robertson Land, Antarctica. They were mapped by Norwegian cartographers from air photos taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37, and named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for R. Lachal, an assistant cook at Mawson Station, who acted as a geological field assistant, 1965.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Falla Bluff". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Falla Bluff". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.