
Protein ITFG3 also known as family with sequence similarity 234 member A (FAM234A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITFG3 gene. Here, the gene is explored as encoded by mRNA found in Homo sapiens. The FAM234A gene is conserved in mice, rats, chickens, zebrafish, dogs, cows, frogs, chimpanzees, and rhesus monkeys. Orthologs of the gene can be found in at least 220 organisms including the tropical clawed frog, pandas, and Chinese hamsters. The gene is located at 16p13.3 and has a total of 19 exons. The mRNA has a total of 3224 bp and the protein has 552 aa. The molecular mass of the protein produced by this gene is 59660 Da. It is expressed in at least 27 tissue types in humans, with the greatest presence in the duodenum, fat, small intestine, and heart.
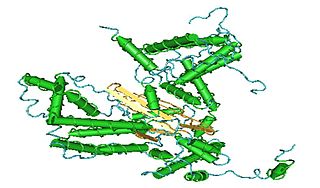
C7orf38 is a gene located on chromosome 7 in the human genome. The gene is expressed in nearly all tissue types at very low levels. Evolutionarily, it can be found throughout the kingdom animalia. While the function of the protein is not fully understood by the scientific community, bioinformatic tools have shown that the protein bares much similarity to zinc finger or transposase proteins. Many of its orthologs, paralogs, and neighboring genes have been shown to possess zinc finger domains. The protein contains a hAT dimerization domain nears its C-terminus. This domain is highly conserved in transposase enzymes.

The FAM185A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM185A gene. The FAM185A gene is found on the positive strand of Chromosome 7 at 7q22.1. The gene begins 102,389,399bp from the p-terminus of the chromosome and ends at 102,449,672bp from the p-terminus; it covers a total of 73,308 basepairs. The protein encoded by this gene is characterized by the presence of multiple copies of DUF4098 near its C-terminus. It is described as a Long Interspersed Nuclear Element (LINE), a subclass of penaeid repetitive elements (PREs).

Family with Sequence Similarity 203, Member B (FAM203B) is a protein encoded by the FAM203B gene (8q24.3) in humans. While FAM203B is only found in humans and possibly non-human primates, its paralog, FAM203A, is highly conserved. The FAM203B protein contains two conserved domains of unknown function, DUF383 and DUF384, and no transmembrane domains. This protein has no known function yet, although the homolog of FAM203A in Caenorhabditis elegans (Y54H5A.2) is thought to help regulate the actin cytoskeleton.

TMEM260 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM260 gene. The function of TMEM260 is not yet clearly understood. TMEM260 is also known as UPF0679, c14orf101, and FLJ0392.

Protein FAM214A, also known as protein family with sequence similarity 214, A (FAM214A) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the FAM214A gene. FAM214A is a gene with unknown function found at the q21.2-q21.3 locus on Chromosome 15 (human). The protein product of this gene has two conserved domains, one of unknown function (DUF4210) and another one called Chromosome_Seg. Although the function of the FAM214A protein is uncharacterized, both DUF4210 and Chromosome_Seg have been predicted to play a role in chromosome segregation during meiosis.

Family with sequence similarity 98, member A, or FAM98A, is a gene that in the human genome encodes the FAM98A protein. FAM98A has two paralogs in humans, FAM98B and FAM98C. All three are characterized by DUF2465, a conserved domain shown to bind to RNA. FAM98A is also characterized by a glycine-rich C-terminal domain. FAM98A also has homologs in vertebrates and invertebrates and has distant homologs in choanoflagellates and green algae.

Transmembrane protein 151B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM151B gene.

Family with sequence similarity 63, member A is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the FAM63A gene. It is located on the minus strand of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21.3.
Family with Sequence Similarity 166, member B, or FAM166B, is an uncharacterized protein in humans that is encoded by the FAM166B gene.

PROSER1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PROSER1 gene.
Cardiac-enriched FHL2-interacting protein (CEFIP) is a protein encoded by the gene C10orf71 on chromosome 10 open reading frame 71. It is primarily understood that this gene is moderately expressed in muscle tissue and cardiac tissue.

FAM71F2 or Family with Sequence Similarity 71 member F2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the Family with Sequence Similarity 71 member F2 gene. This gene is highly active in the reproductive tissues, specifically the testis, and may serve as a potential biomarker for determining metastatic testicular cancer.

Chromosome 9 open reading frame 25 (C9orf25) is a domain that encodes the FAM219A gene. The terms FAM219A and C9orf25 are aliases and can be used interchangeably. The function of this gene is not yet completely understood.

Family with sequence similarity 222 member A or Aggregatin is a protein of unknown function. In humans it is encoded by the gene FAM222A. Aggregatin's cellular function is not well understood, however it has been implicated in Alzheimer's disease.

Family with Sequence Similarity 155 Member B is a protein in humans that is encoded by the FAM155B gene. It belongs to a family of proteins whose function is not yet well understood by the scientific community. It is a transmembrane protein that is highly expressed in the heart, thyroid, and brain.

The FAM214B, also known as protein family with sequence similarity 214, B (FAM214B) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the FAM214B gene located on the human chromosome 9. The protein has 538 amino acids. The gene contain 9 exon. There has been studies that there are low expression of this gene in patients with major depression disorder. In most organisms such as mammals, amphibians, reptiles, and birds, there are high levels of gene expression in the bone marrow and blood. For humans in fetal development, FAM214B is mostly expressed in the brains and bone marrow.

FAM120AOS, or family with sequence similarity 120A opposite strand, codes for uncharacterized protein FAM120AOS, which currently has no known function. The gene ontology describes the gene to be protein binding. Overall, it appears that the thyroid and the placenta are the two tissues with the highest expression levels of FAM120AOS across a majority of datasets.

Family with Sequence Similarity 166, member C (FAM166C), is a protein encoded by the FAM166C gene. The protein FAM166C is localized in the nucleus. It has a calculated molecular weight of 23.29 kDa. It also contains DUF2475, a protein of unknown function from amino acid 19–85. The FAM166C protein is nominally expressed in the testis, stomach, and thyroid.

UBALD1 is a protein encoded by the UBALD1 gene, located on chromosome 16 in humans. UBALD1 has high ubiquitous tissue expression and localizes in the nucleus and cytoplasm. UBALD1 is conserved in animals, including invertebrates. An alias for UBALD1 is FAM100A.



















