
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electrical equipment and systems to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment, by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or even physical damage in operational equipment. The goal of EMC is the correct operation of different equipment in a common electromagnetic environment. It is also the name given to the associated branch of electrical engineering.

The École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) is a public research university in Lausanne, Switzerland. Established in 1853, EPFL has placed itself as a world class university specializing in engineering and natural sciences.
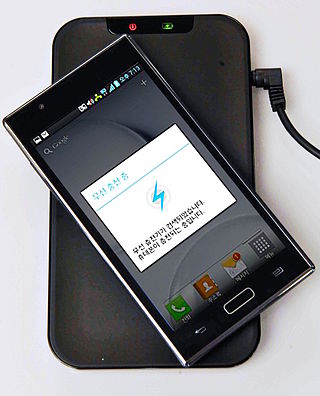
Wireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system, a transmitter device, driven by electric power from a power source, generates a time-varying electromagnetic field, which transmits power across space to a receiver device, which extracts power from the field and supplies it to an electrical load. The technology of wireless power transmission can eliminate the use of the wires and batteries, thus increasing the mobility, convenience, and safety of an electronic device for all users. Wireless power transfer is useful to power electrical devices where interconnecting wires are inconvenient, hazardous, or are not possible.

In radio reception, radio noise is unwanted random radio frequency electrical signals, fluctuating voltages, always present in a radio receiver in addition to the desired radio signal. Radio noise near in frequency to the radio signal being received interferes with it in the receiver's circuits. Radio noise is a combination of natural electromagnetic atmospheric noise created by electrical processes in the atmosphere like lightning, manmade radio frequency interference (RFI) from other electrical devices picked up by the receiver's antenna, and thermal noise present in the receiver input circuits, caused by the random thermal motion of molecules.
Martin Allan Uman is an American engineer. He has been acknowledged by the American Geophysical Union as one of the world's leading authorities on lightning.

Martin Vetterli is the current president of École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland, succeeding Patrick Aebischer. He's a professor of engineering and was formerly the president of the National Research Council of the Swiss National Science Foundation.
James R. Wait was a Canadian electrical engineer and engineering physicist. In 1977, he was elected as a member of National Academy of Engineering in Electronics, Communication & Information Systems Engineering for his contributions to electromagnetic propagation engineering as it affects communication and geophysical exploration.

The Swiss Electromagnetics Research and Engineering Centre (SEREC) is the sole organization for handling electromagnetic research and concerns in Switzerland.
Alain Wegmann was a Swiss computer scientist, professor of Systemic Modeling at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), and Information Technology and Services consultant, known for the development of the Systemic Enterprise Architecture Methodology (SEAM).
Carlo Alberto Nucci is full professor of Electrical Power Systems at the University of Bologna and the Editor in Chief of the Electric Power System Research Journal. He authored or co-authored over 200 science papers in the field of power electrical engineering. Fellow of IEEE and IET. He has also been Chair of the IEEE PowerTech Permanent Steering Committee. Nucci is head of the Power Systems Laboratory at the University of Bologna. Together with prof. F. Rachidi of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology of Lausanne, he has developed a computer code for the appraisal of lightning-induced voltages in electrical network, called LIOV, which is quoted in IEEE standards. Prof. Nucci is also member of the Bologna Science Academy.
Adrian (Mihai) Ionescu is a full Professor at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL) on a special contract.

Levent Gürel is a Turkish scientist and electrical engineer. He was the director of Computational Electromagnetics Research Center (BiLCEM) and a professor in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering at the Bilkent University, Turkey until November 2014. Currently, he is serving as an adjunct professor at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. He is also serving as the founder and CEO of ABAKUS Computing Technologies.
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also a transient electromagnetic disturbance (TED), is a brief burst of electromagnetic energy. The origin of an EMP can be natural or artificial, and can occur as an electromagnetic field, as an electric field, as a magnetic field, or as a conducted electric current. The electromagnetic interference caused by an EMP can disrupt communications and damage electronic equipment. An EMP such as a lightning strike can physically damage objects such as buildings and aircraft. The management of EMP effects is a branch of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) engineering.

David Atienza Alonso is a Spanish/Swiss scientist in the disciplines of computer and electrical engineering. His research focuses on hardware‐software co‐design and management for energy‐efficient and thermal-aware computing systems, always starting from a system‐level perspective to the actual electronic design. He is a full professor of electrical and computer engineering at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL) and the head of the Embedded Systems Laboratory (ESL). He is an IEEE Fellow (2016), and an ACM Fellow (2022).
Marcos Rubinstein is a professor and chair at the University of Applied Sciences and Arts of Western Switzerland in Yverdon-les-Bains, Switzerland.
Vernon Cooray is a Sri Lankan scientist who is an emeritus professor at the Department of Electrical Engineering at Uppsala University, Sweden. As a scientist he has concentrated on solving both physics and engineering problems related to lightning physics, lightning protection and physics of electrical discharges. This research work has resulted in more than 600 research publications. He was the Ph.D. thesis supervisor of more than thirty researchers, both at Uppsala and foreign universities, who are now actively engaged in lightning research and lightning protection in different parts of the world.

Aude G. Billard is a Swiss physicist in the fields of machine learning and human-robot interactions. As a full professor at the School of Engineering at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL), Billard’s research focuses on applying machine learning to support robot learning through human guidance. Billard’s work on human-robot interactions has been recognized numerous times by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and she currently holds a leadership position on the executive committee of the IEEE Robotics and Automation Society (RAS) as the vice president of publication activities.

Michael Unser (born April 9, 1958 in Zug, Switzerland) is a Swiss engineer and a professor at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL). His research focuses on the field of biomedical image processing.

Niels Kuster is a Swiss electrical engineer and Professor. The focus of his research is on the electromagnetic near field, basics for assessing/using the interaction of electromagnetic fields with organisms, and physiological simulations as part of biophysics.










