
Archaeocyatha is a taxon of extinct, sessile, reef-building marine organisms of warm tropical and subtropical waters that lived during the early (lower) Cambrian Period. It is believed that the centre of the Archaeocyatha origin is now located in East Siberia, where they are first known from the beginning of the Tommotian Age of the Cambrian, 525 million years ago (mya). In other regions of the world, they appeared much later, during the Atdabanian, and quickly diversified into over a hundred families. They became the planet's very first reef-building animals and are an index fossil for the Lower Cambrian worldwide.

Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera, are a basal animal clade as a sister of the Diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. The branch of zoology that studies sponges is known as spongiology.

Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed siliceous spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually classified along with other sponges in the phylum Porifera, but some researchers consider them sufficiently distinct to deserve their own phylum, Symplasma. Some experts believe glass sponges are the longest-lived animals on earth; these scientists tentatively estimate a maximum age of up to 15,000 years.

Luffa is a genus of tropical and subtropical vines in the cucumber family (Cucurbitaceae).

SpongeBob SquarePants is a fictional character and the main character of the long-running television series SpongeBob Squarepants. He is characterized by his optimism and childlike attitude, and is influenced by other comedic characters, including Stan Laurel and Pee-Wee Herman.

Squidward Q. Tentacles is a fictional character voiced by actor Rodger Bumpass in the Nickelodeon animated television series SpongeBob SquarePants. Squidward was created and designed by marine biologist and animator Stephen Hillenburg. He first appeared on television in the series' pilot episode "Help Wanted" on May 1, 1999.

The calcareoussponges of class Calcarea are members of the animal phylum Porifera, the cellular sponges. They are characterized by spicules made out of calcium carbonate in the form of calcite or aragonite. While the spicules in most species have three points, in some species they have either two or four points.

Stephen McDannell Hillenburg was an American animator and marine science educator. He is best remembered for creating the Nickelodeon animated television series SpongeBob SquarePants. Hillenburg served as the showrunner for the first three seasons of the show, which has become the fifth-longest-running American animated series.

Demosponges are the most diverse class in the phylum Porifera. They include 76.2% of all species of sponges with nearly 8,800 species worldwide. They are sponges with a soft body that covers a hard, often massive skeleton made of calcium carbonate, either aragonite or calcite. They are predominantly leuconoid in structure. Their "skeletons" are made of spicules consisting of fibers of the protein spongin, the mineral silica, or both. Where spicules of silica are present, they have a different shape from those in the otherwise similar glass sponges. Some species, in particular from the Antarctic, obtain the silica for spicule building from the ingestion of siliceous diatoms.

SpongeBob SquarePants is an American animated comedy television series created by marine science educator and animator Stephen Hillenburg for Nickelodeon. The series chronicles the adventures of the title character and his aquatic friends in the fictional underwater city of Bikini Bottom. Being the fifth-longest-running American animated series, its high popularity has made it a media franchise. It is the highest rated series to air on Nickelodeon as well as the most profitable property for ViacomCBS Consumer Products, having generated over $13 billion in merchandising revenue as of 2019.

A spongivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating animals of the phylum Porifera, commonly called sea sponges, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their diet, spongivore animals like the hawksbill turtle have developed sharp, narrow bird-like beak that allows them to reach within crevices on the reef to obtain sponges.

Sponge reefs are reefs formed by Hexactinellid sponges, which have a skeleton made of silica, and are often referred to as glass sponges. Such reefs are now very rare, and found only on the western Canadian continental shelf. Although common in the late Jurassic period, sponge reefs were believed to have gone extinct during or shortly after the Cretaceous period, until the existing reefs were discovered in 1987–1988 - hence these sometimes being dubbed living fossils.

Homosclerophorida is an order of marine sponges. It is the only order in the monotypic class Homoscleromorpha. The order is composed of two families: Plakinidae and Oscarellidae.

Spicules are structural elements found in most sponges. Sponge spicules are made of calcium carbonate or silica. Large spicules visible to the naked eye are referred to as megascleres, while smaller, microscopic ones are termed microscleres. The meshing of many spicules serves as the sponge's skeleton and thus it provides structural support and potentially defense against predators. The composition, size, and shape of spicules are major characters in sponge systematics and taxonomy.
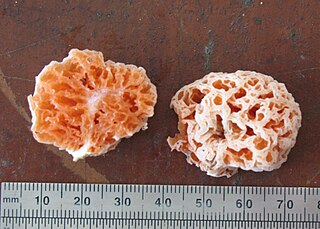
Spongiforma squarepantsii is a species of fungus in the family Boletaceae, genus Spongiforma. Found in Malaysia, it was described as new to science in 2011. It produces sponge-like, rubbery orange fruit bodies that have a fruity or musky odour. The fruit bodies reach dimensions of 10 cm (3.9 in) wide by 7 cm (2.8 in) tall. Like a sponge, they will resume their original shape if water is squeezed out. The spores, produced on the surfaces of the hollows of the sponge, are almond-shaped with rough surfaces, and measure 10‑12.5 μm by 6‑7 μm. The name of the fungus is derived from the Nickelodeon cartoon character SpongeBob SquarePants from the show of the same name. S. squarepantsii is one of two species in Spongiforma; it differs from S. thailandica in its color, odour, and spore structure.

Poecilosclerida is an order of the demosponge class. It is the most speciose demosponge order with over 2200 species. It contains about 25 recognised families. They are characterised by having chelae microscleres, that is, the minute spicules scattered through the tissues, usually in the 10-60 μm range, have a shovel-like structure on the end.
Sea sponge aquaculture is the process of farming sea sponges under controlled conditions. It has been conducted in the world's oceans for centuries using a number of aquaculture techniques. There are many factors such as light, salinity, pH, dissolved oxygen and the accumulation of waste products that influence the growth rate of sponges. The benefits of sea sponge aquaculture are realised as a result of its ease of establishment, minimum infrastructure requirements and the potential to be used as a source of income for populations living in developing countries. Sea sponges are produced on a commercial scale to be used as bath sponges or to extract biologically active compounds which are found in certain sponge species. Techniques such as the rope and mesh bag method are used to culture sponges independently or within an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system setting. One of the only true sustainable sea sponges cultivated in the world occur in the region of Micronesia, with a number of growing and production methods used to ensure and maintain the continued sustainability of these farmed species.
Sponge grounds, also known as sponge aggregations, are intertidal to deep-sea habitats formed by large accumulations of sponges, often dominated by a few massive species. Sponge grounds were already reported more than 150 years ago, but the habitat was first fully recognized, studied and described in detail around the Faroe Islands during the inter-Nordic BIOFAR 1 programme 1987–90. These were called Ostur by the local fishermen and this name has to some extent entered the scientific literature. Sponge grounds were later found elsewhere in the Northeast Atlantic and in the Northwest Atlantic, as well as near Antarctica. They are now known from many other places worldwide and recognized as key marine habitats.

Hecate Strait and Queen Charlotte Sound Glass Sponge Reefs Marine Protected Area is a 2,410-square-kilometre marine protected area located in Hecate Strait and Queen Charlotte Sound off the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada. The marine protected area was established in February 2017 with the goal of conserving the biological diversity, structural habitat, and ecosystem function of four glass sponge reefs. These reefs were the first discovered living specimens and are the largest glass sponge reefs in the world.















