Related Research Articles
The INSEE code is a numerical indexing code used by the French National Institute for Statistics and Economic Studies (INSEE) to identify various entities, including communes and départements. They are also used as national identification numbers given to people.
A United States military occupation code, or a military occupational specialty code, is a nine-character code used in the United States Army and United States Marine Corps to identify a specific job. In the United States Air Force, a system of Air Force Specialty Codes (AFSC) is used. In the United States Navy, a system of naval ratings and designators are used along with the Navy Enlisted Classification (NEC) system. A system of ratings is also used in the United States Coast Guard.
The Joint Electronics Type Designation System (JETDS), which was previously known as the Joint Army-Navy Nomenclature System (AN System. JAN) and the Joint Communications-Electronics Nomenclature System, is a method developed by the U.S. War Department during World War II for assigning an unclassified designator to electronic equipment. In 1957, the JETDS was formalized in MIL-STD-196.

The Defense Logistics Agency (DLA) is a combat support agency in the United States Department of Defense (DoD), with more than 26,000 civilian and military personnel throughout the world. Located in 48 states and 28 countries, DLA provides supplies to the military services and supports their acquisition of weapons, fuel, repair parts, and other materials. The agency also disposes of excess or unusable equipment through various programs.
A service number is an identification code used to identify a person within a large group. Service numbers are most often associated with the military; however, they may be used in civilian organizations as well. National identification numbers may be seen as types of service numbers.
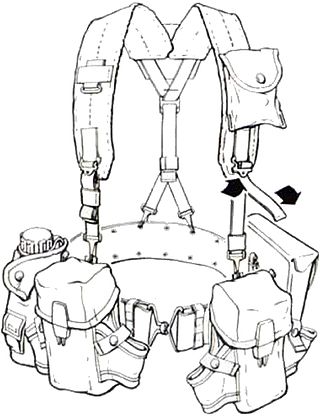
The All-Purpose Lightweight Individual Carrying Equipment (ALICE) is a set of load-carrying equipment adopted as United States Army Standard A on 17 January 1973 to replace the M-1956 Individual Load-Carrying Equipment (ILCE) and M-1967 Modernized Load-Carrying Equipment (MLCE). Although since superseded by MOLLE, ALICE gear is still in some limited use with the U.S. Army National Guard, State Guard, also some ground units of the Navy and Air Force.

The United States Army Ordnance Corps, formerly the United States Army Ordnance Department, is a sustainment branch of the United States Army, headquartered at Fort Lee, Virginia. The broad mission of the Ordnance Corps is to supply Army combat units with weapons and ammunition, including at times their procurement and maintenance. Along with the Quartermaster Corps and Transportation Corps, it forms a critical component of the U.S. Army logistics system.

The Royal Australian Army Ordnance Corps (RAAOC) is the Corps within the Australian Army concerned with supply and administration, as well as the demolition and disposal of explosives and salvage of battle-damaged equipment. The Corps contains clerks, operator supplies, petroleum operators, parachute riggers and ammunition technicians. Members of the Corps are nicknamed Roaches.
The NATO Codification System is a Standardization Agreement approach to identify, classify, and number items of supply. This applies to repetitively used items and stocked. The System has been agreed upon by all signatories of the NATO and sponsored non-NATO nations for use in identifying equipment and supplies. The result is a unique identification and a data set that can be easily shared and understood by a wide range of users. The data set may be shared in the form of printed catalogs, online systems, electronic data exchange, etc. Users include logisticians and manufacturers.

In the United States, all military aircraft display a serial number to identify individual aircraft. These numbers are located on the aircraft tail, so they are sometimes referred to unofficially as "tail numbers". On the Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit bomber, lacking a tail, the number appears on the nose gear door. Individual agencies have each evolved their own system of serial number identification. Aircraft serials are part of the Aircraft Visual Identification System, which also includes the aircraft's tail code and Modex.
MIL-STD-129 standard is used for maintaining uniformity while marking military equipment and supplies that are transported through ships. This standard has been approved to be used by the United States Department of Defense and all other government agencies. Items must be marked for easy identification before they are transported. The marking helps the military personnel to fill the necessary requisition, when a particular stock goes short of the balance level.

A NATO Stock Number, or National Stock Number (NSN) as it is known in the US, is a 13-digit numeric code used by the NATO military alliance, identifying all the 'standardized material items of supply' as they have been recognized by all member states of NATO. Pursuant to the NATO Standardization Agreements, the NSN has come to be used in all treaty countries. However, many countries that use the NSN program are not members of NATO. A two-digit Material Management Aggregation Code (MMAC) suffix may also be appended, to denote asset end use but it is not considered part of the NSN.
The Commercial and Government Entity Code, or CAGE Code, is a unique identifier assigned to suppliers to various government or defense agencies, as well as to government agencies themselves and various organizations. CAGE codes provide a standardized method of identifying a given facility at a specific location.
The MIL-STD-1168 is a set of standard codes used to identify munitions. It was designed to replace the previous confusing Ammunition Identification Code (AIC) system used by the United States Army Ordnance Department.
The National Codification Bureaus or NATO Codification Bureaux (NCB) are a NATO organization that oversees the management of the NATO Codification System (NCS). It is governed by NATO Allied Committee 135 (AC/135), with each member nation's National Codification Bureau controlling and issuing its own unique NATO Stock Numberss. NATO or European Union membership is not required to do so. Non-NATO countries can be allowed to join if recommended, vetted, and approved by AC/135.

The Autocar Model U8144T, officially "5- to 6-Ton, 4×4, Ponton Tractor Truck", was the largest, and most heavy-duty, of a family of heavy four-wheel drive trucks developed for, and deployed primarily with, the United States Army in World War II. They were of a "cab over engine" design, and produced by the Autocar Company from 1941 to 1945 with 2,711 being built.

Gustave F. Perna is a retired United States Army four-star general who last served as the chief operating officer of the federal COVID-19 response for vaccine and therapeutics. He previously served as the chief operating officer of Operation Warp Speed from July 2020 until the operation's duties and responsibilities were transferred to the White House COVID-19 Response Team in February 2021. As chief operating officer of COVID-19 response, he oversaw the logistics in the United States federal government's distribution of the vaccine to the COVID-19 pandemic. The Senate confirmed his nomination as chief operating officer on July 2, 2020, and he assumed the office shortly after.

The Royal New Zealand Army Ordnance Corps (RNZAOC) concerned itself with the provisioning of troops with the means to fight; specifically uniforms, weapons and equipment. Ordnance functions go back hundreds of years; the first Ordnance Officer in the British military appeared in the year 1299. Designated "Keeper of the King's Wardrobe", his duties included the care and accounting of heavy equipment such as battering rams and catapults.
Vocabulary of Army Ordnance Stores (VAOS) was the British Army system of cataloguing parts that started to be superseded in 1956 when the United Kingdom adopted the NATO Codification System.
References
- ↑ DA Supply Catalog SIG 5 FSC GROUP 67 Class 6730 dtd 20 May 1955, however the Wikipedia NSN article says 1953
- ↑ http://www.helpdesk365.org/cataloging.htm NSNs and Cataloging History
- ↑ http://olive-drab.com/od_nsn_explanation.php History of the U.S. Government National Stock Number (NSN)