An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

A Tesla coil is an electrical resonant transformer circuit designed by inventor Nikola Tesla in 1891. It is used to produce high-voltage, low-current, high frequency alternating-current electricity. Tesla experimented with a number of different configurations consisting of two, or sometimes three, coupled resonant electric circuits.

A microphone, colloquially called a mic or mike, is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and public events, motion picture production, live and recorded audio engineering, sound recording, two-way radios, megaphones, and radio and television broadcasting. They are also used in computers for recording voice, speech recognition, VoIP, and for other purposes such as ultrasonic sensors or knock sensors.

A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are separate standalone pieces of equipment, while others are built into the load appliances that they power. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Other functions that power supplies may perform include limiting the current drawn by the load to safe levels, shutting off the current in the event of an electrical fault, power conditioning to prevent electronic noise or voltage surges on the input from reaching the load, power-factor correction, and storing energy so it can continue to power the load in the event of a temporary interruption in the source power.

A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the potential difference between the conductors exceeds the breakdown voltage of the gas within the gap, a spark forms, ionizing the gas and drastically reducing its electrical resistance. An electric current then flows until the path of ionized gas is broken or the current reduces below a minimum value called the "holding current". This usually happens when the voltage drops, but in some cases occurs when the heated gas rises, stretching out and then breaking the filament of ionized gas. Usually, the action of ionizing the gas is violent and disruptive, often leading to sound, light and heat.
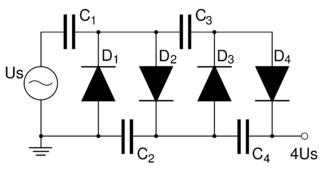
A voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit that converts AC electrical power from a lower voltage to a higher DC voltage, typically using a network of capacitors and diodes.
An integrator in measurement and control applications is an element whose output signal is the time integral of its input signal. It accumulates the input quantity over a defined time to produce a representative output.

An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements.

A variable capacitor is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically. Variable capacitors are often used in L/C circuits to set the resonance frequency, e.g. to tune a radio, or as a variable reactance, e.g. for impedance matching in antenna tuners.

Capacitors are manufactured in many forms, styles, lengths, girths, and from many materials. They all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by an insulating layer. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices.

A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.

A test probe is a physical device used to connect electronic test equipment to a device under test (DUT). Test probes range from very simple, robust devices to complex probes that are sophisticated, expensive, and fragile. Specific types include test prods, oscilloscope probes and current probes. A test probe is often supplied as a test lead, which includes the probe, cable and terminating connector.

Capacitor discharge ignition (CDI) or thyristor ignition is a type of automotive electronic ignition system which is widely used in outboard motors, motorcycles, lawn mowers, chainsaws, small engines, turbine-powered aircraft, and some cars. It was originally developed to overcome the long charging times associated with high inductance coils used in inductive discharge ignition (IDI) systems, making the ignition system more suitable for high engine speeds. The capacitive-discharge ignition uses capacitor discharge current to the coil to fire the spark plugs.

A ceramic capacitor is a fixed-value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric. It is constructed of two or more alternating layers of ceramic and a metal layer acting as the electrodes. The composition of the ceramic material defines the electrical behavior and therefore applications. Ceramic capacitors are divided into two application classes:

A variety of types of electrical transformer are made for different purposes. Despite their design differences, the various types employ the same basic principle as discovered in 1831 by Michael Faraday, and share several key functional parts.

Capacitors have many uses in electronic and electrical systems. They are so ubiquitous that it is rare that an electrical product does not include at least one for some purpose.

A halo antenna, or halo, is a 1 /2 wavelength dipole antenna, which has been bent into a circle with an electrical break directly opposite the feed point. The dipole ends are close but do not meet, and may have an air capacitor between them to adjust the antenna's resonant frequency. If mounted horizontally, this antenna's radiation is approximately omnidirectional and horizontally polarized.

Film capacitors, plastic film capacitors, film dielectric capacitors, or polymer film capacitors, generically called film caps as well as power film capacitors, are electrical capacitors with an insulating plastic film as the dielectric, sometimes combined with paper as carrier of the electrodes.
This glossary of electrical and electronics engineering is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related specifically to electrical engineering and electronics engineering. For terms related to engineering in general, see Glossary of engineering.