
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida.

Charales is an order of freshwater green algae in the division Charophyta, class Charophyceae, commonly known as stoneworts. Depending on the treatment of the genus Nitellopsis, living (extant) species are placed into either one family (Characeae) or two. Further families are used for fossil members of the order. Linnaeus established the genus Chara in 1753.

Characeae is a family of freshwater green algae in the order Charales, commonly known as stoneworts. They are also known as brittleworts or skunkweed, from the fragility of their lime-encrusted stems, and from the foul odor these produce when stepped on.
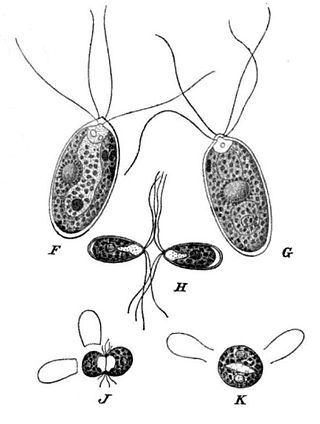
Carteria is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. Carteria are similar in morphology to the common genus Chlamydomonas and differ by having four, rather than two, flagella at the vegetative stage.

Hormotila is a genus of green algae in the family Chaetophoraceae.
Pseudochlorella signiensis is a species of green algae in the family Koliellaceae. Pabia signiensis, the only species in the genus Pabia, is regarded as a synonym. Pabia was sunk into Pseudochlorella in 2016.
Bracteacoccus helveticus is a species of green algae, in the family Bracteacoccaceae. Under its synonym Cryococcus helveticus, it was the only species in the genus Cryococcus.

Sykidion is a genus of green algae. Pseudoneochloris is a synonym of this genus. As of March 2022, Sykidion was the only genus in the family Sykidiacaeae, which was the only family in the order Sykidiales.

The Rivulariaceae are a family of cyanobacteria within the Nostocales in which the filaments (trichomes) are tapered from wider at the base to narrower at the tip.
Sycidiales is an order of fossil charophyte green algae. The reproductive structures in Sycidales have a calcified cover, called a utricle, that is thought to prevent the zygote being desiccated. Other Paleozoic families lack this cover, as do modern charophytes. Fossils of the family Sycidiaceae are found over the longest time span, from the Silurian to the Carboniferous.
Trochiliscaceae is a family of fossil charophyte green algae. It is the only member of the order Trochiliscales. The reproductive structures in Trochiliscaceae have a calcified cover, called a utricle, that is thought to prevent the zygote being desiccated. Other Paleozoic families lack this cover, as do modern charophytes. Fossils of Trochiliscaceae are from the Devonian.







