Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida.

Charales is an order of freshwater green algae in the division Charophyta, class Charophyceae, commonly known as stoneworts. Depending on the treatment of the genus Nitellopsis, living (extant) species are placed into either one family (Characeae) or two. Further families are used for fossil members of the order. Linnaeus established the genus Chara in 1753.

Charophyta is a group of freshwater green algae, called charophytes, sometimes treated as a division, yet also as a superdivision or an unranked clade. The terrestrial plants, the Embryophyta emerged deep within Charophyta, possibly from terrestrial unicellular charophytes, with the class Zygnematophyceae as a sister group.

Adrien René Franchet was a French botanist, based at the Paris Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle.

Toussidé is a potentially active stratovolcano in Chad. Toussidé lies in the Tibesti Mountains, the large Yirrigué caldera and the smaller Trou au Natron and Doon Kidimi craters are close to it. It has an elevation of 3,265 m (10,712 ft) above sea level. The volcano is the source of a number of lava flows, which have flowed westward away from Toussidé and east into the Yirrigué caldera.

Characeae is a family of freshwater green algae in the order Charales, commonly known as stoneworts. They are also known as brittleworts or skunkweed, from the fragility of their lime-encrusted stems, and from the foul odor these produce when stepped on.

Miacidae is a former paraphyletic family of extinct primitive placental mammals that lived in North America, Europe and Asia during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs, about 65–33.9 million years ago. These mammals were basal to order Carnivora, the crown-group within the Carnivoraformes.
The Tetrasporales are a formerly recognized order of green algae, specifically the Chlorophyceae, now included in Chlamydomonadales. AlgaeBase places Tetraspora and Tetrasporaceae in Chlamydomonadales.

Hormotila is a genus of green algae in the family Chaetophoraceae.
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms.

The Scalopinae, or New World moles, are one of three subfamilies of the family Talpidae, which consists of moles and mole-like animals; the other two subfamilies being the Old World talpids and the Chinese shrew-like moles (Uropsilinae). The Scalopinae are the only Talpidae subfamily to consist entirely of undisputed moles and no mole-like close relatives such as shrew-moles or desmans.
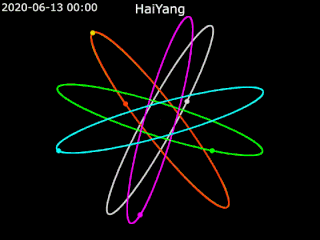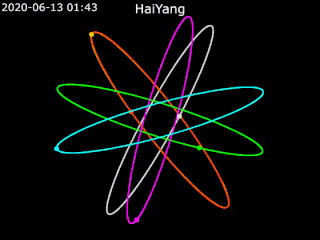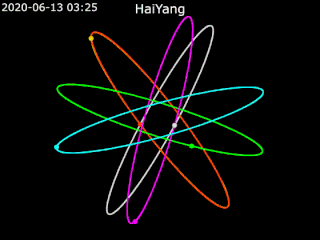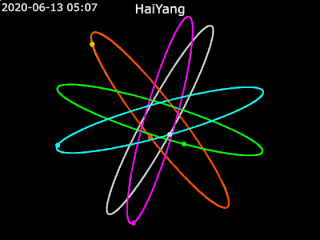
Haiyang is a series of marine remote sensing satellites developed and operated by the People's Republic of China since 2002. As of October 2022, eight satellites have been launched with ten more planned. Built by the state-owned aerospace contractor China Academy of Space Technology (CAST), Haiyang satellites carry a variety of ocean-imaging sensor payloads and are operated by the National Satellite Ocean Application Service (NSOAS), a subordinate agency of the State Oceanic Administration (SOA). Haiyang satellites are launched from Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center (TSLC) into Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO) aboard Long March-series rockets.

Baiera is a genus of prehistoric gymnosperms in the order Ginkgoales. It is one of the oldest fossil foliage types of Ginkgoales, and is related to the genera Ginkgo and Ginkgoites. Fossils of Baiera are found worldwide, and have been known from the Permian to the Cretaceous.

Callithamniaceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Ceramiales. The family was first described by Friedrich Traugott Kützing in 1843.

Tolypella is a genus of green algae belonging to the family Characeae.

Feistiellaceae is a family of freshwater green algae in the order Charales.

Willeya is a genus of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), crustose lichens in the family Verrucariaceae. It has 12 species. Most species are found in southeast Asia, although individual representatives are known from Australia, Europe, and North America.

Halymeniales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae.

Daohugouthallus is an extinct genus of lichen which was found in the Jurassic Haifanggou Formation near Daohugou village, Ningcheng County, China. It contains a single species, D. ciliiferus, and while it is considered to be most closely related to Parmeliaceae, a monogeneric family Daohugouthallaceae has been proposed. This macrolichen has been dated at approximately 165 Ma. It is thought that D. ciliiferus was a gymnosperm epiphyte and thus the earliest fossil example of an epiphytic macrolichen.
















