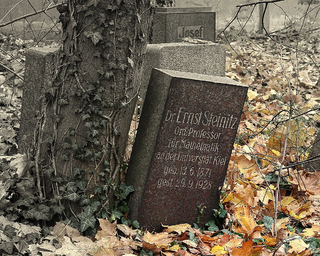Niels Henrik Abel was a Norwegian mathematician who made pioneering contributions in a variety of fields. His most famous single result is the first complete proof demonstrating the impossibility of solving the general quintic equation in radicals. This question was one of the outstanding open problems of his day, and had been unresolved for over 250 years. He was also an innovator in the field of elliptic functions and the discoverer of Abelian functions. He made his discoveries while living in poverty and died at the age of 26 from tuberculosis.

Felix Christian Klein was a German mathematician and mathematics educator, known for his work in group theory, complex analysis, non-Euclidean geometry, and the associations between geometry and group theory. His 1872 Erlangen program classified geometries by their basic symmetry groups and was an influential synthesis of much of the mathematics of the time.

Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riemann was a German mathematician who made profound contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry. In the field of real analysis, he is mostly known for the first rigorous formulation of the integral, the Riemann integral, and his work on Fourier series. His contributions to complex analysis include most notably the introduction of Riemann surfaces, breaking new ground in a natural, geometric treatment of complex analysis. His 1859 paper on the prime-counting function, containing the original statement of the Riemann hypothesis, is regarded as a foundational paper of analytic number theory. Through his pioneering contributions to differential geometry, Riemann laid the foundations of the mathematics of general relativity. He is considered by many to be one of the greatest mathematicians of all time.

Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi was a German mathematician who made fundamental contributions to elliptic functions, dynamics, differential equations, determinants, and number theory.

Leopold Kronecker was a German mathematician who worked on number theory, algebra and logic, and criticized Georg Cantor's work on set theory. Heinrich Weber quoted Kronecker as having said, "Die ganzen Zahlen hat der liebe Gott gemacht, alles andere ist Menschenwerk" . Kronecker was a student and life-long friend of Ernst Kummer.

Ferdinand Georg Frobenius was a German mathematician, best known for his contributions to the theory of elliptic functions, differential equations, number theory, and to group theory. He is known for the famous determinantal identities, known as Frobenius–Stickelberger formulae, governing elliptic functions, and for developing the theory of biquadratic forms. He was also the first to introduce the notion of rational approximations of functions, and gave the first full proof for the Cayley–Hamilton theorem. He also lent his name to certain differential-geometric objects in modern mathematical physics, known as Frobenius manifolds.

Carl Wilhelm Borchardt was a German mathematician.

Franz Ernst Neumann was a German mineralogist and physicist.

Crelle's Journal, or just Crelle, is the common name for a mathematics journal, the Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik.

Abraham Geiger was a German rabbi and scholar who is considered the founding father of Reform Judaism and the academic field of Quranic studies. Emphasizing Judaism's constant development through its history and universalist traits, Geiger sought to re-formulate received forms and design what he regarded as a religion compliant with modern times.

Ferdinand Gotthold Max Eisenstein was a German mathematician who made significant contributions to number theory and analysis. Born in Berlin, Prussia, to Jewish parents who converted to Protestantism before his birth, Eisenstein displayed exceptional mathematical talent from a young age.

Kurt Wilhelm Sebastian Hensel was a German mathematician born in Königsberg.

Maxime Bôcher was an American mathematician who published about 100 papers on differential equations, series, and algebra. He also wrote elementary texts such as Trigonometry and Analytic Geometry. Bôcher's theorem, Bôcher's equation, and the Bôcher Memorial Prize are named after him.
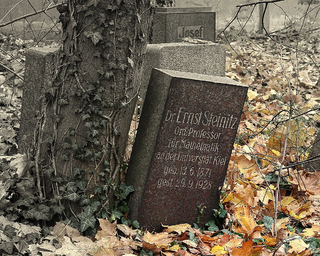
Ernst Steinitz was a German mathematician.

Arthur Korn was a German physicist, mathematician and inventor. He was involved in the development of the fax machine, specifically the transmission of photographs or telephotography, known as the Bildtelegraph, related to early attempts at developing a practical mechanical television system.

Gabriel Gustav Valentin, also Gabriel Valentin, was a German physiologist and professor of physiology at the University of Bern.

Levi Herzfeld was a German rabbi and historian.
Ferdinand Falkson was a German physician and political writer. Born in Königsberg, he was educated at the universities of Königsberg, Berlin, and Halle, graduating from the first-named as M.D. in 1843. In the same year he engaged in practice in his native city, and in 1844 was appointed physician to the poor of the Jewish community, a position which he held until his death.

Ludwig Schlesinger, was a German mathematician known for the research in the field of linear differential equations.

Ernst Ferdinand Peschl was a German mathematician.