This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |

This article may be expanded with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (September 2011)Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Ferdinand Weerth (1 June 1774 in Gemarke – 18 October 1836 in Detmold) was a German pastor and school-reformer in the Principality of Lippe. Between 1805 and 1836 he officiated as the general superintendent (spiritual leader) of the Reformed Church of Lippe . [1] One of his sons was the writer Georg Weerth.
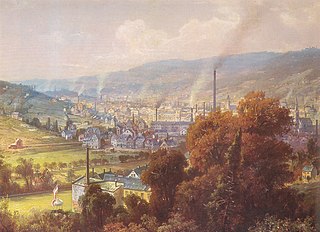
Barmen is a former industrial metropolis of the region of Bergisches Land, Germany, which merged with four other towns in 1929 to form the city of Wuppertal. Barmen was the birthplace of Friedrich Engels and together with the neighbouring town of Elberfeld founded the first electric suspended monorail tramway system, the Schwebebahn floating tram. Barmen was a pioneering centre for both the early industrial revolution on the European mainland, and for the socialist movement and its theory. It was the location of one of the first concentration camps in Nazi Germany, KZ Wuppertal-Barmen, later better known as Kemna concentration camp.

Detmold is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, with a population of about 73,400 (2013). It was the capital of the small Principality of Lippe from 1468 until 1918 and then of the Free State of Lippe until 1947. Today it is the administrative center of the district of Lippe and of the Regierungsbezirk Detmold. The Church of Lippe has its central administration located in Detmold. The Reformed Redeemer Church is the preaching venue of the state superintendent of the Lippe church.

Lippe was a historical state in Germany, ruled by the House of Lippe. It was located between the Weser River and the southeast part of the Teutoburg forest.