Related Research Articles

The country of Brazil occupies roughly half of South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean. Brazil covers a total area of 8,514,215 km2 (3,287,357 sq mi) which includes 8,456,510 km2 (3,265,080 sq mi) of land and 55,455 km2 (21,411 sq mi) of water. The highest point in Brazil is Pico da Neblina at 2,994 m (9,823 ft). Brazil is bordered by the countries of Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela, and France.

Mato Grosso is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP.

Mato Grosso do Sul is one of the Midwestern states of Brazil. Neighboring Brazilian states are Mato Grosso, Goiás, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Paraná. It also borders the countries of Paraguay, to the southwest, and Bolivia, to the west. The economy of the state is largely based on agriculture and cattle-raising. Crossed in the south by the Tropic of Capricorn, Mato Grosso do Sul generally has a warm, sometimes hot, and humid climate, and is crossed by numerous tributaries of the Paraná River. The state has 1.3% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.5% of the Brazilian GDP.
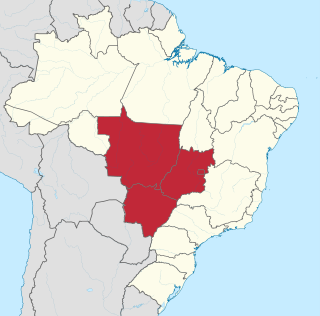
The Central-West or Center-West Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul; along with Distrito Federal, where Brazil's national capital, Brasília, is situated. The region comprises 18.86% of the national territory.

Sinop is a city in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso. The fourth-largest city in the state, its population in 2020 is estimated at more than 199,680 inhabitants, placing Sinop in 229th place in Brazil. It has an area of 3194.339 km ². A Sivam radar has been installed for monitoring the Amazon Basin. Also Embrapa has a branch in Sinop, the only one in the state of Mato Grosso. It is known as the Capital of Nortão, a major city of northern Mato Grosso.

Time in Brazil is calculated using standard time, and the country is divided into four standard time zones: UTC−02:00, UTC−03:00, UTC−04:00 and UTC−05:00.
The Panará are an Indigenous people of Mato Grosso in the Brazilian Amazon. They farm and are hunter-gatherers.
The Xingu Indigenous Park is an indigenous territory of Brazil, first created in 1961 as a national park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Its official purposes are to protect the environment and the several tribes of Xingu indigenous peoples in the area.
The Yudjá or Juruna are an Indigenous people of Brazil. They were formerly the major tribe along the Xingu River, but are now divided into two groups, a westernized northern group near Altamira, Para near the big bend of the Xingu and a more conservative group in the Xingu Indigenous Park at the headwaters of the Xingu in Mato Grosso. The southern group lives in two villages located near the mouth of the Maritsauá-Mitau River. They fish and raise crops, such as manioc.
The Culuene River, or Kuluene River is a 600 km tributary of Xingu River in Mato Grosso, a state in western Brazil. The main economic activities in the region are agriculture and cattle farming.
The Curisevo River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil. It flows through the Xingu Indigenous Park.
The Ronuro River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil, a tributary of the Xingu River.
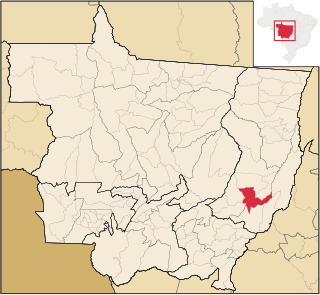
Nova Xavantina is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil. Located in the Legal Amazon and the Araguaia Valley, the Rio das Mortes runs through the center of the municipality. Founded in 1980, today Nova Xavantina serves as an agricultural center, the location of a campus of the State University of Mato Grosso (Unemat), and a tourist destination.

Santa Cruz do Xingu is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil.

São José do Xingu is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso, in the Central-West Region of Brazil.

Raoni Metuktire, also known as Chief Raoni or Ropni, is an Indigenous Brazilian leader and environmentalist. He is a chief of the Kayapo people, a Brazilian Indigenous group from the plain lands of the Mato Grosso and Pará in Brazil, south of the Amazon River and along Xingu River and its tributaries. He is internationally famous as a living symbol of the fight for the preservation of the Amazon rainforest and indigenous culture.

The Campos Amazônicos National Park is a National park in the states of Rondônia, Amazonas and Mato Grosso, Brazil.

The Mato Grosso tropical dry forests (NT0140), also called the Mato Grosso seasonal forests, is an ecoregion in central Brazil to the south of the Amazon region. It contains vegetation in the transition between the Amazon rainforest to the north and the cerrado savanna to the south. The opening of highways through the region has caused rapid population growth, deforestation and pollution.
The Bakairi are an indigenous people of Brazil. They speak the Bakairi language, one of the Cariban languages. They call themselves Kurâ, Bakairi being a Portuguese term of unknown origin. They currently live in the Santana and Bakairi Indigenous Territories of northern Mato Grosso, in the municipality of Paranatinga in the northern cerrado south of the Amazon rain forest. Like most native peoples, they were more numerous before European contact. In 1999 there were about 950 Bakairi, of whom 898 lived in the two Indigenous Territories. In 1965 only 261 were recorded.
Farlowella gianetii is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the upper Xingu River basin in the state of Mato Grosso in Brazil. The species reaches at least 12.1 cm in standard length. It was described in 2016 by Gustavo A. Ballen, Murino N. L. Pastana, and Luiz Peixoto. Its specific name, gianetii, honors Dr. Michel Donato Gianeti, manager of the ichthyological collections of the University of São Paulo. FishBase does not yet list this species.
References
Coordinates: 12°27′13″S54°31′53″W / 12.45361°S 54.53139°W