Related Research Articles

Vortigern, also spelled Vortiger, Vortigan, Voertigern and Vortigen, was a 5th-century warlord in Britain, known perhaps as a king of the Britons or at least connoted as such in the writings of Bede and Gildas. His existence is contested by scholars and information about him is obscure.

Gruffudd ap Cynan was King of Gwynedd from 1081 until his death in 1137. In the course of a long and eventful life, he became a key figure in Welsh resistance to Norman rule.
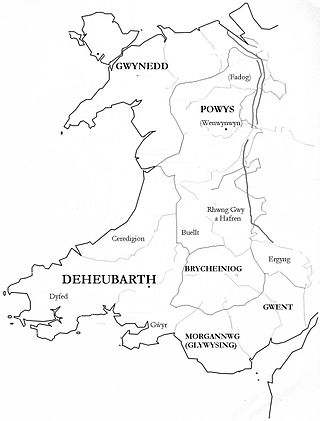
Deheubarth was a regional name for the realms of south Wales, particularly as opposed to Gwynedd. It is now used as a shorthand for the various realms united under the House of Dinefwr, but that Deheubarth itself was not considered a proper kingdom on the model of Gwynedd, Powys, or Dyfed is shown by its rendering in Latin as dextralis pars or as Britonnes dexterales and not as a named land. In the oldest British writers, Deheubarth was used for all of modern Wales to distinguish it from Hen Ogledd, the northern lands whence Cunedda originated.

Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda Wledig, was an important early Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the Royal dynasty of Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of Western Europe.

Rhys ap Tewdwr was a king of Deheubarth in Wales and member of the Dinefwr dynasty, a branch descended from Rhodri the Great. Following the Norman Conquest, he had to pay William the Conqueror to keep his kingdom, which lasted until the end of William's reign.
Vortiporius or Vortipor was a king of Dyfed in the early to mid-6th century. He ruled over an area approximately corresponding to modern Pembrokeshire, and Carmarthenshire, Wales. Records from this era are scant, and virtually nothing is known of him or his kingdom. The only contemporary information about Vortiporius comes from the Welsh ecclesiastic Gildas, in a highly allegorical condemnation from his De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae. At the time the work was written, Gildas says that Vortiporius was king of Dyfed, that he was grey with age, that his wife had died, and that he had at least one daughter.

Merfyn Frych, also known as Merfyn ap Gwriad and Merfyn Camwri, was King of Gwynedd from around 825 to 844, the first of its kings known not to have descended from the male line of King Cunedda.
Catigern is a figure of Welsh tradition, said to be a son of Vortigern, the tyrannical King of the Britons, and the brother of Vortimer. A figure of this name also appears in the Welsh genealogies, though he is given different parentage. Catigern is nearly exclusively known for a tradition in which he fell in battle with the Saxons.
Caradog ap Gruffydd was a Prince of Gwent in south-east Wales in the time of Gruffydd ap Llywelyn and the Norman conquest, who reunified his family's inheritance of Morgannwg and made repeated attempts to reunite southern Wales by claiming the inheritance of the Kingdom of Deheubarth.

Brycheiniog was an independent kingdom in South Wales in the Early Middle Ages. It allied with the Mercian kingdom in the post Roman era, to stabilise and control a central (Marches) area key to dominance over central Proto-England to the east and the south Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth to the west. It was conquered and pacified by the Armorican Normans between 1088 and 1095, though it remained Welsh in character. It was transformed into the Lordship of Brecknock and later formed the southern and larger part of the historic county of Brecknockshire. To its south was the Kingdom of Morgannwg.

Gwrtheyrnion or Gwerthrynion was a commote in medieval Wales, located in Mid Wales on the north side of the River Wye; its historical centre was Rhayader. It is said to have taken its name from the legendary king Vortigern. For most of the medieval era, it was associated with the cantref of Buellt and then Elfael, small regional kingdoms whose rulers operated independently of other powers. In the Norman era, like the rest of the region between Wye and Severn it came to be dominated by Marcher Lordships.

Rhwng Gwy a Hafren was a region of medieval Wales, located in the Welsh Marches between Powys to the north and Brycheiniog to the south. It was bounded by the rivers Wye and Severn. It covered about the same territory as Radnorshire, now part of the county of Powys. The region first came into its own in the 9th or 10th centuries, when it was ruled by leaders who operated independently of the surrounding kingdoms. After the Norman invasion, it comprised the central part of the Welsh Marches and was the site of frequent struggles between Welsh and Norman forces.

Ial or Yale was a commote of medieval Wales within the cantref of Maelor in the Kingdom of Powys. When the Kingdom was divided in 1160, Maelor became part of the Princely realm of Powys Fadog, and belonged to the Royal House of Mathrafal. Yale eventually merged with another commote and became the Lordship of Bromfield and Yale, later a royal lordship under the Tudors and Stuarts.

The Royal House of Mathrafal began as a cadet branch of the Welsh Royal House of Dinefwr, taking their name from Mathrafal Castle. They effectively replaced the House of Gwertherion, who had been ruling the Kingdom of Powys since late Roman Britain, through the politically advantageous marriage of an ancestor, Merfyn the Oppressor. King Bleddyn ap Cynfyn would join the resistance of the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, against the invasion of William the Conqueror, following the Norman Conquest of England. Thereafter, they would struggle with the Plantagenets and the remaining Welsh Royal houses for the control of Wales. Although their fortunes rose and fell over the generations, they are primarily remembered as Kings of Powys and last native Prince of Wales.

Buellt or Builth was a cantref in medieval Wales, located west of the River Wye. Unlike most cantrefs, it was not part of any of the major Welsh kingdoms for most of its history, but was instead ruled by an autonomous local dynasty. During the Norman era it was associated with Rhwng Gwy a Hafren, a region independent of the Welsh monarchies and controlled by Norman Marcher Lords. In the 16th century, it was reorganized as a hundred and joined with the former kingdom of Brycheiniog to form the county of Brecknockshire.
Ffernfael ab Idwal or Ithel was a late 8th-century king of Gwent in southeast Wales.
Einion ab Owain was a medieval Welsh prince of the House of Dinefwr. He was the eldest son and probable edling of King Owain of Dyfed, son of Hywel Dda.
The Lordship of Brecknock was an Anglo-Norman marcher lordship located in southern central Wales.
Arthfael ap Rhys was a prince of Glywsing and Gwent in the late eighth century. He is dated by the genealogist Peter Bartrum to c.760.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Lloyd, John Edward (1912). A History of Wales from the Earliest Times to the Edwardian Conquest. Longmans, Green, and Co. p. 224 and note. Retrieved 6 November 2009.
- 1 2 Todd, James H. & al. (trans.) (1848), Leabhar breathnach annso sis: the Irish version of the Historia Britonum of Nennius , p. 105. Irish Archaeological Society (Dublin), 1848. Accessed February 22, 2013.
- ↑ Rhys, John. Y Cymmrodor, Vol. XVIII. "The Origin of the Welsh Englyn and Kindred Metres". 1905. Accessed 11 Feb 2013.
- ↑ Charles-Edwards, T. Wales and the Britons, 350-1064 , Vol. 1. Oxford Univ. Press, 2012. Accessed 12 Feb 2013.
- ↑ Dumville, David (1992). "The Historical Value of the Historia Brittonum". In Barber, Richard (ed.). Arthurian Literature. Vol. VI. Boydell & Brewer Ltd. p. 21. ISBN 0859912264 . Retrieved 13 February 2012.
- ↑ Thornton, David (2003). "Fratricide, Filacentricity, and the Rise of the Second Dynasty of Gwynedd". Kings, Chronicles and Genealogies: Studies in the Political History of Early Medieval Ireland and Wales. Unit for Prosopographical Research, Linacre College, Oxford. p. 114 and note. ISBN 1900934094 . Retrieved 13 February 2012.