
Fibronectin is a high-molecular weight glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans.

Plasmin is an important enzyme present in blood that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin clots. The degradation of fibrin is termed fibrinolysis. In humans, the plasmin protein is encoded by the PLG gene.

Urokinase, also known as urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), is a serine protease present in humans and other animals. The human urokinase protein was discovered, but not named, by McFarlane and Pilling in 1947. Urokinase was originally isolated from human urine, and it is also present in the blood and in the extracellular matrix of many tissues. The primary physiological substrate of this enzyme is plasminogen, which is an inactive form (zymogen) of the serine protease plasmin. Activation of plasmin triggers a proteolytic cascade that, depending on the physiological environment, participates in thrombolysis or extracellular matrix degradation. This cascade had been involved in vascular diseases and cancer progression.

Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major constituents of the basement membrane, namely the basal lamina. Laminins are vital to biological activity, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion.

Kringle domains are autonomous protein domains that fold into large loops stabilized by 3 disulfide linkages. These are important in protein–protein interactions with blood coagulation factors. Their name refers to the Kringle, a Scandinavian pastry which they somewhat resemble.

The low-density lipoprotein receptor gene family codes for a class of structurally related cell surface receptors that fulfill diverse biological functions in different organs, tissues, and cell types. The role that is most commonly associated with this evolutionarily ancient family is cholesterol homeostasis. In humans, excess cholesterol in the blood is captured by low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and removed by the liver via endocytosis of the LDL receptor. Recent evidence indicates that the members of the LDL receptor gene family are active in the cell signalling pathways between specialized cells in many, if not all, multicellular organisms.
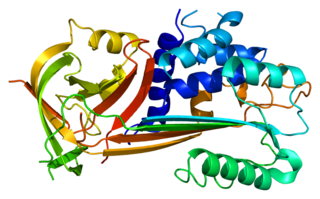
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-2, a serine protease inhibitor of the serpin superfamily, is a coagulation factor that inactivates tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase. It is present in most cells, especially monocytes/macrophages. PAI-2 exists in two forms, a 60-kDa extracellular glycosylated form and a 43-kDa intracellular form.

Matrilysin also known as matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7), pump-1 protease (PUMP-1), or uterine metalloproteinase is an enzyme in humans that is encoded by the MMP7 gene. The enzyme has also been known as matrin, putative metalloproteinase-1, matrix metalloproteinase pump 1, PUMP-1 proteinase, PUMP, metalloproteinase pump-1, putative metalloproteinase, MMP). Human MMP-7 has a molecular weight around 30 kDa.
Platelet membrane glycoproteins are surface glycoproteins found on platelets (thrombocytes) which play a key role in hemostasis. When the blood vessel wall is damaged, platelet membrane glycoproteins interact with the extracellular matrix.

Fibrinogen alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGA gene.

Tenascin C (TN-C) is a glycoprotein that in humans is encoded by the TNC gene. It is expressed in the extracellular matrix of various tissues during development, disease or injury, and in restricted neurogenic areas of the central nervous system. Tenascin-C is the founding member of the tenascin protein family. In the embryo it is made by migrating cells like the neural crest; it is also abundant in developing tendons, bone and cartilage.

The EGF-like domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain, which derives its name from the epidermal growth factor where it was first described. It comprises about 30 to 40 amino-acid residues and has been found in a large number of mostly animal proteins. Most occurrences of the EGF-like domain are found in the extracellular domain of membrane-bound proteins or in proteins known to be secreted. An exception to this is the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase. The EGF-like domain includes 6 cysteine residues which in the epidermal growth factor have been shown to form 3 disulfide bonds. The structures of 4-disulfide EGF-domains have been solved from the laminin and integrin proteins. The main structure of EGF-like domains is a two-stranded β-sheet followed by a loop to a short C-terminal, two-stranded β-sheet. These two β-sheets are usually denoted as the major (N-terminal) and minor (C-terminal) sheets. EGF-like domains frequently occur in numerous tandem copies in proteins: these repeats typically fold together to form a single, linear solenoid domain block as a functional unit.
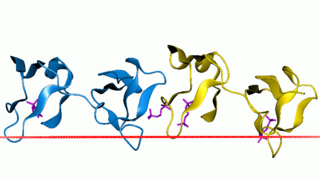
Fibronectin type II domain is a collagen-binding protein domain. Fibronectin is a multi-domain glycoprotein, found in a soluble form in plasma, and in an insoluble form in loose connective tissue and basement membranes, that binds cell surfaces and various compounds including collagen, fibrin, heparin, DNA, and actin. Fibronectins are involved in a number of important functions e.g., wound healing; cell adhesion; blood coagulation; cell differentiation and migration; maintenance of the cellular cytoskeleton; and tumour metastasis. The major part of the sequence of fibronectin consists of the repetition of three types of domains, which are called type I, II, and III.
Potato carboxypeptidase inhibitor (PCI) is a naturally occurring protease inhibitor peptide in potatoes that can form complexes with several metallo-carboxypeptidases, inhibiting them in a strong competitive way with a Ki in the nanomolar range.a
PCI consists of 39 amino acids forming a 27-residue globular core stabilized by three disulfide bridges and a C-terminal tail with residues 35–39. PCI contains a small cysteine-rich module, called a T-knot scaffold, that is shared by several different protein families, including the EGF family.a
Angiogenesis is the process of forming new blood vessels from existing blood vessels, formed in vasculogenesis. It is a highly complex process involving extensive interplay between cells, soluble factors, and the extracellular matrix (ECM). Angiogenesis is critical during normal physiological development, but it also occurs in adults during inflammation, wound healing, ischemia, and in pathological conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, hemangioma, and tumor growth. Proteolysis has been indicated as one of the first and most sustained activities involved in the formation of new blood vessels. Numerous proteases including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), a disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain (ADAM), a disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain with throbospondin motifs (ADAMTS), and cysteine and serine proteases are involved in angiogenesis. This article focuses on the important and diverse roles that these proteases play in the regulation of angiogenesis.

The Fibronectin type III domain is an evolutionarily conserved protein domain that is widely found in animal proteins. The fibronectin protein in which this domain was first identified contains 16 copies of this domain. The domain is about 100 amino acids long and possesses a beta sandwich structure. Of the three fibronectin-type domains, type III is the only one without disulfide bonding present. Fibronectin domains are found in a wide variety of extracellular proteins. They are widely distributed in animal species, but also found sporadically in yeast, plant and bacterial proteins.
Sushi domain is an evolutionarily conserved protein domain. It is also known as complement control protein (CCP) modules or short consensus repeats (SCR). The name derives from the visual similarity of the domain to nigiri sushi when the primary structure is drawn showing the loops created by the disulfide bonds.
SNED1 is an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein expressed at low levels in a wide range of tissues. The gene encoding SNED1 is located in the human chromosome 2 at locus q37.3. The corresponding mRNA isolated from the spleen and is 6834bp in length, and the corresponding protein is 1413 amino-acid long. The mouse ortholog of SNED1 was cloned in 2004 from the embryonic kidney by Leimester et al. SNED1 present domains characteristic of ECM proteins, including an amino-terminal NIDO domain, several calcium binding EGF-like domains (EGF_CA), a Sushi domain also known as complement control protein (CCP) domain, and three type III fibronectin (FN3) domains in the carboxy-terminal region.
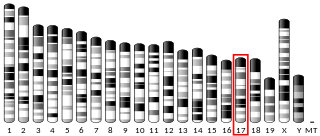
Transmembrane protein 8A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM8A gene (16p13.3.). Evolutionarily, TMEM8A orthologs are found in primates and mammals and in a few more distantly related species. TMEM8A contains five transmembrane domains and one EGF-like domain which are all highly conserved in the ortholog space. Although there is no confirmed function of TMEM8A, through analyzing expression and experimental data, it is predicted that TMEM8A is an adhesion protein that plays a role in keeping T-cells in their resting state.
Megf8 also known as Multiple Epidermal Growth Factor-like Domains 8, is a protein coding gene that encodes a single pass membrane protein, known to participate in developmental regulation and cellular communication. It is located on chromosome 19 at the 49th open reading frame in humans (19q13.2). There are two isoform constructs known for MEGF8, which differ by a 67 amino acid indel. The isoform 2 splice version is 2785 amino acids long, and predicted to be 296.6 kdal in mass. Isoform 1 is composed of 2845 amino acids and predicted to weigh 303.1 kdal. Using BLAST searches, orthologs were found primarily in mammals, but MEGF8 is also conserved in invertebrates and fishes, and rarely in birds, reptiles, and amphibians. A notably important paralog to multiple epidermal growth factor-like domains 8 is ATRNL1, which is also a single pass transmembrane protein, with several of the same key features and motifs as MEGF8, as indicated by Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (SMART) which is hosted by the European Molecular Biology Laboratory located in Heidelberg, Germany. MEGF8 has been predicted to be a key player in several developmental processes, such as left-right patterning and limb formation. Currently, researchers have found MEGF8 SNP mutations to be the cause of Carpenter syndrome subtype 2.















