This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2019) |
Filetab is a decision table-based computer programming language widely used in business in the 1960s and 1970s.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2019) |
Filetab is a decision table-based computer programming language widely used in business in the 1960s and 1970s.
Filetab has a long history, originally designed in the late 1960s and descended from the DETAB programming. Filetab was developed by the National Computing Centre (NCC) [1] and originally used on ICL operating systems such as GEORGE 2/3 and VME, but ported to a large number of others.
The original architect of Filetab was Tom Barnard, who developed the program (LITA - LIst and TAbulate) for Morgan Crucible when employed by them as a programmer on an ICL 1902 from 1965–1968. Its purpose was to produce simple ad hoc reports similar to those created with a plugboard on a punched card tabulator, bypassing the necessity to write an assembly language program in PLAN. It required only a few cards to specify the input and output formats, headings, sequencing and totalling. LITA could not be described as a programming language as it only required run-time parameters indicating field types and locations in records and no compilation. In those days there was no concern by Morgan's regarding ownership or copyright when Barnard left to further develop the software as Filetab.
In 2009 facing financial difficulty NCC sold the rights to Filetab to a newly formed company "NCC Filetab Limited". [2] The Managing Director of NCC Filetab Limited was also the Managing Director of NCC at this time, although NCC Filetab Limited, despite the similarity of its name, was not owned by NCC. In 2010 NCC was declared insolvent and was liquidated.
Versions produced include:
A Linux version was produced in 2001, which although free to use was not Open Source and licensed under the GPL, drawing some criticism from the Open Source Software Community. [4]

Digital Equipment Corporation, using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until he was forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline.
IBM mainframes are large computer systems produced by IBM since 1952. During the 1960s and 1970s, IBM dominated the computer market with the 7000 series and the later System/360, followed by the System/370. Current mainframe computers in IBM's line of business computers are developments of the basic design of the System/360.

A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a type of smaller general-purpose computer developed in the mid-1960s and sold at a much lower price than mainframe and mid-size computers from IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, The New York Times suggested a consensus definition of a minicomputer as a machine costing less than US$25,000, with an input-output device such as a teleprinter and at least four thousand words of memory, that is capable of running programs in a higher level language, such as Fortran or BASIC.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Pascal is an imperative and procedural programming language, designed by Niklaus Wirth as a small, efficient language intended to encourage good programming practices using structured programming and data structuring. It is named after French mathematician, philosopher and physicist Blaise Pascal.

In computing, time-sharing is the sharing of a computing resource among many tasks or users. It enables multi-tasking by a single user or enables multiple-user sessions.

VAX is a series of computers featuring a 32-bit instruction set architecture (ISA) and virtual memory that was developed and sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in the late 20th century. The VAX-11/780, introduced October 25, 1977, was the first of a range of popular and influential computers implementing the VAX ISA. The VAX family was a huge success for DEC, with the last members arriving in the early 1990s. The VAX was succeeded by the DEC Alpha, which included several features from VAX machines to make porting from the VAX easier.

Computer operating systems (OSes) provide a set of functions needed and used by most application programs on a computer, and the links needed to control and synchronize computer hardware. On the first computers, with no operating system, every program needed the full hardware specification to run correctly and perform standard tasks, and its own drivers for peripheral devices like printers and punched paper card readers. The growing complexity of hardware and application programs eventually made operating systems a necessity for everyday use.
DECnet is a suite of network protocols created by Digital Equipment Corporation. Originally released in 1975 in order to connect two PDP-11 minicomputers, it evolved into one of the first peer-to-peer network architectures, thus transforming DEC into a networking powerhouse in the 1980s. Initially built with three layers, it later (1982) evolved into a seven-layer OSI-compliant networking protocol.
A computing platform, digital platform, or software platform is an environment in which software is executed. It may be the hardware or the operating system (OS), a web browser and associated application programming interfaces, or other underlying software, as long as the program code is executed using the services provided by the platform. Computing platforms have different abstraction levels, including a computer architecture, an OS, or runtime libraries. A computing platform is the stage on which computer programs can run.
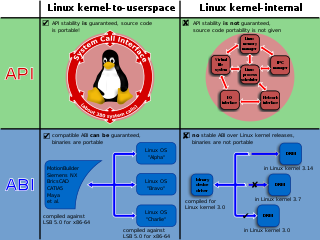
In computing, a system call is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the operating system on which it is executed. This may include hardware-related services, creation and execution of new processes, and communication with integral kernel services such as process scheduling. System calls provide an essential interface between a process and the operating system.
TYPSET is an early document editor that was used with the 1964-released RUNOFF program, one of the earliest text formatting programs to see significant use.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of computer operating systems from 1951 to the current day. For a narrative explaining the overall developments, see the History of operating systems.

International Computers Limited (ICL) was a British computer hardware, computer software and computer services company that operated from 1968 until 2002. It was formed through a merger of International Computers and Tabulators (ICT), English Electric Computers (EEC) and Elliott Automation in 1968. The company's most successful product line was the ICL 2900 Series range of mainframe computers.
DIBOL or Digital's Business Oriented Language is a general-purpose, procedural, imperative programming language that was designed for use in Management Information Systems (MIS) software development. It was developed from 1970 to 1993.
Record Management Services (RMS) are procedures in the VMS, RSTS/E, RT-11 and RSX-11M operating systems that programs may call to process files and records within files. Its file formats and procedures are similar to of those in some IBM access methods for several of its mainframe computer operating systems and by other vendors for file and record management. VMS RMS is an integral part of the system software; its procedures run in executive mode.
ICT 1900 was a family of mainframe computers released by International Computers and Tabulators (ICT) and later International Computers Limited (ICL) during the 1960s and 1970s. The 1900 series was notable for being one of the few non-American competitors to the IBM System/360, enjoying significant success in the European and British Commonwealth markets.
Synergy DBL is a compiled, imperative programming language designed for business use. The language was originally called DBL; later it was referred to as Synergy Language; as of 2012 the official name is Synergy DBL. It is based on Digital Equipment Corporation’s DIBOL programming language.