
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix, known commonly as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He had the distinction of holding the office of consul twice, as well as reviving the dictatorship. Sulla was a skillful general, achieving numerous successes in wars against different opponents, both foreign and Roman. He was awarded a Grass Crown, the most prestigious Roman military honor, during the Social War.

The sablefish is one of two members of the fish family Anoplopomatidae and the only species in the genus Anoplopoma. In English, common names for it include sable (USA), butterfish (USA), black cod, blue cod (UK), bluefish (UK), candlefish (UK), coal cod (UK), coalfish (Canada), beshow, and skil(fish) (Canada), although many of these names also refer to other, unrelated, species. In the US, the FDA accepts only "sablefish" as the Acceptable Market Name; "black cod" is considered a vernacular (regional) name and should not be used as a Statement of Identity for this species. The sablefish is found in muddy sea beds in the North Pacific at depths of 300 to 2,700 m and is commercially important to Japan.
A fimbria is a Latin word that literally means "fringe." It is commonly used in science and medicine, with its meaning depending on the field of study or the context.
Gaius Flavius Fimbria was a Roman politician and a violent partisan of Gaius Marius. He fought in the First Mithridatic War.
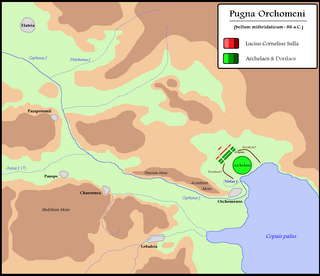
The Battle of Orchomenus was fought in 85 BC between Rome and the forces of Mithridates VI of Pontus. The Roman army was led by Lucius Cornelius Sulla, while Mithridates' army was led by Archelaus. The Roman force was victorious, and Archelaus later defected to Rome. Information on the battle is included in Plutarch's Life of Sulla, chapters 20–21.
Gaius Flavius Fimbria, according to Cicero, rose to the highest honours in the republic through his own merit and talent.

Pitane, near Çandarlı, Turkey, was an ancient Greek town of the ancient region of Aeolis, in Asia Minor.

In the female reproductive system, the fimbria is a fringe of tissue around the ostium of the Fallopian tube, in the direction of the ovary.

The second part of the uterine tube is the infundibulum. It is between the purple ampulla and the fimbriae. The infundibulum terminates with the ostium of Fallopian tube, surrounded by fimbriae, one of which is attached to the ovary. Together, the infundibulum and fimbria find the oocyte after ovulation.
"Tubal Reversal," also called "Tubal Sterilization Reversal," or "Tubal Ligation Reversal," or "Microsurgical Tubal Reanastomosis," is a surgical procedure that can restore fertility to women after a tubal ligation. By rejoining the separated segments of the fallopian tube, tubal reversal can give women the chance to become pregnant again. In some cases, however, the separated segments cannot actually be reattached to each other. In some cases the remaining segment of tube needs to be reimplanted into the uterus. In other cases, when the end of the tube has been removed, a procedure called a neofimbrioplasty must be performed to recreate a functional end of the tube which can then act like the missing fimbria and retrieve the egg that has been released during ovulation.
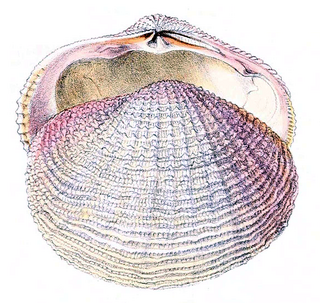
Fimbriidae is a family of saltwater clams. marine bivalve molluscs in the superfamily Lucinoidea. Some modern studies indicate that Fimbriidae should be included in the family Lucinidae. The family contains only one Recent genus, Fimbria, with two known species.

Lucius Valerius Flaccus was the suffect consul who completed the term of Gaius Marius in 86 BC. In the Roman Republic, Marius had fought a series of civil wars against Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix, both leaders of their respective factions. Flaccus was considered a staunch supporter of Marius and Lucius Cornelius Cinna, the latter of whom shared his consulate and succeeded Marius as faction leader.

Tethys fimbria is a species of predatory sea slug, a nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Tethydidae.

Tethys is a genus of sea slugs, nudibranchs, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Tethydidae.
Cavilucina is a genus of bivalves in the family Lucinidae.

Fimbria is a genus of marine bivalve molluscs in the family Lucinidae. Fimbria contains to living species, Fimbria fimbriata and Fimbria soverbii. Several other species are known from fossils.

Prasophyllum fimbria, commonly known as the fringed leek orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a tall orchid with a single smooth, tube-shaped leaf and up to seventy greenish-brown flowers with a white and pink labellum.
Oedura fimbria, also called the western marbled velvet gecko, is a species of geckos endemic to Australia.












