
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix, known commonly as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He had the distinction of holding the office of consul twice, as well as reviving the dictatorship. Sulla was a skillful general, achieving numerous successes in wars against different opponents, both foreign and Roman. He was awarded a Grass Crown, the most prestigious Roman military honor, during the Social War.

The sablefish is one of two members of the fish family Anoplopomatidae and the only species in the genus Anoplopoma. In English, common names for it include sable (USA), butterfish (USA), black cod, blue cod (UK), bluefish (UK), candlefish (UK), coal cod (UK), coalfish (Canada), beshow, and skil(fish) (Canada), although many of these names also refer to other, unrelated, species. In the US, the FDA accepts only "sablefish" as the Acceptable Market Name; "black cod" is considered a vernacular (regional) name and should not be used as a Statement of Identity for this species. The sablefish is found in muddy sea beds in the North Pacific at depths of 300 to 2,700 m and is commercially important to Japan.

The eulachon, also called the candlefish, is a small anadromous ocean fish, a smelt found along the Pacific coast of North America from northern California to Alaska.
A fimbria is a Latin word that literally means "fringe." It is commonly used in science and medicine, with its meaning depending on the field of study or the context.
Gaius Flavius Fimbria was a Roman politician and a violent partisan of Gaius Marius. He fought in the First Mithridatic War.
Gaius Flavius Fimbria, according to Cicero, rose to the highest honours in the republic through his own merit and talent.

Heterodonta is a taxonomic subclass of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs. This subclass includes the edible clams, the cockles and the Venus clams.

In the female reproductive system, the fimbria is a fringe of tissue around the ostium of the Fallopian tube, in the direction of the ovary.

The second part of the uterine tube is the infundibulum. It is between the purple ampulla and the fimbriae. The infundibulum terminates with the ostium of Fallopian tube, surrounded by fimbriae, one of which is attached to the ovary. Together, the infundibulum and fimbria find the oocyte after ovulation.
A dropline is a commercial fishing device, consisting of a long fishing line set vertically down into the water, with a series of fishing hooks attached to snoods.
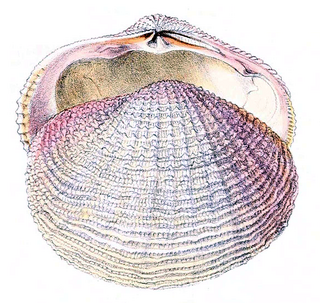
Fimbriidae is a family of saltwater clams. marine bivalve molluscs in the superfamily Lucinoidea. Some modern studies indicate that Fimbriidae should be included in the family Lucinidae. The family contains only one Recent genus, Fimbria, with two known species.

Tethydidae is a family of dendronotid nudibranch gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Tritonioidea.

Vanikoroidea is a superfamily of sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the clade Littorinimorpha. The superfamily Eulimoidea is a synonym of Vanikoroidea.

Tethys fimbria is a species of predatory sea slug, a nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Tethydidae.

Tethys is a genus of sea slugs, nudibranchs, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Tethydidae.
The Blackfin poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae (poachers). It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1890. It is a marine, boreal water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including Komandorski Island and Avachin Bay in Russia, St. Mathew Island in the Bering Sea, and Eureka, California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 18–1290 metres, most often at around 400–700 m, and inhabits soft bottoms. It is known to live for a maximum of 9 years. Males can reach a maximum total length of 24.2 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 20 cm.
Cavilucina is a genus of bivalves in the family Lucinidae.

Fimbria soverbii is a species of marine clams in the family Fimbriidae.

Prasophyllum fimbria, commonly known as the fringed leek orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a tall orchid with a single smooth, tube-shaped leaf and up to seventy greenish-brown flowers with a white and pink labellum.
Oedura fimbria, also called the western marbled velvet gecko, is a species of geckos endemic to Australia.













