
The gallon is a unit of volume in British imperial units and United States customary units. Three different versions are in current use:

The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments.

The kilogram is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo colloquially. It means 'one thousand grams'.
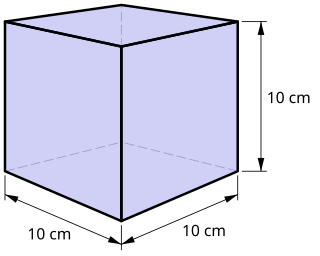
The litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metres (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.

The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in both the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. Various definitions have been used; the most common today is the international avoirdupois pound, which is legally defined as exactly 0.45359237 kilograms, and which is divided into 16 avoirdupois ounces. The international standard symbol for the avoirdupois pound is lb; an alternative symbol is lbm, #, and ℔ or ″̶.

United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and most U.S. territories, since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system developed from English units that were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. The United Kingdom's system of measures was overhauled in 1824 to create the imperial system, which was officially adopted in 1826, changing the definitions of some of its units. Consequently, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their imperial counterparts, there are noticeable differences between the systems.

In recipes, quantities of ingredients may be specified by mass, by volume, or by count.

A peck is an imperial and United States customary unit of dry volume, equivalent to 2 dry gallons or 8 dry quarts or 16 dry pints. An imperial peck is equivalent to 9.09 liters and a US customary peck is equivalent to 8.81 liters. Two pecks make a kenning (obsolete), and four pecks make a bushel. Although the peck is no longer widely used, some produce, such as apples, are still often sold by the peck in the U.S..

The pint is a unit of volume or capacity in both the imperial and United States customary measurement systems. In both of those systems it is traditionally one eighth of a gallon. The British imperial pint is about 20% larger than the American pint because the two systems are defined differently. Almost all other countries have standardized on the metric system, so although some of them still also have traditional units called pints, the volume varies by regional custom.

A fluid ounce is a unit of volume typically used for measuring liquids. The British Imperial, the United States customary, and the United States food labeling fluid ounce are the three that are still in common use, although various definitions have been used throughout history.

A bushel is an imperial and US customary unit of volume based upon an earlier measure of dry capacity. The old bushel is equal to 2 kennings (obsolete), 4 pecks, or 8 dry gallons, and was used mostly for agricultural products, such as wheat. In modern usage, the volume is nominal, with bushels denoting a mass defined differently for each commodity.

The stone or stone weight is an English and British imperial unit of mass equal to 14 avoirdupois pounds (6.35 kg). The stone continues in customary use in the United Kingdom and Ireland for body weight.
English units were the units of measurement used in England up to 1826, which evolved as a combination of the Anglo-Saxon and Roman systems of units. Various standards have applied to English units at different times, in different places, and for different applications.
The spread of metrication around the world in the last two centuries has been met with both support and opposition.

Metrication, the process of introducing the metric system of measurement in place of imperial units, has made steady progress in the United Kingdom since the mid-20th century but today remains equivocal and varies by context. Most of government, industry, commerce, and scientific research use the metric system. Imperial units are officially used to specify journey distances, vehicle speeds and the sizes of returnable milk containers, beer and cider glasses, fresh milk is often still sold in multiples of pints, with the metric equivalent also marked, and precious metals are sold by the troy ounce. Metric units must be used when selling other packaged or loose goods, and imperial units can stand alongside the metric units, but it cannot stand out more than the metric units. Imperial units are also often used to describe body measurements and vehicle fuel economy. The national curriculum requires metric units and imperial units that still remain in common usage to be taught in state schools.

The cup is a cooking measure of volume, commonly associated with cooking and serving sizes. In the US, it is traditionally equal to one-half US pint (236.6 ml). Because actual drinking cups may differ greatly from the size of this unit, standard measuring cups may be used, with a metric cup being 250 millilitres.

Scottish or Scots units of measurement are the weights and measures peculiar to Scotland which were nominally replaced by English units in 1685 but continued to be used in unofficial contexts until at least the late 18th century. The system was based on the ell, stone, and boll and firlot. This official system coexisted with local variants, especially for the measurement of land area.

Weights and Measures Acts are acts of the British Parliament determining the regulation of weights and measures. It also refers to similar royal and parliamentary acts of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland and the medieval Welsh states. The earliest of these were originally untitled but were given descriptive glosses or titles based upon the monarch under whose reign they were promulgated. Several omnibus modern acts have the short title "Weights and Measures Act" and are distinguished by the year of their enactment.

The imperial and US customary measurement systems are both derived from an earlier English system of measurement which in turn can be traced back to Ancient Roman units of measurement, and Carolingian and Saxon units of measure.
The Exchequer Standards may refer to the set of official English standards for weights and measures created by Queen Elizabeth I, and in effect from 1588 to 1825, when the Imperial units system took effect, or to the whole range of English unit standards maintained by the Court of the Exchequer from the 1200s, or to the physical reference standards physically kept at the Exchequer and used as the legal reference until the such responsibility was transferred in the 1860s, after the Imperial system had been established.

















