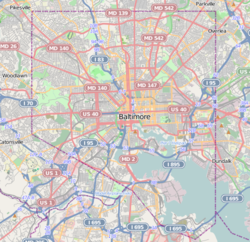
Mount Vernon is a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland, located immediately north of the city's downtown. It is named for George Washington's Mount Vernon estate in Virginia, as the site of the city's Washington Monument.

Virginia Theological Seminary (VTS), formally called the Protestant Episcopal Theological Seminary in Virginia, located at 3737 Seminary Road in Alexandria, Virginia is the largest and second oldest accredited Episcopal seminary in the United States.

Oella is a mill town on the Patapsco River in western Baltimore County, Maryland, United States, located between Catonsville and Ellicott City. It is a 19th-century village of millworkers' homes.

John Rudolph Niernsee was an American architect. He served as the head architect for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. Rudolph also largely contributed to the design and construction of the South Carolina State House located in Columbia, South Carolina. Along with his partner, James Crawford Neilson, Rudolph established the standard for professional design and construction of public works projects within Baltimore and across different states in the United States.

Lansdowne Christian Church was established in 1903 in Lansdowne, Maryland. Part of the Christian Church denomination, Lansdowne Christian Church is located at 101 Clyde Avenue, Lansdowne, Baltimore, Maryland 21227 in southwest Baltimore County, on the southwestern outskirts of the City of Baltimore. Rev. J. B. DeHoff was the first pastor in the early 20th century. The church is currently led by the Rev. Trent Owings.

The former First Church of Christ, Scientist, built in 1939, is an historic Classical revival style Christian Science church edifice located at 501 Riverside Drive, overlooking the Truckee River in Reno, Nevada. Anna Frandsen Loomis, a wealthy local Christian Scientist, underwrote the $120,000 cost of the building, including land acquisition and architect's fees. She was responsible for hiring noted Los Angeles architect Paul Revere Williams, the first African-American member of the AIA. In 1998 the congregation sold the building and used the funds from the sale to construct a new church at 795 West Peckham Lane. Church member and local theater patron Moya Lear donated $1.1 million to the Reno-Sparks Theater Community Coalition, which used the funding to purchase the First Church of Christ, Scientist and renamed it the Lear Theater.

Trinity Church is a historic Episcopal church located at Elkridge, Howard County, Maryland. The post road site was also known as Waterloo, Pierceland, Jessop and Jessup throughout the years.

The Christ Church is a historic Episcopal church located at Port Republic, Calvert County, Maryland, United States. The church is a three-bay-wide, five bays long, beige stucco covered structure featuring stained glass in most of the tall paired round-arched sash windows. It is the mother Episcopal Church of Calvert County and its oldest continually worshipping congregation. Middleham Chapel was started from this congregation as a Chapel of Ease. Christ Church Parish was one of the original 30 Anglican parishes in the Province of Maryland. Burials in the church cemetery include former U. S. Representative Thomas Parran Sr. and United States Coast Guard Admiral Merlin O'Neill.

Middleham Chapel is a historic Episcopal church located in Lusby, Calvert County, Maryland. It is a one-story, cruciform, Flemish bond brick structure with exposed fieldstone foundations. It was built in 1748, to replace an earlier frame or log structure believed to have been erected as early as 1684, as a Chapel of Ease of Christ Church Parish. The date of construction is worked into the brick on the front of the church.

The Epiphany Chapel and Church House is a historic church at Odenton, Anne Arundel County, Maryland, United States. It is a two-story gable-roofed frame building constructed in 1918 and laid out in cruciform plan in the Arts and Crafts style. It is significant for its association with the mobilization of the United States military for World War I, since it was constructed adjacent to Camp Meade, a major training camp for troops bound for the Western Front in Europe. Its design was an early work of the prominent Baltimore architect Riggin T. Buckler (1882-1955) of the partnership/firm of Sill, Buckler & Fenhagen.

St. Ignatius Roman Catholic Church, also known as St. Inigoes Church or The Cove Church, is a historic Catholic parish located in St. Inigoes, St. Mary's County, Maryland. It is a direct descendant of Maryland's first Catholic chapel, in St. Mary's City, whose communicants formed the first nucleus of American Catholicism. The parish fell under the umbrella of the first establishment of religious freedom in America by George Calvert and his sons, who established the Maryland colony as a refuge for persecuted Catholics.

Christ Episcopal Church and Cemetery is an historic Episcopal church and cemetery located at Cambridge, Dorchester County, Maryland, United States.

St. Michael's Church, also known as St. Michael's Chapel and Hannah More Chapel, is a historic Episcopal Church located at Academy Lane and Reisterstown Road in Reisterstown, Baltimore County, Maryland. It is a small, Carpenter Gothic-style, board and batten frame structure, featuring a simple bell-gable. It was designed by New York architect John W. Priest (1825-1859), and constructed about 1853. It was named after Hannah More. It was deconsecrated on May 12, 1978.

Lovely Lane United Methodist Church is a historic United Methodist church at 2200 St. Paul Street in the Charles Village neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland, United States.

Taylor's Chapel is an historic chapel located at Baltimore, Maryland, United States. It is a Greek Revival style chapel located in a quarter acre fenced-in plot, which also includes a graveyard, within Mount Pleasant Park in northeast Baltimore. The structure is a small, mid-19th-century country church, built of stone, covered with stucco, painted white, and has a gable roof. The interior features frescoes on the walls and ceiling, attributed by tradition to the Italian-American painter Constantino Brumidi. The frescoes are trompe-l'œil paintings of classical architectural detailing, including pilasters, panels, coffering, and ornaments. It has remained completely unaltered since its construction in 1853. It was built as a Methodist chapel by the Taylor family on their Mt. Pleasant plantation. In 1925 the City of Baltimore purchased the land surrounding the chapel and burial grounds for use as a public golf course. The site of the chapel and burial grounds was left to a self-perpetuating board of trustees. Taylor's Chapel is considered the mother church of St. John's United Methodist Church of Hamilton.

Holy Cross Roman Catholic Church is a historic Roman Catholic church complex located within the Archdiocese of Baltimore in the Federal Hill neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland, United States.
Charles Emmett Cassell was a Baltimore, Maryland-based architect.

James Crawford Neilson, or J. Crawford Neilson, was a Baltimore, Maryland-based architect. He was born in Baltimore, Maryland in 1816. After the death of his father in 1822 the family moved to England and in 1824 to Brussels. In 1833, he returned to Baltimore and in 1835, became a member of the survey party working on the Baltimore and Port Deposit Railroad,. His supervisor was Benjamin Henry Latrobe, II, (1806-1878), later supervising engineer on the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad,, son of an equally famous architect, Benjamin Henry Latrobe, (1764-1820). It was at this time that he first became acquainted with John Rudolph Niernsee, (1814-1885), while helping to survey in the area of Martinsburg, Virginia, for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad.
The Morgan State University Memorial Chapel, also known as the Student Center for Morgan State College, Morgan Christian Center, Morgan Interfaith Center, and Susie Carr Love Chapel, is a historic building located on the campus of Morgan State University in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. It is significant for its association with the nationally recognized African American architect who designed it, Albert Irvin Cassell. He is noteworthy for his designs for buildings at several Historically Black Colleges and Universities, including other projects at Morgan State. This was the first student center built on campus, and in addition to worship services, the building housed other social activities.