
Seafood is any form of sea life regarded as food by humans, prominently including fish and shellfish. Shellfish include various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Historically, marine mammals such as cetaceans as well as seals have been eaten as food, though that happens to a lesser extent in modern times. Edible sea plants such as some seaweeds and microalgae are widely eaten as sea vegetables around the world, especially in Asia.

Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus Gadus, belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus Gadus is commonly not called cod.

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem — causing declines in some populations.

Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally, resulting in the species becoming increasingly underpopulated in that area. Overfishing can occur in water bodies of any sizes, such as ponds, wetlands, rivers, lakes or oceans, and can result in resource depletion, reduced biological growth rates and low biomass levels. Sustained overfishing can lead to critical depensation, where the fish population is no longer able to sustain itself. Some forms of overfishing, such as the overfishing of sharks, has led to the upset of entire marine ecosystems. Types of overfishing include: growth overfishing, recruitment overfishing, ecosystem overfishing.

The fishing industry includes any industry or activity concerned with taking, culturing, processing, preserving, storing, transporting, marketing or selling fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including recreational, subsistence and commercial fishing, and the related harvesting, processing, and marketing sectors. The commercial activity is aimed at the delivery of fish and other seafood products for human consumption or as input factors in other industrial processes. The livelihood of over 500 million people in developing countries depends directly or indirectly on fisheries and aquaculture.

The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) is a non-profit organization which aims to set standards for sustainable fishing. Fisheries that wish to demonstrate they are well-managed and sustainable compared to the MSC's standards are assessed by a team of Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs).

Seafood Watch is a sustainable seafood advisory list, and has influenced similar programs around the world. It is best known for developing science-based seafood recommendations that consumers, chefs, and business professionals use to inform their seafood purchasing decisions.
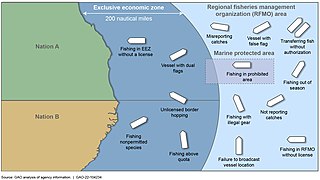
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) is an issue around the world. Fishing industry observers believe IUU occurs in most fisheries, and accounts for up to 30% of total catches in some important fisheries.
Mowi ASA, formerly known as Marine Harvest ASA, , is a Norwegian seafood company with operations in a number of countries around the world. The company's primary interest is fish farming, primarily salmon, the operations of which are focused on Norway, Scotland, Canada, the Faroe Islands, Ireland and Chile. The group has a share of 25 to 30% of the global salmon and trout market, making it the world's largest company in the sector. Mowi also owns a 'value added processing' unit, which prepares and distributes a range of seafood products, and a number of smaller divisions.
Sustainable seafood is seafood that is caught or farmed in ways that consider the long-term vitality of harvested species and the well-being of the oceans, as well as the livelihoods of fisheries-dependent communities. It was first promoted through the sustainable seafood movement which began in the 1990s. This operation highlights overfishing and environmentally destructive fishing methods. Through a number of initiatives, the movement has increased awareness and raised concerns over the way our seafood is obtained.

Canada's fishing industry is a key contributor to the success of the Canadian economy. In 2016, Canada's fishing industry exported $6.6 billion in fish and seafood products and employed approximately 72,000 people in the industry. Aquaculture, which is the farming of fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in fresh or salt water, is the fastest growing food production activity in the world and a growing sector in Canada. In 2015, aquaculture generated over $1 billion in GDP and close to $3 billion in total economic activity. The Department Of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) oversees the management of Canada's aquatic resources and works with fishermen across the country to ensure the sustainability of Canada's oceans and in-land fisheries.

Until the 1960s, agriculture and fishing were the dominant industries of the economy of South Korea. The fishing industry of South Korea depends on the existing bodies of water that are shared between South Korea, China and Japan. Its coastline lies adjacent to the Yellow Sea, the East China Sea and the Sea of Japan, and enables access to marine life such as fish and crustaceans.

China has one-fifth of the world's population and accounts for one-third of the world's reported fish production as well as two-thirds of the world's reported aquaculture production. It is also a major importer of seafood and the country's seafood market is estimated to grow to a market size worth US$53.5 Billion by 2027.

As with other countries, the 200 nautical miles (370 km) exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off the coast of the United States gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 11.4 million square kilometres, which is the second largest zone in the world, exceeding the land area of the United States.

The coastline of the Russian Federation is the fourth longest in the world after the coastlines of Canada, Greenland, and Indonesia. The Russian fishing industry has an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 7.6 million km2 including access to twelve seas in three oceans, together with the landlocked Caspian Sea and more than two million rivers.
Seafood in Australia comes from local and international commercial fisheries, aquaculture and recreational anglers. It is an economically important sector, and along with agriculture and forestry contributed $24,744 million to Australia's GDP in year 2007–2008, out of a total GDP of $1,084,146 million. Commercial fisheries in Commonwealth waters are managed by the Australian Fisheries Management Authority, while commercial and recreational fishing in state waters is managed by various state-level agencies.
Organic aquaculture is a holistic method for farming fish and other marine species in line with organic principles. The ideals of this practice established sustainable marine environments with consideration for naturally occurring ecosystems, use of pesticides, and the treatment of aquatic life. Managing aquaculture organically has become more popular since consumers are concerned about the harmful impacts of aquaculture on themselves and the environment.
Seafood species can be mislabelled in misleading ways. This article examines the history and types of mislabelling, and looks at the current state of the law in different locations.

Spain is an eminently maritime country with a long continental shelf running along the entire periphery of the Spanish coast. This narrow continental shelf is extremely rich in fish resources since the shelf is close to land.
Fish-booking is the process of pre-ordering delivery of freshly caught, unfrozen fish, crustaceans and mollusks of ocean, sea or river origin directly from the fishermen, fisheries using a specialized service aggregator or directly. Fish-booking is adherent to zero waste concept aimed at the reduction and minimization of waste in the areas, where it is possible.














