
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters n and p is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent experiments, each asking a yes–no question, and each with its own Boolean-valued outcome: success or failure. A single success/failure experiment is also called a Bernoulli trial or Bernoulli experiment, and a sequence of outcomes is called a Bernoulli process; for a single trial, i.e., n = 1, the binomial distribution is a Bernoulli distribution. The binomial distribution is the basis for the binomial test of statistical significance.
A likelihood function measures how well a statistical model explains observed data by calculating the probability of seeing that data under different parameter values of the model. It is constructed from the joint probability distribution of the random variable that (presumably) generated the observations. When evaluated on the actual data points, it becomes a function solely of the model parameters.
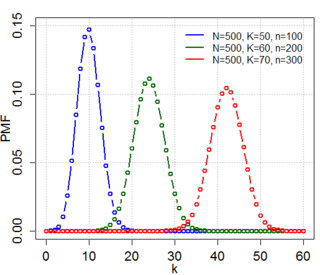
In probability theory and statistics, the hypergeometric distribution is a discrete probability distribution that describes the probability of successes in draws, without replacement, from a finite population of size that contains exactly objects with that feature, wherein each draw is either a success or a failure. In contrast, the binomial distribution describes the probability of successes in draws with replacement.
Pearson's chi-squared test or Pearson's test is a statistical test applied to sets of categorical data to evaluate how likely it is that any observed difference between the sets arose by chance. It is the most widely used of many chi-squared tests – statistical procedures whose results are evaluated by reference to the chi-squared distribution. Its properties were first investigated by Karl Pearson in 1900. In contexts where it is important to improve a distinction between the test statistic and its distribution, names similar to Pearson χ-squared test or statistic are used.

A chi-squared test is a statistical hypothesis test used in the analysis of contingency tables when the sample sizes are large. In simpler terms, this test is primarily used to examine whether two categorical variables are independent in influencing the test statistic. The test is valid when the test statistic is chi-squared distributed under the null hypothesis, specifically Pearson's chi-squared test and variants thereof. Pearson's chi-squared test is used to determine whether there is a statistically significant difference between the expected frequencies and the observed frequencies in one or more categories of a contingency table. For contingency tables with smaller sample sizes, a Fisher's exact test is used instead.
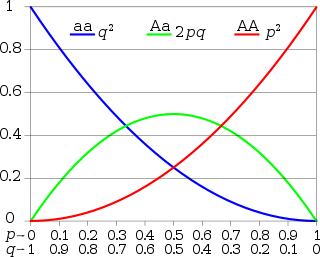
In population genetics, the Hardy–Weinberg principle, also known as the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium, model, theorem, or law, states that allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences. These influences include genetic drift, mate choice, assortative mating, natural selection, sexual selection, mutation, gene flow, meiotic drive, genetic hitchhiking, population bottleneck, founder effect,inbreeding and outbreeding depression.
An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B. The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of event A taking place in the presence of B, and the odds of A in the absence of B. Due to symmetry, odds ratio reciprocally calculates the ratio of the odds of B occurring in the presence of A, and the odds of B in the absence of A. Two events are independent if and only if the OR equals 1, i.e., the odds of one event are the same in either the presence or absence of the other event. If the OR is greater than 1, then A and B are associated (correlated) in the sense that, compared to the absence of B, the presence of B raises the odds of A, and symmetrically the presence of A raises the odds of B. Conversely, if the OR is less than 1, then A and B are negatively correlated, and the presence of one event reduces the odds of the other event occurring.
In statistics, G-tests are likelihood-ratio or maximum likelihood statistical significance tests that are increasingly being used in situations where chi-squared tests were previously recommended.
In statistics, a contingency table is a type of table in a matrix format that displays the multivariate frequency distribution of the variables. They are heavily used in survey research, business intelligence, engineering, and scientific research. They provide a basic picture of the interrelation between two variables and can help find interactions between them. The term contingency table was first used by Karl Pearson in "On the Theory of Contingency and Its Relation to Association and Normal Correlation", part of the Drapers' Company Research Memoirs Biometric Series I published in 1904.
Binomial test is an exact test of the statistical significance of deviations from a theoretically expected distribution of observations into two categories using sample data.
In probability theory, the multinomial distribution is a generalization of the binomial distribution. For example, it models the probability of counts for each side of a k-sided die rolled n times. For n independent trials each of which leads to a success for exactly one of k categories, with each category having a given fixed success probability, the multinomial distribution gives the probability of any particular combination of numbers of successes for the various categories.

The Kruskal–Wallis test by ranks, Kruskal–Wallis test, or one-way ANOVA on ranks is a non-parametric statistical test for testing whether samples originate from the same distribution. It is used for comparing two or more independent samples of equal or different sample sizes. It extends the Mann–Whitney U test, which is used for comparing only two groups. The parametric equivalent of the Kruskal–Wallis test is the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
This glossary of statistics and probability is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in the mathematical sciences of statistics and probability, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. For additional related terms, see Glossary of mathematics and Glossary of experimental design.
A permutation test is an exact statistical hypothesis test making use of the proof by contradiction. A permutation test involves two or more samples. The null hypothesis is that all samples come from the same distribution . Under the null hypothesis, the distribution of the test statistic is obtained by calculating all possible values of the test statistic under possible rearrangements of the observed data. Permutation tests are, therefore, a form of resampling.
An exact (significance) test is a statistical test such that if the null hypothesis is true, then all assumptions made during the derivation of the distribution of the test statistic are met. Using an exact test provides a significance test that maintains the type I error rate of the test at the desired significance level of the test. For example, an exact test at a significance level of , when repeated over many samples where the null hypothesis is true, will reject at most of the time. This is in contrast to an approximate test in which the desired type I error rate is only approximately maintained, while this approximation may be made as close to as desired by making the sample size sufficiently large.
In combinatorics, the twelvefold way is a systematic classification of 12 related enumerative problems concerning two finite sets, which include the classical problems of counting permutations, combinations, multisets, and partitions either of a set or of a number. The idea of the classification is credited to Gian-Carlo Rota, and the name was suggested by Joel Spencer.
McNemar's test is a statistical test used on paired nominal data. It is applied to 2 × 2 contingency tables with a dichotomous trait, with matched pairs of subjects, to determine whether the row and column marginal frequencies are equal. It is named after Quinn McNemar, who introduced it in 1947. An application of the test in genetics is the transmission disequilibrium test for detecting linkage disequilibrium.
In statistics, the Kendall rank correlation coefficient, commonly referred to as Kendall's τ coefficient, is a statistic used to measure the ordinal association between two measured quantities. A τ test is a non-parametric hypothesis test for statistical dependence based on the τ coefficient. It is a measure of rank correlation: the similarity of the orderings of the data when ranked by each of the quantities. It is named after Maurice Kendall, who developed it in 1938, though Gustav Fechner had proposed a similar measure in the context of time series in 1897.

In probability theory and statistics, Fisher's noncentral hypergeometric distribution is a generalization of the hypergeometric distribution where sampling probabilities are modified by weight factors. It can also be defined as the conditional distribution of two or more binomially distributed variables dependent upon their fixed sum.
Boschloo's test is a statistical hypothesis test for analysing 2x2 contingency tables. It examines the association of two Bernoulli distributed random variables and is a uniformly more powerful alternative to Fisher's exact test. It was proposed in 1970 by R. D. Boschloo.











































