Related Research Articles

Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.

A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions. A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often has large impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annual dry seasons in the tropics significantly increase the chances of a drought developing, with subsequent increased wildfire risks. Heat waves can significantly worsen drought conditions by increasing evapotranspiration. This dries out forests and other vegetation, and increases the amount of fuel for wildfires.

Evapotranspiration (ET) refers to the combined processes which move water from the Earth's surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation and transpiration. Evapotranspiration is an important part of the local water cycle and climate, and measurement of it plays a key role in water resource management agricultural irrigation.

A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor (anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus.

A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica and are found in most ecoregions of the Earth. Furthermore, grasslands are one of the largest biomes on Earth and dominate the landscape worldwide. There are different types of grasslands: natural grasslands, semi-natural grasslands, and agricultural grasslands. They cover 31–69% of the Earth's land area.

Sustainable agriculture is farming in sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an understanding of ecosystem services. There are many methods to increase the sustainability of agriculture. When developing agriculture within sustainable food systems, it is important to develop flexible business processes and farming practices. Agriculture has an enormous environmental footprint, playing a significant role in causing climate change, water scarcity, water pollution, land degradation, deforestation and other processes; it is simultaneously causing environmental changes and being impacted by these changes. Sustainable agriculture consists of environment friendly methods of farming that allow the production of crops or livestock without causing damage to human or natural systems. It involves preventing adverse effects on soil, water, biodiversity, and surrounding or downstream resources, as well as to those working or living on the farm or in neighboring areas. Elements of sustainable agriculture can include permaculture, agroforestry, mixed farming, multiple cropping, and crop rotation.

A meadow is an open habitat or field, vegetated by grasses, herbs, and other non-woody plants. Trees or shrubs may sparsely populate meadows, as long as these areas maintain an open character. Meadows can occur naturally under favourable conditions, but are often artificially created from cleared shrub or woodland for the production of hay, fodder, or livestock. Meadow habitats, as a group, are characterized as "semi-natural grasslands", meaning that they are largely composed of species native to the region, with only limited human intervention.

Ecosystem ecology is the integrated study of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of ecosystems and their interactions within an ecosystem framework. This science examines how ecosystems work and relates this to their components such as chemicals, bedrock, soil, plants, and animals.

Fire ecology is a scientific discipline concerned with the effects of fire on natural ecosystems. Many ecosystems, particularly prairie, savanna, chaparral and coniferous forests, have evolved with fire as an essential contributor to habitat vitality and renewal. Many plant species in fire-affected environments use fire to germinate, establish, or to reproduce. Wildfire suppression not only endangers these species, but also the animals that depend upon them.

In ecology, resilience is the capacity of an ecosystem to respond to a perturbation or disturbance by resisting damage and subsequently recovering. Such perturbations and disturbances can include stochastic events such as fires, flooding, windstorms, insect population explosions, and human activities such as deforestation, fracking of the ground for oil extraction, pesticide sprayed in soil, and the introduction of exotic plant or animal species. Disturbances of sufficient magnitude or duration can profoundly affect an ecosystem and may force an ecosystem to reach a threshold beyond which a different regime of processes and structures predominates. When such thresholds are associated with a critical or bifurcation point, these regime shifts may also be referred to as critical transitions.

Climate change in California has resulted in higher than average temperatures, leading to increased occurrences of droughts and wildfires. Over the next few decades in California, climate change is likely to further reduce water availability, increase wildfire risk, decrease agricultural productivity, and threaten coastal ecosystems. The state will also be impacted economically due to the rising cost of providing water to its residents along with revenue and job loss in the agricultural sector. Economic impacts also include inflation from rising insurance premiums, energy costs and food prices. California has taken a number of steps to mitigate impacts of climate change in the state.

Wetland conservation is aimed at protecting and preserving areas of land including marshes, swamps, bogs, and fens that are covered by water seasonally or permanently due to a variety of threats from both natural and anthropogenic hazards. Some examples of these hazards include habitat loss, pollution, and invasive species. Wetland vary widely in their salinity levels, climate zones, and surrounding geography and play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity, ecosystem services, and support human communities. Wetlands cover at least six percent of the Earth and have become a focal issue for conservation due to the ecosystem services they provide. More than three billion people, around half the world's population, obtain their basic water needs from inland freshwater wetlands. They provide essential habitats for fish and various wildlife species, playing a vital role in purifying polluted waters and mitigating the damaging effects of floods and storms. Furthermore, they offer a diverse range of recreational activities, including fishing, hunting, photography, and wildlife observation.
A fire regime is the pattern, frequency, and intensity of the bushfires and wildfires that prevail in an area over long periods of time. It is an integral part of fire ecology, and renewal for certain types of ecosystems. A fire regime describes the spatial and temporal patterns and ecosystem impacts of fire on the landscape, and provides an integrative approach to identifying the impacts of fire at an ecosystem or landscape level. If fires are too frequent, plants may be killed before they have matured, or before they have set sufficient seed to ensure population recovery. If fires are too infrequent, plants may mature, senesce, and die without ever releasing their seed.
The effects of climate change in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan are now being observed in parts of the province. There is evidence of reduction of biomass in Saskatchewan's boreal forests that is linked by researchers to drought-related water stress stemming from global warming, most likely caused by greenhouse gas emissions. While studies, as early as 1988 have shown that climate change will affect agriculture, whether the effects can be mitigated through adaptations of cultivars, or crops, is less clear. Resiliency of ecosystems may decline with large changes in temperature. The provincial government has responded to the threat of climate change by introducing a plan to reduce carbon emissions, "The Saskatchewan Energy and Climate Change Plan", in June 2007.

A peatland is a type of wetland whose soils consist of organic matter from decaying plants, forming layers of peat. Peatlands arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to water-logging and subsequent anoxia. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface patterning.

Woody plant encroachment is a natural phenomenon characterised by the area expansion and density increase of woody plants, bushes and shrubs, at the expense of the herbaceous layer, grasses and forbs. It refers to the expansion of native plants and not the spread of alien invasive species. Woody encroachment is observed across different ecosystems and with different characteristics and intensities globally. It predominantly occurs in grasslands, savannas and woodlands and can cause regime shifts from open grasslands and savannas to closed woodlands.
Climate change and agriculture are complexly related processes. In the United States, agriculture is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gases (GHG), behind the energy sector. Direct GHG emissions from the agricultural sector account for 8.4% of total U.S. emissions, but the loss of soil organic carbon through soil erosion indirectly contributes to emissions as well. While agriculture plays a role in propelling climate change, it is also affected by the direct and secondary consequences of climate change. USDA research indicates that these climatic changes will lead to a decline in yield and nutrient density in key crops, as well as decreased livestock productivity. Climate change poses unprecedented challenges to U.S. agriculture due to the sensitivity of agricultural productivity and costs to changing climate conditions. Rural communities dependent on agriculture are particularly vulnerable to climate change threats.
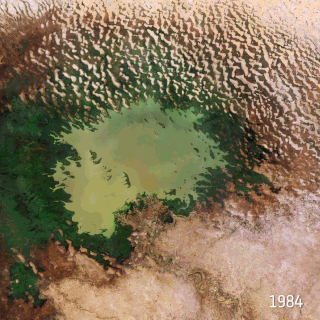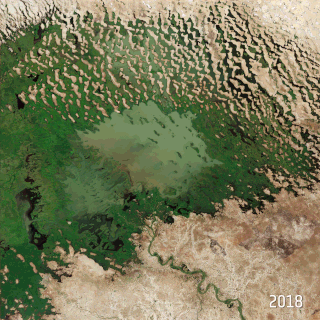
Climate Change in Nigeria is evident from temperature increase, rainfall variability. It is also reflected in drought, desertification, rising sea levels, erosion, floods, thunderstorms, bush fires, landslides, land degradation, more frequent, extreme weather conditions and loss of biodiversity. All of which continue to negatively affect human and animal life and also the ecosystems in Nigeria. Although, depending on the location, regions experience climate change with significant higher temperatures during the dry seasons while rainfalls during rainy seasons help keep the temperature at milder levels. The Effects of Climate Change prompted the World Meteorological Organization, in its 40th Executive Council 1988, to establish a new international scientific assessment panel to be called the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The 2007 IPCC's fourth and final Assessment Report (AR4) revealed that there is a considerable threat of Climate Change that requires urgent global attention. The report further attributed the present global warming to largely anthropogenic practices. The Earth is almost at a point of no return as it faces environmental threats which include atmospheric and marine pollution, global warming, ozone depletion, the dangers of pollution by nuclear and other hazardous substances, and the extinction of various wildlife species.
Beverly Law is an American forest scientist. She is professor emeritus at Oregon State University known for her research on forest ecosystems, especially with respect to carbon cycling, fire, and how human actions impact future climate.

Natural disasters in Nigeria are mainly related to the climate of Nigeria, which has been reported to cause loss of lives and properties. A natural disaster might be caused by flooding, landslides, and insect infestation, among others. To be classified as a disaster, there is needs to be a profound environmental effect or human loss which must lead to financial loss. This occurrence has become an issue of concern, threatening large populations living in diverse environments in recent years.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Lisonbee, J. N.; Otkin, J. A.; Anderson, M. C. (2021). "Characterizing Flash Droughts in the United States". Journal of Hydrometeorology. 22 (5): 1297–1315. doi:10.1175/JHM-D-20-0159.1. S2CID 230582878.
- ↑ Otkin, J. A.; Anderson, M. C.; Hain, C. (2018). "Examining the relationship between drought and rapid intensification of Hurricane Harvey (2017)". Geophysical Research Letters. 45 (12): 6636–6643. doi: 10.1029/2018GL077597 . OSTI 1559277.
- ↑ Anderson, M. C.; Zolin, C. A.; Sentelhas, P. C. (2019). "Agrometeorological screening of major world climatic types with the FAO aridity index". Agricultural and Forest Meteorology. 265: 171–183. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.11.007. hdl: 2268/232468 . S2CID 92150576.
- 1 2 Christian, Jordan I.; et al. (2024). "Flash drought: A state of the science review". WIREs Water. 11 (3). doi:10.1002/wat2.1714. ISSN 2049-1948.
- ↑ Jain, Piyush; et al. (2024-08-20). "Drivers and Impacts of the Record-Breaking 2023 Wildfire Season in Canada". Nature Communications. 15 (1). Nature Publishing Group: 1–14. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-51154-7. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 11335882 . Retrieved 2024-08-21.