
Bertelsmann is a German private multinational conglomerate corporation based in Gütersloh, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is one of the world's largest media conglomerates and also active in the service sector and education.

A textbook is a book containing a comprehensive compilation of content in a branch of study with the intention of explaining it. Textbook are produced to meet the needs of educators, usually at educational institutions. Schoolbooks are textbooks and other books used in schools. Today, many textbooks are published in both print and digital formats.

Public Interest Research Groups (PIRGs) are a federation of U.S. and Canadian non-profit organizations that employ grassroots organizing and direct advocacy on issues such as consumer protection, public health and transportation. The PIRGs are closely affiliated with the Fund for the Public Interest, which conducts fundraising and canvassing on their behalf.
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley, is an American multinational publishing company founded in 1807 that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students.

Pearson plc is a British multinational publishing and education company headquartered in London, England.
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing.

Open educational resources (OER) are freely accessible, openly licensed text, media, and other digital assets that are useful for teaching, learning, and assessing as well as for research purposes.
Pearson Education is a British-owned education publishing and assessment service to schools and corporations, as well for students directly. Pearson owns educational media brands including Addison–Wesley, Peachpit, Prentice Hall, eCollege, Longman, Scott Foresman, and others. Pearson is part of Pearson plc, which formerly owned the Financial Times. It claims to have been formed in 1840, with the current incarnation of the company created when Pearson plc purchased the education division of Simon & Schuster from Viacom and merged it with its own education division, Addison-Wesley Longman, to form Pearson Education. Pearson Education was rebranded to Pearson in 2011 and split into an International and a North American division.
The Ohio Library and Information Network (OhioLINK) is a consortium of Ohio's college and university libraries and the State Library of Ohio. Serving more than 800,000 students, faculty, and staff at 88 institutions with 117 libraries, OhioLINK's membership includes 16 public universities, 23 community/technical colleges, 48 private colleges and the State Library of Ohio. OhioLINK serves faculty, students, staff and other researchers via campus-based integrated library systems, the OhioLINK central site, and Internet resources.
A digital textbook is a digital book or e-book intended to serve as the text for a class. Digital textbooks may also be known as e-textbooks or e-texts. Digital textbooks are a major component of technology-based education reform. They may serve as the texts for a traditional face-to-face class, an online course or degree, or massive open online courses (MOOCs). As with physical textbooks, digital textbooks can be either rented for a term or purchased for lifetime access. While accessible, digital textbooks can be downloaded, printed, or accessed online via a compatible device. To access content online, users must often use a 3rd party hosting provider or "digital bookshelf" through which digital textbooks can be served.

Michael Edmund Kolowich is a new media and internet content entrepreneur and documentary filmmaker. He is chief content officer of OpenExchange Inc. and is founding producer of DigiNovations, a digital multimedia production company in Acton, Massachusetts. He was founder and CEO of KnowledgeVision Systems Incorporated, which merged into OpenExchange in October, 2019. He was a partner at Bain & Company, chief marketing officer for Lotus Development Corporation, founding publisher and columnist for PC/Computing magazine, was founder and president of Ziff-Davis Interactive, served as president of AT&T New Media, was chairman, president and CEO of Individual Incorporated, and co-founded NewsEdge Corporation.

Kno, Inc. was a software company that worked with publishers to offer digital textbooks and other educational materials. In November 2013, after raising nearly $100 million in venture capital, the company was acquired by Intel. The website was stopped and the service renamed to Intel Education Study later on.
An open textbook is a textbook licensed under an open copyright license, and made available online to be freely used by students, teachers and members of the public. Many open textbooks are distributed in either print, e-book, or audio formats that may be downloaded or purchased at little or no cost.

Knewton is an adaptive learning company that has developed a platform to personalize educational content as well as has developed courseware for higher education concentrated in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. The company was founded in 2008 by Jose Ferreira, a former executive at Kaplan, Inc. The Knewton platform allows schools, publishers, and developers to provide adaptive learning for any student. In 2011, Knewton announced a partnership with Pearson Education to enhance the company's digital content, including the MyLab and Mastering series. Additional partners announced include Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Macmillan Education, Triumph Learning, and over a dozen others.
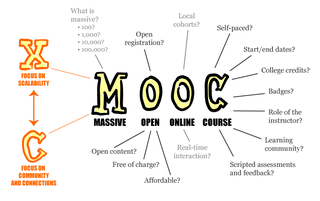
A massive open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012.
OpenStax is a nonprofit educational technology initiative based at Rice University. Since 2012, OpenStax has created peer-reviewed, openly-licensed textbooks, which are available in free digital formats and for a low cost in print. Most books are also available in Kindle versions on Amazon.com and in the iBooks Store. OpenStax's first textbook was College Physics, which was published online, in print, and in iBooks in 2012. OpenStax has also launched OpenStax Tutor Beta, adaptive courseware based on cognitive science principles, machine learning, and OpenStax content.

Boundless was an American company, founded in 2011, which created free and low-cost textbooks and distributed them online. In April 2015, it was acquired by Valore. The combined company is based in Boston, Massachusetts.
Open Course Library (OCL) is an effort by the State of Washington to identify and make available digitally, to community and technical college instructors and students across that state, free textbooks, interactive assignments, and videos. Instructional materials can be "a smorgasbord of teaching modules and exercises developed by other open-learning projects.. . Interactive-learning Web sites and even instructional videos on YouTube. . ." However, OCL is not an OER publishing project, although it did contribute to the development of some widely used resources. Goals include: lowering textbook costs for students, providing new resources for faculty to use in their courses; and fully engaging in the global OER or open educational resources discussion.
BibliU is an education technology company, specialising in digital textbook and monograph provision for universities, libraries and other higher education institutions. BibliU is currently partnered with over 130 higher education institutions globally, including the University of Coventry, University of Liverpool and the University of Phoenix.
LibreTexts is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit online educational resource project. The project provides open access to its content on its website, and the site is built on the Mindtouch platform. LibreTexts was started in 2008 by Professor Delmar Larsen at the University of California Davis and has since expanded to 400 texts in 154 courses, making it one of the largest and most visited online educational resources. LibreTexts currently has 13 library disciplines ranging from chemistry to work-force to humanities.










