
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and or nails.

The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.
A podiatrist is a medical professional devoted to the treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and related structures of the leg. The term originated in North America but has now become the accepted term in the English-speaking world for all practitioners of podiatric medicine. The word chiropodist was previously used in the United States, but it is now regarded as antiquated.
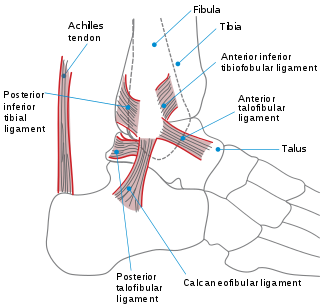
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.

Podiatry, or podiatric medicine, also known as chiropody, is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of the foot, and ankle. The healthcare professional is known as a podiatrist. The US podiatric medical school curriculum includes lower extremity anatomy, general human anatomy, physiology, general medicine, physical assessment, biochemistry, neurobiology, pathophysiology, genetics and embryology, microbiology, histology, pharmacology, women's health, physical rehabilitation, sports medicine, research, ethics and jurisprudence, biomechanics, general principles of orthopedic surgery, and foot and ankle surgery.
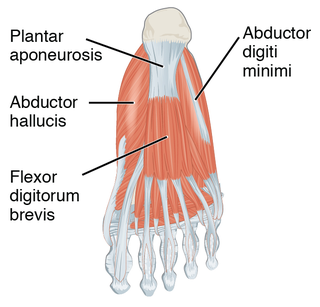
The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom of the foot. It runs from the tuberosity of the calcaneus forward to the heads of the metatarsal bones.

Plantar fasciitis or plantar heel pain is a disorder of the plantar fascia, which is the connective tissue which supports the arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by bending the foot and toes up towards the shin. The pain typically comes on gradually, and it affects both feet in about one-third of cases.
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot and hindfoot.

The tibialis posterior muscle is the most central of all the leg muscles, and is located in the deep posterior compartment of the leg. It is the key stabilizing muscle of the lower leg.

An exostosis, also known as a bone spur, is the formation of new bone on the surface of a bone. Exostoses can cause chronic pain ranging from mild to debilitatingly severe, depending on the shape, size, and location of the lesion. It is most commonly found in places like the ribs, where small bone growths form, but sometimes larger growths can grow on places like the ankles, knees, shoulders, elbows and hips. Very rarely are they on the skull.
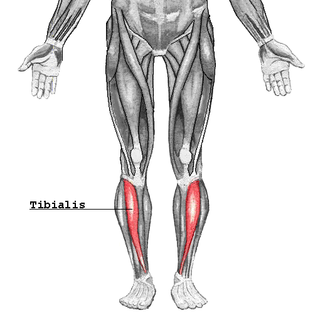
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle in humans that originates along the upper two-thirds of the lateral (outside) surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.

Neuropathic arthropathy, also known as Charcot joint after the first to describe it, Jean-Martin Charcot, refers to progressive degeneration of a weight-bearing joint, a process marked by bony destruction, bone resorption, and eventual deformity due to loss of sensation. Onset is usually insidious.
A leglock is a joint lock that is directed at joints of the leg such as the ankle, knee or hip joint. A leglock which is directed at joints in the foot, is sometimes referred to as a foot lock and a lock at the hip as a hip lock. Leglocks are featured, with various levels of restrictions, in combat sports and martial arts such as Sambo, Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu, catch wrestling, mixed martial arts, Shootwrestling and submission wrestling, but are banned in some sports featuring joint locks such as judo. The technique has been seen across a wide range of different combat sports and is reportedly over 2,500 years old, having been seen in the lost art of Pankration in the original Olympic Games.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

A sprained ankle is an injury where sprain occurs on one or more ligaments of the ankle. It is the most common injury to occur in ball sports, such as basketball, volleyball, football, and racquet sports.
Foot and ankle surgery is a sub-specialty of orthopedics and podiatry that deals with the treatment, diagnosis and prevention of disorders of the foot and ankle. Orthopaedic surgeons are medically qualified, having been through four years of college, followed by 4 years of medical school or osteopathic medical school to obtain an M.D. or D.O. followed by specialist training as a resident in orthopaedics, and only then do they sub-specialise in foot and ankle surgery. Training for a podiatric foot and ankle surgeon consists of four years of college, four years of podiatric medical school (D.P.M.), 3–4 years of a surgical residency and an optional 1 year fellowship.

Toe walking refers to a condition where a person walks on their toes without putting much or any weight on the heel or any other part of the foot. This term also includes the inability to connect one's foot fully to the ground while in the standing phase of the walking cycle. Toe walking in toddlers is common. Children who toe walk as toddlers commonly adopt a heel-toe walking pattern as they grow older. If a child continues to walk on their toes past the age of three, or can't get their heels to the ground at all, they should be evaluated by a health professional who is experienced in assessing children's walking.

A slingback is a type of woman's footwear characterized by an ankle strap that crosses only around the back and sides of the ankle and heel, whereas a typical strap completely encircles the ankle all the way around it. It typically has a low vamp front similar to that of classic full shoe heels.
A high ankle sprain, also known as a syndesmotic ankle sprain (SAS), is a sprain of the syndesmotic ligaments that connect the tibia and fibula in the lower leg, thereby creating a mortise and tenon joint for the ankle. High ankle sprains are described as high because they are located above the ankle. They comprise approximately 15% of all ankle sprains. Unlike the common lateral ankle sprains, when ligaments around the ankle are injured through an inward twisting, high ankle sprains are caused when the lower leg and foot externally rotates.

Orthotics is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An orthosis is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the neuromuscular and skeletal systems."















