
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications such as curtain walls with towers, bastions and gates for access to the city. From ancient to modern times, they were used to enclose settlements. Generally, these are referred to as city walls or town walls, although there were also walls, such as the Great Wall of China, Walls of Benin, Hadrian's Wall, Anastasian Wall, and the Atlantic Wall, which extended far beyond the borders of a city and were used to enclose regions or mark territorial boundaries. In mountainous terrain, defensive walls such as letzis were used in combination with castles to seal valleys from potential attack. Beyond their defensive utility, many walls also had important symbolic functions – representing the status and independence of the communities they embraced.

A fortification is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin fortis ("strong") and facere.

The fortifications of Portsmouth are extensive due to its strategic position on the English Channel and role as home to the Royal Navy. For this reason, Portsmouth was, by the 19th century, one of the most fortified cities in the world. The fortifications have evolved over the centuries in response to changes in tactics and technology and the area defended has increased. While the first defences focused on Portsmouth harbour, in step with the fortifications of Gosport, later defensive structures protected the whole of Portsea Island and an increasing distance inland. At the same time, the fortifications of Portsmouth and Gosport became part of the wider fortifications of the Solent. Old Portsmouth, on the southwest corner of Portsea Island, has been walled for much of its history.

The Western Heights of Dover is a series of forts and ditches in Dover, England. They were created in the 18th and 19th centuries to augment the existing defences and protect the key port of Dover from both seaward and landward attack; by the start of the 20th century Dover Western Heights was collectively reputed to be the 'strongest and most elaborate' fortification in the country. The Army finally withdrew from the Heights in 1956–61; they are now a local nature reserve.

Pendennis Castle is an artillery fort constructed by Henry VIII near Falmouth, Cornwall, England between 1540 and 1542. It formed part of the King's Device programme to protect against invasion from France and the Holy Roman Empire, and defended the Carrick Roads waterway at the mouth of the River Fal. The original, circular keep and gun platform was expanded at the end of the century to cope with the increasing Spanish threat, with a ring of extensive stone ramparts and bastions built around the older castle. Pendennis saw service during the English Civil War, when it was held by the Royalists, and was only taken by Parliament after a long siege in 1646. It survived the interregnum and Charles II renovated the fortress after his restoration to the throne in 1660.

Kastellet is a citadel located in Copenhagen, Denmark. It is one of the best preserved fortresses in Northern Europe. It is constructed in the form of a pentagon with bastions at its corners. Kastellet was continuous with the ring of bastioned ramparts which used to encircle Copenhagen but of which only the ramparts of Christianshavn remain today.

A bastion fort or trace italienne is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to dominate the battlefield. It was first seen in the mid-fifteenth century in Italy. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era.

Indre By, also known as Copenhagen Center or K or Downtown Copenhagen, is an administrative district (bydel) in central Copenhagen, the capital of Denmark. It covers an area of 4.65 square kilometres (1.80 sq mi), has a population of 26,223, and a population density of 5,638 per km2.

The Séré de Rivières system was an ensemble of fortifications built from 1874 along the frontiers, ridges and coasts of France. The fortifications were named after their architect, Brigadier-General Raymond Adolphe Séré de Rivières. The fortresses were obsolescent by 1914 but were used during the First World War.

The fortifications of Kotor are an integrated historical fortification system that protected the medieval town of Kotor containing ramparts, towers, citadels, gates, bastions, forts, cisterns, a castle, and ancillary buildings and structures. They incorporate military architecture of Illyria, the Byzantine Empire, Venice, and Austria. Together with the old town and its natural surroundings the fortifications were inscribed in the list of World Heritage Sites in 1979 labelled Natural and Culturo-Historical Region of Kotor and represent the only such site of cultural significance in Montenegro.

The fortifications of Copenhagen underwent a comprehensive modernization and expansion in the 17th century. The project was commenced and was largely the masterplan of Christian IV in the early 17th century but was continued and completed by his successors. The new fortifications relied on the existing, medieval fortifications of the city but the fortified area was extended and a defensive ring around the city completed particularly with new edifices facing the sea. The ring fortification consisted of four bastioned ramparts and an annexed citadel as well as various outworks.

Christianshavns Vold is a former rampart which was part of the bastioned fortification ring which used to surround Copenhagen, Denmark. Running along the full south-eastern perimeter of Christianshavn and Holmen, it used to form a protective barrier towards the island of Amager. It consists of earthworks with 12 bastions and in front of it ran a moat, Stadsgraven, now forming a broad canal which separates Christianshavn from the rest of Amager. On the other side of Stadsgraven. on Amager, was a lower system of outworks called Christianshavns Enveloppe of which only the northern half survives. Along with Kastellet on the other side of the harbour, it is the only intact part of the fortification system.

Coastal defenceand coastal fortification are measures taken to provide protection against military attack at or near a coastline, for example, fortifications and coastal artillery. Because an invading enemy normally requires a port or harbour to sustain operations, such defences are usually concentrated around such facilities, or places where such facilities could be constructed. Coastal artillery fortifications generally followed the development of land fortifications, usually incorporating land defences; sometimes separate land defence forts were built to protect coastal forts. Through the middle 19th century, coastal forts could be bastion forts, star forts, polygonal forts, or sea forts, the first three types often with detached gun batteries called "water batteries". Coastal defence weapons throughout history were heavy naval guns or weapons based on them, often supplemented by lighter weapons. In the late 19th century separate batteries of coastal artillery replaced forts in some countries; in some areas these became widely separated geographically through the mid-20th century as weapon ranges increased. The amount of landward defence provided began to vary by country from the late 19th century; by 1900 new US forts almost totally neglected these defences. Booms were also usually part of a protected harbor's defences. In the middle 19th century underwater minefields and later controlled mines were often used, or stored in peacetime to be available in wartime. With the rise of the submarine threat at the beginning of the 20th century, anti-submarine nets were used extensively, usually added to boom defences, with major warships often being equipped with them through early World War I. In World War I railway artillery emerged and soon became part of coastal artillery in some countries; with railway artillery in coast defence some type of revolving mount had to be provided to allow tracking of fast-moving targets.

The fortifications of Malta consist of a number of walled cities, citadels, forts, towers, batteries, redoubts, entrenchments and pillboxes. The fortifications were built over hundreds of years, from around 1450 BC to the mid-20th century, and they are a result of the Maltese islands' strategic position and natural harbours, which have made them very desirable for various powers.

Fort Davis, is a coastal defence fortification close to Whitegate, County Cork, Ireland. Together with similar structures at Fort Mitchel, Fort Camden (Crosshaven), and Templebreedy Battery, the fort was built to defend the mouth of Cork Harbour. Though used as a fortification from the early 17th century, the current structures of the 74-acre site date primarily from the 1860s. Originally named Fort Carlisle and operated by the British Armed Forces, the fort was handed-over to the Irish Defence Forces in 1938, and renamed Fort Davis. The facility is owned by the Department of Defence, and is used as a military training site with no public access.

The fortifications of Valletta are a series of defensive walls and other fortifications which surround Valletta, the capital city of Malta. The first fortification to be built was Fort Saint Elmo in 1552, but the fortifications of the city proper began to be built in 1566 when it was founded by Grand Master Jean de Valette. Modifications were made throughout the following centuries, with the last major addition being Fort Lascaris which was completed in 1856. Most of the fortifications remain largely intact today.

The fortifications of Mdina are a series of defensive walls which surround Mdina, the former capital city of Malta from antiquity to the medieval period. The city was founded as Maleth by the Phoenicians in around the 8th century BC, and it later became part of the Roman Empire under the name Melite. The ancient city was surrounded by walls, but very few remains of these have survived.

The fortifications of Plymouth in Devon are extensive due to its natural harbour, its commanding position on the Western Approaches and its role as the United Kingdom's largest naval base. The first medieval defences were built to defend Sutton Harbour on the eastern side of Plymouth Sound at the mouth of the River Plym, but by the 18th century, naval activity had begun to shift westward to Devonport at the mouth of the River Tamar. During the Victorian era, advances in military technology led to a huge programme of fortification encompassing the whole of Plymouth Sound together with the overland approaches. Many of these works remained in military use well into the 20th century.
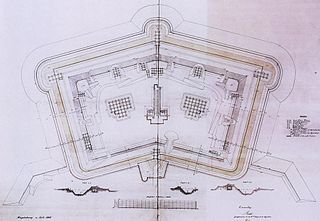
A polygonal fort is a type of fortification originating in France in the late 18th century and fully developed in Germany in the first half of the 19th century. Unlike earlier forts, polygonal forts had no bastions, which had proved to be vulnerable. As part of ring fortresses, polygonal forts were generally arranged in a ring around the place they were intended to protect, so that each fort could support its neighbours. The concept of the polygonal fort proved to be adaptable to improvements in the artillery which might be used against them, and they continued to be built and rebuilt well into the 20th century.



















