
Agnico Eagle Mines Limited is a Canadian-based gold producer with operations in Canada, Finland, Australia and Mexico and exploration and development activities extending to the United States. Agnico Eagle has full exposure to higher gold prices consistent with its policy of no-forward gold sales. It has paid a cash dividend every year since 1983.

Peñoles is a subsidiary company owned by Grupo BAL. Peñoles is the second largest Mexican mining company, the first Mexican producer of gold, zinc and lead and the world leader in silver production. Peñoles is a company with active mines within Mexico and with some prospection projects in South America. Holdings includes the Fresnillo Silver Mine / Mina Proaño, the Met-Mex Peñoles metallurgical complex and Química del Rey; a Chemical facility; three operations. Peñoles produces about 80,500,000 troy ounces (2,500,000 kg) of silver and 756,100 troy ounces (23,520 kg) of gold annually. Other metals that the company produces are zinc, lead, copper, bismuth, and cadmium.
Yamana Gold Inc. is a Canadian company that owns and operates gold, silver and copper mines in Canada, Chile, Brazil and Argentina. Headquartered in Toronto, the company was founded in 1994 and became listed on the Toronto Stock Exchange in 1995, the New York Stock Exchange in 2007, and the London Stock Exchange in 2020. The company became a gold producer after its 2003 re-restructuring in which Peter Marrone took over as chief executive officer and it merged with Brazilian company Santa Elina Mines Corporation. The combined company was able to use Yamana's access to capital with Santa Elina development properties to bring the Chapada mine into production. From there the company combined with other TSX-listed companies RNC Gold, Desert Sun Mining, Viceroy Exploration, Northern Orion Resources, Meridian Gold, Osisko Mining and Extorre Gold Mines which each contributed either a producing mine or a development project that was able to come into commercial production. The company was acquired by Pan American Silver in March 2023.
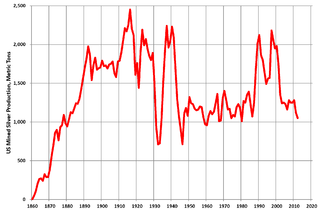
Silver mining in the United States began on a major scale with the discovery of the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1858. The industry suffered greatly from the demonetization of silver in 1873 by the Coinage Act of 1873, known pejoratively as the "Crime of 73", but silver mining continues today.
Silver mining in Colorado has taken place since the 1860s. In the past, Colorado called itself the Silver State.
Silver mining in Nevada, a state of the United States, began in 1858 with the discovery of the Comstock Lode, the first major silver-mining district in the United States. Nevada calls itself the "Silver State." Nevada is the nation's second-largest producer of silver, after Alaska. In 2014 Nevada produced 10.93 million troy ounces of silver, of which 6.74 million ounces were as a byproduct of the mining of gold. The largest byproducers were the Hycroft Mine, the Phoenix Mine, the Midas Mine and Round Mountain.
Gold mining in Alaska, a state of the United States, has been a major industry and impetus for exploration and settlement since a few years after the United States acquired the territory in 1867 from the Russian Empire. Russian explorers discovered placer gold in the Kenai River in 1848, but no gold was produced. Gold mining started in 1870 from placers southeast of Juneau, Alaska.
The Admiralty mining district is a mining area in the U.S. state of Alaska which consists of Admiralty Island. Silver and base metals are mined, with gold recovered as a by-product.
Lundin Mining Corporation is a Canadian company that owns and operates mines in Sweden, United States, Chile, Portugal and Brazil that produce base metals such as copper, zinc, and nickel. Headquartered in Toronto, the company was founded by Adolf Lundin and operated by Lukas Lundin. While it was incorporated to pursue an interest in a diamond mine in Brazil, the company re-structured and raised funds to develop the Storliden mine in Sweden. It purchased the Swedish Zinkgruvan Mine from Rio Tinto and then merged with Arcon International Resources for its Galmoy Mine in Ireland and with Eurozinc for its Neves-Corvo mine in Portugal. The company subsequently purchased and operated the Eagle mine, Candelaria mine, and Chapada mine.
Coeur Mining, Inc. is a precious metals mining company listed on the New York Stock exchange. It operates five mines located in North America. Coeur employs 2,200 people and in 2012 it was the world's 9th largest silver producer. In 2013 the company changed its name to Coeur Mining, Inc. from Coeur d'Alene Mines and moved its head office to Chicago, Illinois from Coeur d'Alene, Idaho.

Hecla Mining is a gold, silver, and other precious metals mining company based in Coeur d'Alene, Idaho. Founded in 1891, it is the second-largest mining company that produces silver in the country. This area is known as the Silver Valley (Idaho). In 1983, this entire area was designated as a Superfund site by the Environmental Protection Agency, because of land, water, and air contamination resulting from a century of mostly unregulated silver and gold mining.
The Telfer Mine is a gold, copper and silver mine located at Telfer on the land of the Martu people, in the Great Sandy Desert of Western Australia. It is owned by Newmont, having acquired the previous owner, Newcrest Mining, formerly the largest gold producer listed on the Australian Securities Exchange, in November 2023.

The Daisy Milano Gold Mine is a gold mine located 50 km south east of Kalgoorlie at Mount Monger Station, Western Australia.
The Davyhurst Gold Mine is a gold mine located 53 km south-west of Menzies, near Davyhurst.

The Randalls Gold Mine is a gold mine, recently developed, located 36 km east-north-east of Kambalda, Western Australia, near Mount Monger Station.
The Edna May Gold Mine is a gold mine located at Westonia, Western Australia.
Wheaton Precious Metals Corp. is a Canadian multinational precious metals streaming company. It produces over 26 million ounces and sells over 29 million ounces of silver mined by other companies as a by-product of their main operations.
New Gold Inc. is a Canadian mining company that owns and operates the New Afton gold-silver-copper mine in British Columbia and the Rainy River gold-silver mine in Ontario, Canada. Through a Mexican subsidiary company, they also own the Cerro San Pedro gold-silver mine in San Luis Potosí, Mexico, which ceased operation in 2017. While New Gold was founded in 1980 for the purposes of mineral exploration, the company became a mine operator with its merger of Peak Gold and Metallica Resources in 2008. A fourth company, Western Goldfields, joined in 2009. Together they operated the Peak mine in Australia and Mesquite Mine in California but sold both in 2018. Headquartered in Toronto, shares of the company are traded on the Toronto Stock Exchange and NYSE American.






